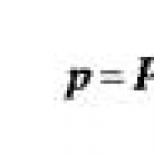What do they drink before indap or lisinopril. Lisinopril indapamide combination drug. Can it be taken at the same time
The drugs Lisinopril and Indapamide are effective in stabilizing blood pressure. In order to enhance the effect, they can be prescribed for simultaneous use. This combination not only improves heart function, but also contributes to the removal of excess fluid, vasodilation and general improvement in well-being with hypertension.
Characteristics of Lisinopril
This medicine is an ACE inhibitor. Its active ingredient is lisinopril dihydrate. The drug inhibits the synthesis of angiotensin octapeptide, which provokes high blood pressure. Against the background of the use of the drug, the blood vessels expand, the pressure decreases and the load on the heart is minimized.
As a result of the action of Lisinopril, the body begins to quickly get used to physical activity against the background of heart failure. The drug has antihypertensive activity, prevents pathological growth of the myocardium and reduces the risk of cardiovascular disorders. The medicine is completely and in the shortest possible time absorbed from the intestine. Its effect is noted 1-1.5 hours after oral administration and increases during the day.
Action of Indapamide
This drug is a diuretic. It contains the same active substance. The medicine promotes the excretion of magnesium, chlorine, calcium and sodium from the body. When it is taken, there is an increase in diuresis and a decrease in the sensitivity of the walls of blood vessels to the effects of angiotensin type 2, as a result of which blood pressure decreases.
The pharmaceutical product prevents the occurrence of free radicals, reduces the concentration of moisture in tissues and expands blood vessels. However, it does not affect the level of triglycerides, glucose and cholesterol in the blood serum. About 25% of indapamide is absorbed from the esophagus. After a single application, the pressure returns to normal within 24 hours. General well-being improves after 1.5-2 weeks of treatment.

Joint effect
Both drugs lower blood pressure. Indapamide provides vascular relaxation and fluid loss. Lisinopril dihydrate also relaxes blood vessels and prevents a re-increase in blood pressure. The combination of these drugs allows you to achieve the maximum hypotensive effect.
Indications for the simultaneous use of Lisinopril and Indapamide
The combined use of drugs is prescribed for a prolonged increase in pressure. At the same time, indapamide also eliminates puffiness when chronic form insufficiency of the heart muscle.
Contraindications
Medicines have a number of contraindications. They are not assigned:
- for patients under the age of 18;
- during the period breastfeeding and bearing a fetus;
- at kidney failure;
- with allergies to the ingredients of medicines;
- in the presence of Quincke's edema in history;
- in old age;
- with impaired ability to convert galactose into glucose;
- at diabetes;
- when the level of creatinine is less than 30 mmol / l;
- with a low concentration of potassium in the blood plasma;
- with hypersensitivity to lactose.
Against the background of the use of the combination Indapamide + Lisinopril, it is forbidden to use drugs based on aliskiren. Caution drugs are used with elevated concentrations of uric acid in the blood serum, dehydration, cardiac ischemia, chronic renal and heart failure.
It is forbidden to start therapy simultaneously with surgical intervention, the use of anesthetics and potassium-containing medicines.
The average dose for pressure stabilization is 5.4 mg of lisinopril dihydrate and 1.5 mg of indapamide. Duration of application - about 14 days.
How to take Lisinopril and Indapamide together
You can take medicines in the morning or in the evening, regardless of food. Their dosage regimen is selected taking into account the response to treatment and the condition of the patient's body.

Before using medications, you must consult your doctor and undergo a series of examinations.
Side effects of Lisinopril and Indapamil
When using combinations of these drugs, side effects may occur. The most common of them:
- coughing;
- dizziness;
- allergic manifestations;
- fainting states;
- tremor;
- breathing problems;
- increase in heart rate;
- decrease in the level of chlorides in the blood serum;
- angioedema;
- feeling sleepy;
- increased activity of liver enzymes;
- headache;
- disruption of the liver and kidneys.
If such manifestations occur, the medicines should be discontinued and a doctor should be consulted.
Doctors' opinion
Svetlana Bugrova (cardiologist), 42, Lipetsk
An effective combination of an ACE inhibitor and a diuretic. In all my practice, I have not yet met more effective and safe analogues. Blood pressure when using these medications is normalized in 2-4 weeks.
Arkady Vasilkov (cardiologist), 51, Ivanovo
Drugs rarely cause adverse reactions. However, their combination is not prescribed for minor patients. Elderly people and in case of impaired functioning of the kidneys and liver require correction of the dosing regimen.
Base Interactions (Indapamide)
It is not recommended to use indapamide and lithium preparations at the same time because of the possibility of developing a toxic effect of lithium against the background of a decrease in its renal clearance. Joint application indapamide with astemizole, erythromycin (iv), pentamidine, sultopride, terfenadine, vincamine, class Ia (quinidine, disopyramide) and class III antiarrhythmic drugs (amiodarone, bretilium, sotalol) can weaken the hypotensive effect of indapamide and lead to the development of an arrhythmia of the type " pirouette" due to a synergistic effect (lengthening) on the duration of the QT interval.NSAIDs, GCs, tetracosactide, adrenostimulants reduce the hypotensive effect, baclofen enhances.
Saluretics (loop, thiazide), cardiac glycosides, gluco- and mineralocorticoids, tetracosactide, laxatives, amphotericin B (iv) increase the risk of hypokalemia.
When taken simultaneously with cardiac glycosides, the likelihood of developing digitalis intoxication increases. With calcium preparations - hypercalcemia. With metformin - aggravation of lactic acidosis is possible.
The combination with potassium-sparing diuretics may be effective in some categories of patients, however, the possibility of developing hypo- or hyperkalemia is not completely excluded, especially in patients with diabetes mellitus and renal insufficiency.
ACE inhibitors increase the risk of developing arterial hypotension and / or acute renal failure (especially with existing renal artery stenosis).
Indapamide increases the risk of developing renal failure when using iodine-containing contrast agents in high doses Ah, dehydration. Before using iodine-containing contrast agents, patients need to restore fluid loss.
Tricyclic antidepressants and antipsychotics may enhance the antihypertensive effect of the drug and increase the risk of orthostatic hypotension.
With simultaneous use with cyclosporine, an increase in plasma creatinine levels is possible.
Reduces effect indirect anticoagulants(derivatives of coumarin or indandione) due to an increase in the concentration of coagulation factors as a result of a decrease in circulating blood volume and an increase in their production by the liver (dose adjustment may be required).
It enhances the blockade of neuromuscular transmission, which develops under the influence of non-depolarizing muscle relaxants.
Interactions from Trade Names (Tenzar)
Undesirable drug combinationlithium preparations.
With the simultaneous use of indapamide and lithium preparations, an increase in the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma may be observed due to a decrease in its excretion, accompanied by the appearance of signs of an overdose. If necessary, diuretic drugs can be used in combination with lithium preparations, while the dose of drugs should be carefully selected, constantly monitoring the content of lithium in the blood plasma.
Combination of drugs requiring special attention
Drugs that can cause pirouette-type arrhythmia.
- class IA antiarrhythmic drugs (quinidine, hydroquinidine, disopyramide);
Class III antiarrhythmic drugs (amiodarone, sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide);
- some antipsychotics: phenothiazines (chlorpromazine, cyamemazine, levomepromazine, thioridazine, trifluoroperazine), benzamides (amisulpride, sulpiride, sultopride, tiapride), butyrophenones (droperidol, haloperidol);
- others: bepridil, cisapride, diphemanil, erythromycin (IV), halofantrine, mizolastine, pentamidine, sparfloxacin, moxifloxacin, astsmizol, vincamine (IV).
Increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias, especially torsades de pointes (risk factor - hypokalemia).
Plasma potassium should be determined and adjusted if necessary prior to initiating combination therapy with indalamide and the above drugs. Need control clinical condition patient, control of blood plasma electrolytes, ECG parameters.
In patients with hypokalemia, it is necessary to use drugs that do not cause arrhythmia of the "pirouette" type.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (with systemic administration), including selective COX-2 inhibitors, high doses of salicylates (≥ 3 g / day).
May reduce the antihypertensive effect of indapamide. With a significant loss of fluid, acute renal failure may develop (due to a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate).
Patients need to compensate for fluid loss and carefully monitor renal function at the beginning of treatment.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
The appointment of ACE inhibitors to patients with a reduced concentration of sodium ions in the blood (especially patients with renal artery stenosis) is accompanied by a risk of sudden arterial hypotension and / or acute renal failure.
Patients with arterial hypertension and possibly reduced, due to the intake of diuretics, the content of sodium ions in the blood plasma is necessary.
- 3 days before the start of treatment with an ACE inhibitor, stop taking diuretics. In the future, if necessary, diuretics can be resumed;
- or start therapy with an ACE inhibitor at low doses, followed by a gradual increase in dose if necessary.
In chronic heart failure, treatment with ACE inhibitors should be started at low doses, with a possible preliminary reduction in diuretic doses.
In all cases, in the first week of taking ACE inhibitors in patients, it is necessary to monitor kidney function (plasma creatinine concentration).
Other drugs that can cause hypokalemia. Amphotericin B (IV), gluco- and mineralocorticosteroids (with systemic administration), tetracosactide, laxatives that stimulate intestinal motility
Increased risk of hypokalemia (additive effect). It is necessary to regularly monitor the content of potassium in the blood plasma, if necessary - its correction. Particular attention should be paid to patients simultaneously receiving cardiac glycosides. It is recommended to use laxatives that do not stimulate intestinal motility.
Baclofen.
There is an increase in the antihypertensive effect. Patients need to compensate for fluid loss and carefully monitor renal function at the beginning of treatment.
cardiac glycosides.
Hypokalemia enhances toxic effect cardiac glycosides. With the simultaneous use of indapamide and cardiac glycosides, the content of potassium in the blood plasma should be monitored, ECG indicators and, if necessary, adjust therapy.
Combination of drugs requiring attention
Potassium-sparing diuretics (amiloride, spironolactone, triamterene).
Combination therapy with indapamide and potassium-sparing diuretics is appropriate in some patients, but the possibility of developing hypokalemia (especially in patients with diabetes mellitus and patients with renal insufficiency) or hyperkalemia is not excluded.
It is necessary to monitor the content of potassium in the blood plasma, ECG parameters and, if necessary, adjust the therapy.
Metformin.
Functional renal failure, which can occur against the background of diuretics, especially "loop", while the appointment of metformin increases the risk of developing lactic acidosis.
Metformin should not be used if the creatinine concentration exceeds 15 mg/l (135 µmol/l) in men and 12 mg/l (110 µmol/l) in women.
Iodine-containing contrast agents.
Dehydration while taking diuretic drugs increases the risk of developing acute renal failure, especially when using high doses of iodine-containing contrast agents.
Before using iodine-containing contrast agents, patients need to compensate for fluid loss.
Tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics (neuroleptics).
These classes of drugs enhance the antihypertensive effect of indapamide and increase the risk of orthostatic hypotension (additive effect).
Salts of calcium.
With simultaneous administration, hypercalcemia may develop due to a decrease in the excretion of calcium ions by the kidneys.
Cyclosporine, tacrolimus.
It is possible to increase the concentration of creatinine in the blood plasma without changing the concentration of circulating cyclosporine, even with a normal content of fluid and sodium ions.
Corticosteroid drugs, tetracosactide (with systemic administration).
Reduced antihypertensive effect (fluid retention and sodium ions as a result of the action of corticosteroids).
To Lisinopril (text from instructions)⇒ Indapamide (found him)
With the simultaneous use of lisinopril with potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, eplerenone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium preparations, salt substitutes containing potassium, cyclosporine, the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases, especially with impaired renal function, so they can be used together only with regular monitoring of the potassium content in serum and kidney function.Simultaneous use with beta-blockers, CCBs, diuretics and other antihypertensive drugs enhances the severity of the antihypertensive effect.
Lisinopril slows down the excretion of lithium preparations. Therefore, when used together, it is necessary to regularly monitor the concentration of lithium in the blood serum.
Antacids and cholestyramine reduce the absorption of lisinopril from the gastrointestinal tract.
Hypoglycemic agents (insulin, oral hypoglycemic agents). The use of ACE inhibitors can enhance the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents up to the development of hypoglycemia. As a rule, this is observed in the first weeks of simultaneous therapy and in patients with impaired renal function.
NSAIDs (including selective COX-2 inhibitors), estrogens, adrenomimetics reduce the antihypertensive effect of lisinopril. The simultaneous use of ACE inhibitors and NSAIDs can lead to deterioration of renal function, including the development of acute renal failure, and an increase in serum potassium, especially in patients with reduced renal function. Caution should be exercised when prescribing this combination, especially in elderly patients. Patients should receive adequate fluids, and careful monitoring of renal function is recommended, both at the beginning and during treatment.
With the simultaneous use of ACE inhibitors and gold preparations (sodium aurothiomalate) intravenously, a symptom complex is described, including facial flushing, nausea, vomiting, and a decrease in blood pressure.
Co-administration with SSRIs can lead to severe hyponatremia.
Combined use with allopurinol, procainamide, cytostatics can lead to leukopenia.
Double blockade of the RAAS
It has been reported in the literature that in patients with established atherosclerotic disease, heart failure, or diabetes mellitus with end organ damage, concomitant therapy with an ACE inhibitor and ARA II is associated with a higher incidence of arterial hypotension, syncope, hyperkalemia, and worsening renal function (including acute renal failure). ) compared with the use of only one drug that affects the RAAS. Double blockade (for example, when an ACE inhibitor is combined with ARA II) should be limited to individual cases with careful monitoring of renal function, potassium levels and blood pressure.
Simultaneous use is contraindicated (see "Contraindications")
Aliskiren. Patients with diabetes mellitus or impaired renal function (GFR less than 60 ml/min) have an increased risk of hyperkalemia, deterioration of renal function, and an increased incidence of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Estramustine. Simultaneous use may lead to an increased risk of side effects such as angioedema.
Baclofen. Enhances the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. Blood pressure should be carefully monitored and, if necessary, the dosage of antihypertensive drugs.
Gliptins (linagliptin, saxagliptin, sitagliptin, vitagliptin). Co-administration with ACE inhibitors may increase the risk of angioedema due to inhibition of DPP-4 activity by gliptin.
Sympathomimetics. May weaken the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors.
Tricyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics and general anesthetics. Simultaneous use with ACE inhibitors may lead to an increase in the antihypertensive effect (see "Precautions").
Combination treatment is the simultaneous administration of two or more antihypertensive drugs. various groups. Compared to monotherapy, it allows you to achieve a faster, stronger effect, less often accompanied by unwanted reactions.
An integrated approach is used to treat hypertension in people with high, very high risk cardiovascular complications ( , ), as well as when it is impossible to achieve targets in other patients.
For ease of administration, preparations have been developed, one tablet of which immediately contains 2, less often 3 active components. Consider the advantages, disadvantages combined tablets from hypertension, which combinations are considered optimal, and which are dangerous.
Combination therapy: pros and cons
The advantages of treatment with combined drugs include:
- ease of administration - there is no need to take several tablets at the same time;
- adherence to therapy - a lower percentage of discontinuation of medication;
- reduction in the frequency, severity of side effects;
- solving several problems with one medicine;
- the best overall result;
- reducing the risk of using unwanted, irrational combinations;
- confidence in the optimal combinations;
- lower cost of therapy.
However, this approach has its downsides. The main disadvantages of combined treatment for hypertension include:
- the inability to adjust the dose of one of the components;
- limited choice;
- when adverse reactions occur, it can be difficult to determine which active substance the patient has reacted to.
Principles of drug combination for hypertension
The effectiveness of the combination of active substances depends on the correct selection of them. The components of the drug must meet the following conditions:
- complement each other's positive action;
- neutralize the negative effects of each other;
- improve performance compared to the use of active substances separately;
- have a similar duration of action;
- convenient reception mode.
Combination options

- preferred (solid blue line) - assigned first;
- appropriate (blue dotted line) - it is allowed to use certain categories of patients with some restrictions;
- possible (black dotted line) - little studied combinations;
- deprecated (orange line).
Preferred combinations include:
- thiazide diuretics + ACE inhibitors;
- thiazide diuretics + calcium antagonists;
- thiazide diuretics + angiotensin II receptor blockers (sartans);
- angiotensin II receptor blockers (sartans) + calcium antagonists;
- ACE inhibitors + calcium antagonists.
Thiazides and ACE inhibitors/sartans
Joint application antihypertensive drugs blocking the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), diuretic drugs are considered one of the best combinations. She is a prime example of how members of different classes can eliminate each other's negative effects.

The intake of diuretics is accompanied by undesirable stimulation of the RAAS activity, the release of a large amount of potassium, magnesium, and a violation of carbohydrate and fat metabolism. ACE inhibitors, sartans, on the contrary, block the RAAS, reduce the excretion of these ions. Some members of the class also normalize lipid, carbohydrate metabolism.
Due to the effect on the two main mechanisms of increasing blood pressure (sodium retention, fluid in the body, activation of the RAAS), the simultaneous use of thiazides, ACE inhibitors or sartans allows you to achieve a better result. Successful control of blood pressure can be achieved in 80-85% of patients. For comparison: ACE inhibitor monotherapy is effective only in half of patients, sartans - 56-70%.
Thiazides and beta blockers
Level the main shortcomings of each other, increase the effectiveness of treatment. Diuretics eliminate the sodium retention that may accompany the intake. And vice versa: the use of drugs of the second group minimizes the risk of developing tachycardia, potassium deficiency, activation of the RAAS caused by a diuretic. The use of combined drugs for hypertension of the thiazide group, calcium channel blockers makes it possible to achieve control over pressure in 75% of patients.

ACE inhibitors and calcium antagonists
The ability of these two groups of drugs to enhance the effectiveness of each other is explained by the effect on various mechanisms blood pressure control. inhibit the activity of the RAAS, the sympathetic nervous system, which reduce the effectiveness of the action of calcium antagonists.

With such a combined treatment of hypertension, there is a decrease in the risk of developing adverse reactions: swelling of the legs, tachycardia, characteristic of calcium channel blockers.
The combination of the two drugs also made it possible to significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications (by 20%) compared with the group of patients who received the classic ACE inhibitor + diuretic duo (3).
Sartans and calcium antagonists
Of all the preferred combinations, this combination has the most indications (4). They are prescribed for:
- isolated systolic arterial hypertension;
- thickening of the wall of the left ventricle of the heart;
- chronic heart failure;
- nephropathy;
- urinary excretion of albumin (albuminuria);
- metabolic syndrome;
- diabetes mellitus;
- dry cough caused by taking ACE;
- suitable for elderly patients.

More pronounced hypotensive effect with joint admission due to the mutual complement of the mechanism of action of drugs. Calcium channel blockers reduce the entry of calcium into the muscle cells of the vessels, and - prevent the binding of their receptors to angiotensin 2. Also, both drugs eliminate some of the negative effects of each other.
Beta-blockers and dihydropyridine calcium antagonists
The combined use of these medications is not recommended for most patients with hypertension. However, their use is more than justified in certain categories of persons. First of all, these are patients with angina pectoris. Several large-scale studies have proven: in heart failure, the simultaneous administration of calcium channel blockers, beta receptors can reduce overall, cardiovascular mortality.
Combination of two or more drugs
With persistent arterial hypertension, even the use of two active substances may be ineffective. In this case, it is recommended to connect a third, sometimes even a fourth component.

There are also three-component drugs, in which two active substances are antihypertensive drugs, and the third one solves the problem associated with hypertension. Most often, which reduces the level of total, bad cholesterol, neutral fats, increases the concentration of good.

Combined drugs for hypertension: a list of the most effective drugs
Most often, doctors prescribe combinations of drugs that they know best. The most popular representatives of complex therapy are shown in the table.
| Active ingredients | Trade names |
|---|---|
| Thiazide + ACE inhibitor | |
| Hydrochlorothiazide + lisinopril |
|
| Hydrochlorothiazide + enalapril |
|
| Hydrochlorothiazide + ramipril |
|
| Indapamide + enalapril |
|
| Hydrochlorothiazide + captopril | |
| Thiazide + sartan | |
| Hydrochlorothiazide + losartan |
|
| Hydrochlorothiazide + telmisartan |
|
| Thiazide + beta-blocker | |
| Chlorthalidone + atenolol |
|
| Hydrochlorothiazide + metoprolol |
|
| Hydrochlorothiazide + propranolol |
|
| Thiazide + calcium antagonist | |
| Hydrochlorothiazide + amlodipine |
|
| Amlodipine + indapamide |
|
| Sartan + calcium antagonist | |
| Valsartan + amlodipine |
|
| Irbesartan + amlodipine |
|
| Losartan + amlodipine |
|
| ACE inhibitor + calcium antagonist | |
| Benazepril + amlodipine |
|
| Lisinopril + amlodipine |
|
| Trandolapril + verapamil ER |
|
| Enalapril + felodipine |
|
| Beta blocker + calcium antagonist | |
| bisoprolol + amlodipine |
|
| metoprolol + felodipine |
|
List of dangerous combinations
Using medicines together may increase each other's negative effects or be ineffective. Therefore, in the combined treatment of hypertension, it is not recommended to combine the following drugs (5).
| Combination | Possible consequences |
|---|---|
| ACE inhibitors + sartans | Increased risk of end-stage kidney disease, stroke, especially in diabetic patients |
| Diuretic + vasodilators | hypokalemia |
| Diuretic + beta blocker | Hypokalemia, dyslipidemia |
| Non-dihydropyridine calcium antagonist + beta-blocker | Atrioventricular block, bradycardia |
| Dihydropyridine calcium antagonist + alpha-blocker | Low pressure |
| Alpha blocker + diuretic | Orthostatic hypotension, "first dose effect" |
| ACE inhibitor/sartan + potassium-sparing diuretic | Increasing the concentration of potassium |
| ACE inhibitor + alpha/blocker | Hypotension |
| Hydralazine + dihydropyridine AA | Tachycardia, myocardial ischemia |
Also, when appointing complex means the status of the patient, the presence of concomitant diseases is taken into account:
- the combination of calcium antagonist + sartan / ACE inhibitor is contraindicated in severe renal problems, severe liver failure, heart failure after myocardial infarction, narrowing of the aorta;
- beta-blockers + thiazides are not used to treat patients with bradycardia, low blood pressure, atrioventricular blockade, sinus node syndrome, pheochromocytoma, uncontrolled heart failure;
- co-administration of diuretics + ACE inhibitors / sartans is not recommended for patients with obstruction / narrowing biliary tract, severe liver/kidney dysfunction, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia.
Most combined drugs are contraindicated in pregnant, lactating women.
Literature
- J.D. Kobalava. Place of combined antihypertensive therapy in modern treatment arterial hypertension, 2007
- ON THE. Vaulin. Combination Therapy arterial hypertension: focus on non-fixed combinations, 2011
- Skvortsov B.V. , Tumarenko A.V. Combined treatment of hypertension: focus on the combination of calcium antagonists and ACE inhibitors, 2011
- Zadionchenko V.S., Shchikota A.M. and others. Algorithm for choosing a drug for the treatment of arterial hypertension, 2017
- Guidelines for the treatment of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension and the European Society of Cardiology, 2013
The only indication of Indapamide is arterial hypertension. Especially often it is prescribed if the increase in blood pressure is accompanied by severe edema and fluid retention. Due to the removal of excess fluid, blood pressure indicators decrease.
Such funds often form the basis of treatment. They are usually supplemented with other antihypertensive drugs. At what pressure are such medicines required? Usually they are prescribed if arterial hypertension persists constantly, full-fledged arterial hypertension develops, pressure indicators are constantly kept above 140 to 100.
Indapamide - diuretic or not? Since this drug is a diuretic, it has a diuretic effect, removes fluid from the body. It should be borne in mind that increasing the dosage does not lead to an increase in the hypotensive effect, since only the diuretic is enhanced. Therefore, do not overestimate the dosage of this remedy, especially on your own.
The average price of the drug is 20–50 rubles, depending on the pharmacy chain. The drug is one of the cheapest diuretic drugs used for arterial hypertension.
Important! In no case should you start taking diuretics on your own, especially with signs of impaired kidney function.

Instructions for use
Usually this drug taken once a day, the standard dosage is 2.5 mg of the substance. It is usually not changed - it can only be adjusted by adding other drugs with an antihypertensive effect to the therapy.
How to take - before meals or after - does not matter. The instructions for the drug say that the time of day and meals do not affect the effect of the drug, so it is not necessary to focus on them.
Usually, the course of treatment with various antihypertensive drugs during the acute stage of hypertension does not last long - up to several weeks. Then, when the blood pressure drops sufficiently steadily, the course of treatment is stopped. In the future, to maintain pressure within normal limits, it is important to observe proper diet and other medical advice.
Regarding the duration of taking this drug, you should first consult with your doctor. In each individual case, the course of therapy will be different - it all depends on the severity of the disease and the condition of the patient as a whole.

Contraindications
Indapamide has a number of fairly strict contraindications. This drug should not be used in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. In case of violations of the functions of these organs, a diuretic is taken exclusively under the strict supervision of a doctor, constantly monitoring the situation and the dynamics of changes.
- Also, this drug should not be used in case of intolerance to the components of the composition, primarily the diuretic itself, as well as other substances included in the drug.
- In particular, you should not use the remedy for lactose intolerance, since it is part of the tablet itself.
- A strict contraindication is childhood. Until the age of eighteen, this is a medicine against high blood pressure should not be used as there is no evidence of its safety in children.
- Indapamide should not be used during pregnancy either: childbearing and breastfeeding are quite strict contraindications to taking the medicine.
Important! It is advisable to take this diuretic in the elderly under the strict supervision of a physician. In older people, the drug can adversely affect the body.

Side effects
This diuretic has quite a few possible side effects. They do not appear so often if you take Indapamide according to the instructions. Usually, the following groups of side effects are distinguished:
- dizziness, headaches, sleep disturbances, asthenia, other disorders of the nervous system;
- hypotension, arrhythmias, others side effects from the circulatory system;
- severe cough, pharyngitis, sinusitis;
- various infections from the excretory system;
- violations of hematopoiesis, changes in blood tests;
- all kinds of allergic reactions, skin rashes, urticaria.
These side effects are most common with indapamide. but with the right reception, the likelihood of their occurrence is quite small.
Consider which drug can replace Indapamide and which one is better.
Concor and Indapamide: compatibility
Concor and Indapamide have good compatibility, they are often prescribed as joint complex therapy. Indapamide may also combine well with other beta-blockers.
Lorista and Indapamide: can they be taken together?
Lorista (an angiotensin receptor antagonist) and Indapamide can be combined together with your doctor's permission. Quite often, these two drugs are prescribed simultaneously for complex therapy.
Prestarium and Indapamide: joint use
Prestarium is a medicine used for hypertension and heart failure. It happens that it is prescribed together with diuretics, in particular - with Indapamide. These drugs work well together.

Lisinopril and Indapamide: Can I take it at the same time?
The combination of Lisinopril and Indapamide allows you to quickly and effectively lower blood pressure, while they remain within the normal range for a long time, and hypertension recedes. Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor. In this case, you should not start taking such a combination of funds on your own - you must first consult with a specialist.
Analogues and their comparison
Direct analogues of Indapamide are other diuretics based on the same active substance. They primarily include Arifon. You can also use other diuretics aimed at lowering blood pressure. Before using the analog, you must definitely read the instructions for use.
In terms of effects, only drugs of the same group can be compared - diuretics, which include Indapamide. It is difficult to say which is better: Indapamide or Concor. These medicines are different types drugs and affect the body in different ways. It is also impossible to say which is better: Indapamide or Enalapril. This is a completely different tool with a different effect on the body. However, it is worth noting that diuretics should first of all be paid attention to if hypertension is accompanied by swelling.
Arifon Retard or Indapamide
Arifon Retard is also based on the action of the substance Indapamide, but the price of this analogue is higher. One pack of medicine costs up to 300-350 rubles. At the same time, these tools practically do not differ in action.
Nevertheless, it should be borne in mind that Arifon has fewer contraindications. At an older age and in the presence of liver and kidney diseases, it is better to choose it. Indapamide has a more negative effect on the body.

Indapamide or Veroshpiron
Veroshpiron is also a fairly effective diuretic for arterial hypertension. However, it is worth noting that this drug can be used for a number of other diseases, while it has fewer contraindications than Indapamide. Therefore, when choosing drugs, it is worth paying attention to it as well.
Hypothiazide or Indapamide
Hypothiazide is also effective diuretic with hypertension, which is often prescribed for this disease. At the same time, it has a wider range of applicability. According to contraindications, these drugs are very similar.

Indapamide or Furosemide
With arterial hypertension, it is better to choose the first diuretic, since this drug is intended for the treatment this disease. Furosemide is commonly used for other conditions.
hydrochlorothiazide or indapamide
Hydrochlorothiazide is also a thiazide diuretic, like Hypothiazide. In action, these drugs are more similar. choose the most suitable group drugs should be taken depending on the indications, the course of the disease, comorbidities.
Diuver or Indapamide
Diuver is more similar in effect to Furosemide, while it is also quite often prescribed for arterial hypertension. This remedy is especially helpful with increased edema formation. It has more contraindications, so before using it, you must definitely read the instructions for use.
Detailed instructions for the use of Lisinopril tablets: at what pressure is used, patient reviews

High blood pressure (BP) traditionally occupies a leading position among diseases that develop with age. Arterial hypertension (AH) affects up to 50% of the population, and in the elderly group this figure is 80% or even more.
Therapy of hypertension is carried out with various medications. One of the most used are inhibitors of dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase, also called angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Lisinopril occupies a special place among ACE inhibitors.
Instructions for using this medicinal product is the subject of this article. To this end, questions will be studied on how to take Lisinopril for pressure, what time of day is best to do it, as well as contraindications, side effects and other aspects.
The composition of the drug
The composition of the drug, in addition to active substance- an ACE inhibitor, represented by auxiliary components that do not have a therapeutic effect: various salts, starch, dyes, etc.
Mechanism of action
The pharmacological effect of the drug is explained by the inhibitory effect of lisinopril on the activity of dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase. This enzyme catalyzes transformation processes in two systems:
In the renin-angiotensin system, dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase stimulates the transition of angiotensin from the first form to the second, which leads to the tone of the vascular wall, thereby increasing blood pressure. In the kallikrein-kinin system, this enzyme stimulates the breakdown of bradykinin, a peptide that has a vasodilating effect.
The instructions for use noted that the drug Lisinopril, the active substance of which is lisinopril dihydrate, inhibits the processes in both systems, that is:
- prevents the transformation of angiotensin;
- reduces the rate of cleavage of bradykinin.
Due to this, a vasodilating effect is achieved, normalizing blood pressure.
In addition, the active substance affects the metabolism of other biologically active substances in the body. It is with this that numerous side effects of the drug Lisinopril are associated, the main of which is cough.
What are Lisinopril tablets for?
The mechanism of action described in the previous paragraph gives an understanding of the indications for the use of Lisinopril. What these tablets do is determined by the ability of the active substance to block the transformation of angiotensin and bradykinin, resulting in a decrease in blood pressure.
Additionally, Lisinopril, as indicated in the instructions for use, has the following effects: 
- reduces left ventricular hypertrophy;
- improves the pumping function of the heart;
- increases renal blood flow;
- improves renal function;
- has a nephroprotective effect.
Due to the complex action, the indications for the use of Lisinopril tablets, in accordance with the instructions for use, include not only hypertension, but also heart failure (as part of complex measures), myocardial infarction, and impaired renal function against the background of diabetes mellitus.
At what pressure is it taken?
People suffering from high blood pressure should be aware that hypertension therapy involves the constant intake of appropriate drugs, regardless of current blood pressure levels. This is indirectly confirmed by the instructions for use for Lisinopril: the pressure at which to take the drug is not noted in the annotation.
Moreover, as a result of clinical studies, it was shown that the therapeutic effect of taking the drug, in particular the regression of left ventricular hypertrophy, manifests itself only during long-term use.
Which manufacturer is better?
Lisinopril, as an active ingredient, is part of dozens of mono and complex preparations. A large number of one of them is called Lisinopril. Manufacturers are both national and international pharmaceutical enterprises.
 The drug Lisinopril from the Russian company Organika is the most budgetary option for the drug today. For this reason, it is often chosen by patients who cannot afford imported analogues lisinopril tablets. Reviews of this drug are positive.
The drug Lisinopril from the Russian company Organika is the most budgetary option for the drug today. For this reason, it is often chosen by patients who cannot afford imported analogues lisinopril tablets. Reviews of this drug are positive.
The drug Lisinopril is produced by the Russian Nizhny Novgorod pharmaceutical holding, as well as by non-Russian companies that are part of the international concern Stada AG. Many patients choose a drug from this manufacturer, although it is 2 times more expensive than Organics.
Among the hundreds of drugs produced by the famous German pharmaceutical holding, there is also Lisinopril. Its use is similar to all other medicines with this active substance. The difference can be significant for some patients: Ratiopharm, and this is indicated in the instructions for use, makes the drug lactose-free.
Ukrainian pharmaceutical factory Astrapharm offers one of the most budget options drug Lisinopril. Patients' reviews about it are mostly positive, which is determined by the price factor, as well as the absence of lactose in the composition of the drug.
For the Eastern European market, Lisinopril from the international concern Teva is manufactured at a Hungarian drug factory. Therefore, this version of the drug, as an imported remedy, is more expensive than those discussed above.
This is not a complete list of all variations of the drug under the same name: there are at least two dozen of them.

Stages of development of hypertension
Instructions for use
Like any medication, Lisinopril should only be used after being prescribed by a doctor. As described above, the active substance has a complex effect on the body, adjusting the concentration of biologically active enzymes. Despite the fact that the description of Lisinopril given in the instructions for use is exhaustive, specialist advice is necessary before starting use.
How to use?
Each person who has read the instructions for use will find information about the medical use of the drug Lisinopril. Above, we have already considered the question at what pressure it is necessary to take a pill. Once again, we note that this should be done daily, regardless of the current indicators on the tonometer.
Another question that is often asked by hypertensive patients at the beginning of treatment with Lisinopril is how long this drug can be taken. With good tolerability, therapy with hypertension can last for a long time: as long as it has the desired effect. In cases of time-limited use, for example, after a myocardial infarction, the duration of administration is determined individually.
In the morning or evening?
The instructions for use do not contain an imperative clarification on how to take Lisinopril correctly - in the morning or in the evening. Nevertheless, therapeutic practice shows that morning intake is preferable.
Before meals or after?
The tablet is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, and in accordance with the instructions for use, the contents digestive system does not affect the absorption of the substance lisinopril. How to take - before or after meals - with constant therapy does not matter.
How long does it take to work?
 Lisinopril is not a "rapid" ACE inhibitor. Its effect, as noted in the instructions for use, develops slowly towards the end of the first hour after administration, then gradually increases within 6 hours and persists for another 15-17 hours.
Lisinopril is not a "rapid" ACE inhibitor. Its effect, as noted in the instructions for use, develops slowly towards the end of the first hour after administration, then gradually increases within 6 hours and persists for another 15-17 hours.
For this reason, it does not matter for patients how long the drug acts. Lisinopril is not a drug emergency assistance and should not be used as a rapid blood pressure lowering pill.
The treatment regimen, as for other ACE inhibitors, involves starting therapy with a minimum dose, which can then be increased if necessary. In pharmacies, you can find Lisinopril tablets with an active ingredient content of 2.5 to 40 mg, which is convenient for the treatment of any degree of hypertension.
Depending on the severity of hypertension, the drugs received, the initial dosage of Lisinopril, in accordance with the instructions for use, is 2.5 or 5 mg. If treatment at a dose of 2.5 mg shows its effectiveness, then the dosage of the drug should not be increased.
Instructions for use for Lisinopril 5 mg clarifies that in most cases this dose is standard and sufficient for mild treatment and average AH. In the event that the desired effect does not occur, the amount of the drug taken can be increased by 5 mg every 3 days. When increasing the dose taken, the following features of the antihypertensive effect of lisinopril should be borne in mind:
- a decrease in pressure becomes noticeable in the first days of admission;
- the hypotensive effect accumulates and reaches a maximum within 1-2 months of treatment.
Increasing the dose of the drug in accordance with the instructions for use is possible up to 20 mg per day (usually) or up to 40 mg per day (maximum). A further increase in dosage (over 40 mg) does not enhance the therapeutic effect.
Lisinopril is also prescribed as part of a complex of drugs in the treatment of heart failure, in the post-infarction period, and in diabetic nephropathy. The dosage in these cases is set individually, but in general terms, the algorithm for its appointment corresponds to the above scheme.
Is an overdose possible?
Compliance with the dosage is a necessary condition for treatment with Lisinopril. An overdose of them is possible: in the instructions for use it is noted that, mainly, it is expressed in an excessive decrease in blood pressure and the appearance of symptoms accompanying this condition: 
- drowsiness;
- apathy;
- dizziness;
- orthostatic hypotension;
- nausea.
An excessive decrease in blood pressure is also possible with a slight excess of the usual dosage. Therefore, patients should be careful, study the instructions for use and always follow the regimen prescribed by the doctor.
Side effects
Above, we noted that the active substance of the drug has an effect on various biologically active substances in the body. Some effects have not yet been adequately studied, but it is they that cause effects that are commonly called side effects.
Among them, the instructions for use primarily note dry cough, which, according to available data, accompanies every tenth patient taking Lisinopril. Side effects, in addition, can often manifest as:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- excessive decrease in blood pressure;
- apathy, drowsiness and fatigue;
- nausea and diarrhea.
Instructions for use contains a fairly extensive list of possible side effects. However, they are all marked "rarely".
Contraindications
 As well as side effects, contraindications to Lisinopril are standard for all ACE inhibitors:
As well as side effects, contraindications to Lisinopril are standard for all ACE inhibitors:
- intolerance to lisinopril or other drugs of the ACE group, as well as auxiliary components in the composition;
- pregnancy, lactation;
- age up to 18 years;
- predisposition to allergic edema.
The use of the drug has an impressive list of restrictions that require caution in the treatment of certain groups of patients. More details about this information can be found in the official instructions for use.
Does it affect potency?
The instructions for use do not contain information on whether Lisinopril pressure pills affect erectile function. In studies conducted on this topic, an increase in the level of free testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in the blood during therapy with ACE inhibitors was noted. This allows you to answer the question of whether Lisinopril affects potency, negatively.
Nevertheless, patients with hypertension should understand that hypertension and erectile dysfunction have a common pathogenetic mechanism, which consists in a violation of vascular tone, including those responsible for the formation of an erection. Men who experience problems with potency against the background of hypertension should definitely receive antihypertensive therapy with ACE inhibitors (in the absence of contraindications to this).
Lisinopril and alcohol compatibility
As is clear from the instructions for use, Lisinopril leads to a decrease in vascular tone and normalization of blood pressure, for which this drug is prescribed. Alcohol also has a vasodilating effect, which, when taken simultaneously with an antihypertensive agent, increases the risk of side effects of the latter: an excessive decrease in blood pressure, headache, weakness, and others.
Doctors do not recommend taking Lisinopril and alcohol at the same time. Their compatibility is quite real, in particular, many hypertensive patients note that such a combination does not bring any tangible harm and does not worsen the condition. Nevertheless, readers should understand that alcohol, being a cardio- and vascular toxic agent, largely levels the therapy received and worsens the long-term prognosis for a patient with hypertension.
Reviews of patients taking the drug
For the treatment of hypertension, ACE inhibitors are often prescribed, as one of the most effective drugs, including the drug Lisinopril. Reviews of patients taking the drug, for this reason, are numerous. The vast majority of them are positive.
 People note the following important characteristics of the drug:
People note the following important characteristics of the drug:
- "holds pressure well";
- must be taken once a day;
- inexpensive.
In some cases, patients noted too strong a decrease in blood pressure, the appearance of weakness, depression - typical signs of an overdose of the drug, indicating that the dose was chosen incorrectly.
Reviews of cardiologists about the drug
Instructions for use notes such an important characteristic of the drug Lisinopril as non-biotransformability in the body. Reviews of cardiologists also focus on the fact that the active substance is not metabolized in the liver, but is excreted unchanged. This distinguishes lisinopril from other substances that inhibit dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase.
On the other hand, this requires more careful monitoring of kidney function, in particular the level of creatinine, which is noted in the instructions for use. With a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate, the level of lisinopril in the blood increases, which creates a risk of overdose symptoms.
In general, cardiologists speak positively about Lisinopril, characterizing it as an effective means for lowering blood pressure, which has a long-term effect. It is the drug of choice for patients with liver failure, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis.
Recipe in Latin
Today, more and more doctors, even highly qualified, write out prescriptions not in Latin. Having received a prescription for the purchase of medicine in your national language, do not be surprised. For those who were among the lucky ones who received a prescription for Lisinopril in Latin, here is its general form:
Rp.: Tabulettae Lisinopril (dosage is indicated, for example, 5 mg or 0.005 g).
S. 1 tablet inside 1 r / d.
Can it be taken at the same time?
Treatment of hypertension, heart failure, post-infarction condition in most cases is carried out using a combination of drugs from different pharmacological groups. This is also true for Lisinopril.
With Amlodipine and Rosuvastatin
 This combination medicinal substances is one of the most effective in the practice of treating numerous cardiological diseases accompanied by hypertension and a pronounced atherosclerotic process.
This combination medicinal substances is one of the most effective in the practice of treating numerous cardiological diseases accompanied by hypertension and a pronounced atherosclerotic process.
The combination of amlodipine, lisinopril and rosuvastatin, in the absence of contraindications to each of them, can be prescribed for:
A combination drug containing all three components is produced by the Hungarian pharmaceutical company Gedeon Richter under trade name Equamer.
With hydrochlorothiazide
The combination of an ACE inhibitor and a diuretic is the most common treatment for hypertension. Lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide allow more successful control of pressure in cases where the desired effect is not achieved by taking one of these drugs. In pharmacies, you can find numerous preparations containing both substances (at a dosage of 10 or 20 mg of lisinopril and 12.5 mg of hydrochlorothiazide):
- Iruzid;
- Co-Diroton;
- Lisinoton N;
- Lysoretic;
- Rileys-Sanovel plus.
With Indapamide
Doctors do not prescribe Lisinopril together with Indapamide, replacing the latter with hydrochlorothiazide. There are no combination drugs with such a composition. Therefore, if you are interested in the question of whether it is possible to take Indapamide and Lisinopril at the same time, then you should refrain from such a combination. Indapamide is usually combined with Lisinopril analogue - Enalapril.
Analogues and replacements: which is better
The pharmacological group to which Lisinopril belongs (drugs that inhibit dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase) is represented by several dozen drugs. In addition, there are drugs from other groups:
- angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs);
- slow calcium channel blockers (CBCC);
- beta-blockers (BAB), -
All of them have an antihypertensive effect and, under certain conditions, can act as an analogue and replacement for Lisinopril.
 Enalapril-based drugs have traditionally been widely used in the treatment of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
Enalapril-based drugs have traditionally been widely used in the treatment of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
They do not have any advantages over lisinopril. As a rule, require the appointment of a 2-fold dose per day.
At the heart of the drug Berlipril is the above-mentioned enalapril. If we talk about what is better, then Lisinopril for many patients is a better choice.
Prestarium
When choosing Lisinopril or Prestarium, which is better for hypertension, it should be noted that perindopril, which is part of Prestarium, is metabolized in the liver, which may be important for patients with cirrhosis and liver failure. In addition, perindopril shows its maximum effect faster (after 3 hours), but it must be drunk strictly before meals, since the presence of food reduces its absorption.
Synonyms for the drug Lisinopril are numerous. One of the most expensive is the drug produced by the Hungarian Gedeon Richter, Diroton. Considered over quality analogue, which is reflected in the reviews on the topic of which is better - Lisinopril or Diroton. Patients who are not constrained by financial resources opt for the latter.
Preparations based on captopril act faster (within half an hour), but the effect does not last long, which is why they require 3 times a day. Because of this, captopril-containing drugs are not very suitable for continuous therapy: it has been proven that only a small proportion of patients are able to adhere to a high-frequency regimen for a long time. This should be kept in mind when choosing Lisinopril or Captopril, which is better.
 Among the dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase inhibitors, ramipril is one of five that have been shown in large clinical trials to reduce mortality in hypertensive patients.
Among the dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase inhibitors, ramipril is one of five that have been shown in large clinical trials to reduce mortality in hypertensive patients.
In this sense, the choice between the drugs Ramipril or Lisinopril, which is better of them, cannot be made on the basis of objective data. However, it is possible that the individual tolerance of one or another drug will be different.
If the cough is from Lisinopril, then the question of how to replace it is of particular relevance. One option might be Lorista.
The active substance, losartan potassium, has a different mechanism of action and therefore does not cause coughing. However, when deciding whether Lisinopril or Lorista is better, it should be borne in mind that the latter drug reduces pressure less effectively (by 8 mm Hg versus 20 mm Hg for lisinopril - according to clinical studies). In addition, Lorista should be drunk 2 times a day, and it also has an impressive list of side effects and contraindications, outlined in the instructions for use.
The medicine Valz (active ingredient - valsartan) belongs to the same pharmaceutical group as Lorista, however, compared with the latter, it has an important advantage - the duration of the effect, which allows it to be taken once a day. Like other ARBs, valsartan is usually combined with other drugs. If we talk about monotherapy, then Lisinopril can be considered better and more effective.
bisoprolol
Preparations based on bisoprolol block the adrenergic receptors of the heart and aorta, thereby reducing the heart rate and minute blood volume, lowering blood pressure. It should be noted that the mechanism of pressure reduction in drugs of the BAB group is not completely clear, which is noted in the instructions for use. When choosing Lisinopril or Bisoprolol, which is best for the patient, the doctor will take into account numerous factors and make the most correct appointment.
Useful video
For more information about arterial hypertension, see this video:
Compatibility of Enalapril and Indapamide
Enalapril and Indapamide are drugs prescribed by cardiologists for hypertension and symptomatic hypertension. They act in different ways, enhancing each other's action and lowering blood pressure.

Action Enalapril
Enalapril - antihypertensive drug. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. Reduces blood pressure by blocking the activity of an enzyme that converts angiotensin to angiotensin 2, which constricts blood vessels, increasing overall peripheral resistance.
Enalapril stops the reaction of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Expands blood vessels. Reduces pre- and afterload on the heart. Increases blood levels of bradykinin - a substance that expands the renal vessels, improves renal blood flow. Due to this, diuresis increases, the volume of circulating blood and blood pressure decrease.
Action of Indapamide
Diuretic drug. Causes the excretion of sodium, calcium, chlorine, magnesium, water by the kidneys. Reduces sensitivity renal vessels to the action of vasoconstrictors - angiotensin 2 and norepinephrine. Stimulates the formation of vasodilators that dilate blood vessels.






Thanks to diuretic effect reduces the volume of circulating blood.
Can I take Enalapril and Indapamide at the same time?
Both drugs are used to treat hypertension, as well as symptomatic (renal) hypertension. They can be taken together in tablet form.
Sometimes beta-blockers are added to the regimen.
Indications for simultaneous use
Essential and symptomatic hypertension, hypertensive crisis, congestive heart failure, coronary heart disease, hyperthyroidism.

Contraindications when using Enalapril and Indapamide
Quincke's edema in history, intolerance, renal artery stenosis, pregnancy, lactation, renal, hepatic failure, prolongation of the QT interval.
How to take Enalapril and Indapamide together
Enalapril starting dose complex treatment- 2.5 mg. Then it increases to 5-15 mg until reaching desired effect. The initial dose of the diuretic is 1.5 mg.
Side effects
Enalapril: hypotension, cough, oliguria.
Indapamide: hypokalemia, dizziness, convulsions, increased urea content, hyperuricemia.
Gorbunov A.P., cardiologist, Moscow
I prescribe a diuretic with an ACE inhibitor for the treatment of hypertension. The therapy gives good results and stabilizes the condition of patients.
Lavrov A.L., therapist, Nizhny Novgorod
For patients with high blood pressure, especially lower blood pressure, I prescribe this combination. Patients note a positive trend.
Lyudmila, 40 years old, Nizhnevartovsk
I am taking these drugs. The pressure is 160 to 90. Now it stays at around 130 to 75. Sometimes I feel weak and dizzy.
Andrey, 48 years old, Cheboksary
I've got a heart problem, chronic diseases kidney, high pressure- rose to 180. Now I take a diuretic and Enap (active ingredient enalapril) - I feel better, my head does not hurt.
Lorista diuretic or not
Essential hypertension: symptoms, treatment

Have you struggled with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
Essential hypertension is the most common type of arterial hypertension (96% of all cases), which is accompanied by a stable increase in systolic pressure above 140 mm. rt. Art. and diastolic pressure above 90 mm. rt. Art. The relationship between the rise in blood pressure (BP) and dysfunction of other organs in this type of hypertension is not detected, this is its hallmark. The increase in pressure in essential hypertension occurs at rest, and such pressure surges primarily lead to disruption of the functioning of the arteries and the heart. With the progression of this pathology and the absence of its adequate treatment, the patient may experience severe complications leading to his disability and death (stroke, heart failure, myocardial infarction).
Causes and risk factors
There is no clear understanding of the causes of essential hypertension in modern medicine. Doctors believe that this disease is caused by various factors, and other predisposing causes contribute to its consolidation and development. To provoke the appearance of essential hypertension can:
For the treatment of hypertension, our readers have successfully used ReCardio. Seeing the popularity of this tool, we decided to bring it to your attention.
Read more here…
- heredity;
- bad habits;
- age over 50;
- obesity;
- hypodynamia;
- frequent stressful situations and emotional overstrain;
- malnutrition and excessive salt intake;
- lack of calcium and magnesium in the body.
Stages of development
During essential hypertension, I distinguish the following stages:
- Stage I: Blood pressure does not rise to more than 140-160 / 90-99 mm. rt. Art., is asymptomatic, the risk of stroke or heart failure is about 5%, 15% of patients may develop cardiovascular pathologies;
- Stage III: BP rises above 180/115-120 mm. rt. Art., the patient has signs of atherosclerosis, more frequent hypertensive crises, the risk of complications is 30%.
 Patients with essential hypertension often experience headaches and tinnitus.
Patients with essential hypertension often experience headaches and tinnitus.
At stage II, symptoms may also be absent, but when the patient is examined, signs of damage to target organs are revealed. Sometimes there are hypertensive crises.
At the III stage of essential hypertension, the patient has signs of vascular damage and develops severe diseases of the vessels, heart, brain and kidneys. Patients complain about:
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- painful reaction to changing weather;
- pain in the region of the heart;
- shortness of breath
- visual impairment;
- noise in ears;
- tachycardia;
- weakness;
- flashing flies before the eyes;
- sweating;
- swelling;
- nausea;
- redness of the face.
Complications
- Hypertensive crisis: accompanied by a sharp increase in blood pressure above the individual norm, cardiovascular and brain disorders that can lead to stroke and myocardial infarction.
- Hypertensive heart: accompanied by a violation of myocardial contractility and thickening of the walls of the heart, can lead to myocardial infarction, sudden coronary death, arrhythmias, or heart failure.
- Kidney damage: manifested in the form of polyuria, nocturia, renal failure.
- Fundus lesions: hemorrhages, vasoconstriction, decreased visual acuity, blindness.
- CNS lesions: memory impairment, headaches, absent-mindedness, decreased performance and intellectual abilities, hypertensive encephalopathy, cerebrovascular accidents, dementia, stroke.
Treatment of essential hypertension can be carried out after collecting a thorough history, examination and comprehensive examination of the patient using instrumental and laboratory techniques. It includes non-drug and drug therapy.
Non-drug therapy is aimed at preventing complications of the disease and includes the following measures:
- Limit salt intake to 5-6 g per day.
- Exclusion from the diet of foods containing polyunsaturated fats.
- The fight against excess weight.
- The inclusion in the diet of vegetables, fruits, cereals, lean meat and pasta from durum wheat.
- Compliance with the drinking regime.
- Quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages.
- Sleep normalization.
- Elimination of psycho-emotional stress and overwork.
- Daily outdoor walks.
- Physical activity adapted to the state of health.
- Normalization of the regime and occupational health (exclusion of work that is associated with noise and vibration).
With a systematically increasing blood pressure, patients with essential hypertension are advised to take antihypertensive drugs. The selection of drugs can only be carried out by a doctor, after analyzing all the data diagnostic examination. To lower blood pressure, you can use:
- sedatives: Reserpine, Raunatin, Vincamine, Apressin, Magnesium sulfate;
- antiadrenergic drugs: Isobarin, Redegram, Dopegyt;
- calcium antagonists: Nifedipine, Verampil, Diltiazem, Corinfar;
- angiotensin II receptor blockers: Naviten, Valsartan, Losartan, Lorista N;
- diuretics: Hydrochlorothiazide, Bumetanide, Brinaldix, Triamteren, Hygroton, Chlorthalidone, Spironolactone;
- beta-blockers: Anaprilin, Timol, Trazikor, Atenolol;
- ACE inhibitors: Lisinopril, Captopril, Enalapril;
- vasodilators: Apressin, Minoxidil, Hyperstat.
Algorithm for prescribing antihypertensive therapy
Antispasmodics (Dibazol), α2-adrenergic agonists (Clonidine, Clonidine), ganglioblockers (Benzohexonium, Pentamine) and other drugs can be used to stop a hypertensive crisis.
Indications for hospitalization of patients with essential hypertension are:
- the complexity of the selection of complex drug therapy;
- hypertensive crises that cannot be stopped on an outpatient basis, and hypertensive crises with signs of hypertensive encephalopathy (confusion, nausea, vomiting);
- the need for complex and invasive diagnostic techniques;
- complications due to hypertension.
Essential arterial hypertension: drugs used during pregnancy ... This article will focus on the principles of drug treatment of arterial hypertension (high blood pressure) in pregnant women, from ...
Prevention of hypertension Prevention of hypertension is a top priority for many people. Particularly relevant is knowledge about the measures to prevent this severe ...
Hypertension: classification and symptoms Hypertension is a disease that is accompanied by a prolonged increase in systolic and diastolic blood pressure and impaired ...
At what pressure is Indapamide taken?

Diuretics that help remove excess fluid from the body are often prescribed for arterial hypertension. One of the most common drugs of this kind is Indapamide, the instructions for use of which, as well as at what pressure it is taken, should be considered in detail.
- Why are they prescribed
- Instructions for use
- How long can you take without a break?
- Contraindications
- Side effects
- Compatibility with other drugs
- Analogues and their comparison
- Arifon Retard or Indapamide
- Indapamide or Veroshpiron
- Hypothiazide or Indapamide
- Indapamide or Furosemide
- hydrochlorothiazide or indapamide
- Diuver or Indapamide
Can I take indapamide and lisinopril at the same time?
Yes. Only indapamide, a mild diuretic, is taken once a day in the morning. If the pressure remains high in the evening, lisinopril is taken at night. Considered a good combination for non-critical pressure buildup. In fact, this should be recommended by a doctor specifically for your case. And then they look to see if this combination is suitable or if another one needs to be selected. In my case, this is a combination: bisoprolol in the morning, lisinopril in the evening. If an hour after taking bisoprolol, the pressure is high, take indapamide. If the pressure is still high in the evening, lisinopril at night. With this scheme, the pressure is within the normal range, without a headache, without problems.
If the pressure is above 180/100, you need a capoten under the tongue.
This combination of Indapamide (Arifon), a drug that is classified as a diuretic, but it is not a diuretic drug.
Arifon retard is a vascular dilator (“expander”) of the microvascular bed, it reduces the total peripheral vascular resistance (OPSS), thereby reducing blood pressure (blood pressure). Arifon retard is included in the "gold standard" for the treatment of hypertension (arterial hypertension) in diabetes mellitus, in which the microvascular bed is damaged throughout the body, especially with damage to target organs (kidney - nephropathy, brain - encephalopathy, retina - angiopathy, peripheral vessels - diabetic angiopathy), which is achieved by the treatment process in this case.
Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor (angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor). The period of action of the drug reaches 30 hours, which is good for older patients who may forget to take the drug and for young people who have an active lifestyle, who may also forget to take the drug on time. It will not be scary if yesterday the patient took a pill at 9 am, and today, for example, at 12.00.
Such combined use of the drug is justified, it is included in two-component reception scheme.
Lisinopril - instructions for use, analogs, testimonials and release forms (tablets 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg) for the treatment of hypertension and pressure reduction in adults, children and pregnancy. Composition and interaction with alcohol
In this article, you can read the instructions for use medicinal product Lisinopril. Reviews of site visitors - consumers of this medicine, as well as opinions of doctors of specialists on the use of Lisinopril in their practice are presented. A big request to actively add your reviews about the drug: did the medicine help or not help get rid of the disease, what complications and side effects were observed, perhaps not declared by the manufacturer in the annotation. Analogues of Lisinopril in the presence of existing structural analogues. Use for the treatment of arterial hypertension and pressure reduction in adults, children, as well as during pregnancy and lactation. The composition and interaction of the drug with alcohol.
Lisinopril- ACE inhibitor, reduces the formation of angiotensin 2 from angiotensin 1. A decrease in the content of angiotensin 2 leads to a direct decrease in the release of aldosterone. Reduces the degradation of bradykinin and increases the synthesis of prostaglandins. It reduces the total peripheral vascular resistance, blood pressure (BP), preload, pressure in the pulmonary capillaries, causes an increase in the minute volume of blood and an increase in myocardial tolerance to stress in patients with chronic heart failure. Expands the arteries more than veins. Some effects are explained by the effect on the tissue renin-angiotensin systems. With prolonged use, hypertrophy of the myocardium and walls of resistive arteries decreases. Improves blood supply to ischemic myocardium.
ACE inhibitors prolong life expectancy in patients with chronic heart failure, slow down the progression of left ventricular dysfunction in patients with myocardial infarction without clinical manifestations heart failure. The antihypertensive effect begins after about 6 hours and lasts for 24 hours. The duration of the effect also depends on the dose. The onset of action is after 1 hour. The maximum effect is determined after 6-7 hours. In arterial hypertension, the effect is noted in the first days after the start of treatment, a stable effect develops after 1-2 months.
With a sharp withdrawal of the drug, no pronounced increase in blood pressure was observed.
In addition to lowering blood pressure, lisinopril reduces albuminuria. In patients with hyperglycemia, it contributes to the normalization of the function of the damaged glomerular endothelium.
Lisinopril does not affect the concentration of glucose in the blood in patients with diabetes mellitus and does not lead to an increase in cases of hypoglycemia.
Lisinopril (in the form of dihydrate) + excipients.
After taking the drug inside, about 25% of lisinopril is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Eating does not affect the absorption of the drug. Almost does not bind to plasma proteins. Permeability through the blood-brain and placental barrier is low. Lisinopril is not biotransformed in the body. Excreted by the kidneys unchanged.
- arterial hypertension (in monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive agents); chronic heart failure (as part of combination therapy for the treatment of patients taking digitalis and / or diuretics); early treatment acute myocardial infarction (in the first 24 hours with stable hemodynamic parameters to maintain these parameters and prevent left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure); diabetic nephropathy(reduction of albuminuria in insulin-dependent patients with normal blood pressure and non-insulin-dependent patients with arterial hypertension).
Tablets 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg.
Instructions for use and dosage
The full effect usually develops after 2-4 weeks from the start of treatment, which should be taken into account when increasing the dose. With insufficient clinical effect it is possible to combine the drug with other antihypertensive drugs.
If the patient received prior treatment with diuretics, then taking such drugs should be stopped 2-3 days before the start of Lisinopril. If this is not feasible, then the initial dose of Lisinopril should not exceed 5 mg per day. In this case, after taking the first dose, it is recommended medical supervision within a few hours (the maximum effect is reached after about 6 hours), since a pronounced decrease in blood pressure may occur.
In case of renovascular hypertension or other conditions with increased activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, it is also advisable to prescribe a low initial dose - 2.5-5 mg per day, under increased medical supervision (control of blood pressure, kidney function, serum potassium concentration). The maintenance dose, while continuing strict medical supervision, should be determined depending on the dynamics of blood pressure.
In chronic heart failure - start with 2.5 mg 1 time per day, followed by an increase in dose by 2.5 mg after 3-5 days to the usual maintenance daily dose of 5-20 mg. The dose should not exceed 20 mg per day.
In elderly people, a more pronounced long-term hypotensive effect is often observed, which is associated with a decrease in the rate of excretion of lisinopril (it is recommended to start treatment with 2.5 mg per day).
Acute myocardial infarction (as part of combination therapy)
On the first day - 5 mg orally, then 5 mg every other day, 10 mg two days later and then 10 mg 1 time per day. In patients with acute myocardial infarction, the drug should be used for at least 6 weeks. At the beginning of treatment or during the first 3 days after acute myocardial infarction in patients with low systolic blood pressure (120 mm Hg or below), a lower dose of 2.5 mg should be prescribed. In the event of a decrease in blood pressure (systolic blood pressure less than or equal to 100 mm Hg), the daily dose of 5 mg can, if necessary, be temporarily reduced to 2.5 mg. In the case of a prolonged pronounced decrease in blood pressure (systolic blood pressure below 90 mm Hg for more than 1 hour), treatment with Lisinopril should be discontinued.
In patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus, Lisinopril 10 mg is used once a day. The dose may, if necessary, be increased to 20 mg 1 time per day in order to achieve diastolic blood pressure values below 75 mm Hg. in a sitting position. In patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, the dosage is the same, in order to achieve diastolic blood pressure values below 90 mm Hg. in a sitting position.
- dizziness; headache; weakness; diarrhea; dry cough; nausea, vomiting; skin rash; chest pain; angioedema (face, lips, tongue, larynx or epiglottis, upper and lower limbs); pronounced decrease in blood pressure; orthostatic hypotension; impaired renal function; heart rhythm disturbances; cardiopalmus; fatigue; drowsiness; convulsive twitching of the muscles of the limbs and lips; leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia; heartbeat; tachycardia; myocardial infarction; cerebrovascular stroke in patients with an increased risk of the disease, due to a pronounced decrease in blood pressure; dry mouth; anorexia; dyspepsia; taste changes; stomach ache; hives; increased sweating; pruritus; alopecia; impaired renal function; oliguria; anuria; acute renal failure; asthenic syndrome; mood lability; confusion; decrease in potency; myalgia; fever; fetal development disorder.
- angioedema in history, incl. and from the use of ACE inhibitors; hereditary angioedema; age up to 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established); hypersensitivity to lisinopril or other ACE inhibitors.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
The use of lisinopril during pregnancy is contraindicated. When pregnancy is established, the drug should be stopped as soon as possible. Taking ACE inhibitors in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy has an adverse effect on the fetus (a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, renal failure, hyperkalemia, skull hypoplasia, intrauterine death are possible). There are no data on the negative effects of the drug on the fetus if used during the 1st trimester. For newborns and infants who have been exposed to ACE inhibitors in utero, it is recommended to conduct careful monitoring for the timely detection of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, oliguria, hyperkalemia.
Lisinopril crosses the placenta. There are no data on the penetration of Lisinopril into breast milk. For the period of treatment with the drug, it is necessary to stop breastfeeding.
Most often, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure occurs with a decrease in fluid volume caused by diuretic therapy, a decrease in the amount of salt in food, dialysis, diarrhea, or vomiting. In patients with chronic heart failure with simultaneous renal failure or without it, a pronounced decrease in blood pressure is possible. It is more often detected in patients with severe chronic heart failure, as a result of the use of large doses of diuretics, hyponatremia, or impaired renal function. In such patients, treatment with Lisinopril should be started under the strict supervision of a physician (with caution, select the dose of the drug and diuretics).
Similar rules should be followed when prescribing to patients with coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular insufficiency, in which a sharp decrease in blood pressure can lead to myocardial infarction or stroke.
A transient hypotensive reaction is not a contraindication for taking the next dose of the drug.
When using Lisinopril in some patients with chronic heart failure, but with normal or low blood pressure, there may be a decrease in blood pressure, which is usually not a reason to stop treatment.
Before starting treatment with Lisinopril, if possible, it is necessary to normalize the concentration of sodium and / or replenish the lost volume of fluid, carefully monitor the effect of the initial dose of Lisinopril on the patient.
In case of renal artery stenosis (especially with bilateral stenosis, or in the presence of stenosis of the artery of a single kidney), as well as in circulatory failure due to lack of sodium and / or fluid, the use of Lisinopril can also lead to impaired renal function, acute renal failure, which is usually is irreversible after discontinuation of the drug.
At acute infarction myocardium
The use of standard therapy (thrombolytics, acetylsalicylic acid, beta-blockers). Lisinopril can be used in conjunction with intravenous administration or using therapeutic transdermal nitroglycerin systems.
Surgery/general anesthesia
With extensive surgical interventions, as well as when using other drugs that cause a decrease in blood pressure, lisinopril, blocking the formation of angiotensin 2, can cause a pronounced unpredictable decrease in blood pressure.
In elderly patients, the same dose leads to a higher concentration of the drug in the blood, so special care is required when determining the dose.
Since the potential risk of agranulocytosis cannot be excluded, periodic monitoring of the blood picture is required. When using the drug in dialysis conditions with a polyacryl-nitrile membrane, anaphylactic shock therefore, either a different type of dialysis membrane or other antihypertensive agents are recommended.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and mechanisms
There is no data on the effect of lisinopril on the ability to drive vehicles and mechanisms used in therapeutic doses, however, it must be borne in mind that dizziness may occur, so caution should be exercised.
Lisinopril reduces the excretion of potassium from the body during treatment with diuretics.
Special care is required while using the drug with:
- potassium-sparing diuretics (spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride), potassium, table salt substitutes containing potassium (the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases, especially with impaired renal function), so they can be jointly prescribed only on the basis of an individual decision of the attending physician with regular monitoring of serum potassium levels blood and kidney function.
Use with caution together:
- with diuretics: with the additional administration of a diuretic to a patient taking Lisinopril, as a rule, an additive antihypertensive effect occurs - the risk of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure; with other antihypertensive drugs (additive effect); with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (indomethacin, etc.), estrogens, as well as adrenostimulants - a decrease in the antihypertensive effect of lisinopril; with lithium (lithium excretion may decrease, therefore, the concentration of lithium in the blood serum should be regularly monitored); with antacids and colestyramine - reduce absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Alcohol enhances the effect of the drug.
Analogues of the drug Lisinopril
Structural analogues for the active substance:
The article was written based on materials from sites: gipertonia03.ru, cardiolog.online, my-pochki.ru, giperton-med.ru, vita-site.ru.
Katerina Ryzhova
Articles written
In contact with
classmates
Diuretics that help remove excess fluid from the body are often prescribed for arterial hypertension. One of the most common drugs of this kind is Indapamide, the instructions for use of which, as well as at what pressure it is taken, should be considered in detail.
Read more here…
- Why are they prescribed
- Instructions for use
- How long can you take without a break?
- Contraindications
- Side effects
- Compatibility with other drugs
- Analogues and their comparison
- Arifon Retard or Indapamide
- Indapamide or Veroshpiron
- Hypothiazide or Indapamide
- Indapamide or Furosemide
- hydrochlorothiazide or indapamide
- Diuver or Indapamide
Why are they prescribed
Worried about pressure?
YesNot
The only indication of Indapamide is arterial hypertension. Especially often it is prescribed if the increase in blood pressure is accompanied by severe edema and fluid retention. Due to the removal of excess fluid, blood pressure indicators decrease.
Such funds often form the basis of treatment. They are usually supplemented with other antihypertensive drugs. At what pressure are such medicines required? Usually they are prescribed if arterial hypertension persists constantly, full-fledged arterial hypertension develops, pressure indicators are constantly kept above 140 to 100.
Indapamide - diuretic or not? Since this drug is a diuretic, it has a diuretic effect, removes fluid from the body. It should be borne in mind that increasing the dosage does not lead to an increase in the hypotensive effect, since only the diuretic is enhanced. Therefore, do not overestimate the dosage of this remedy, especially on your own.
The average price of the drug is 20–50 rubles, depending on the pharmacy chain. The drug is one of the cheapest diuretic drugs used for arterial hypertension.
Instructions for use
Usually this drug is taken once a day, the standard dosage is 2.5 mg of the substance. It is usually not changed - it can only be adjusted by adding other drugs with an antihypertensive effect to the therapy.
How to take - before meals or after - does not matter. The instructions for the drug say that the time of day and meals do not affect the effect of the drug, so it is not necessary to focus on them.
How long can you take without a break?
Usually, the course of treatment with various antihypertensive drugs during the acute stage of hypertension does not last long - up to several weeks. Then, when the blood pressure drops sufficiently steadily, the course of treatment is stopped. In the future, to maintain pressure within normal limits, it is important to follow the right diet and other doctor's recommendations.
Regarding the duration of taking this drug, you should first consult with your doctor. In each individual case, the course of therapy will be different - it all depends on the severity of the disease and the condition of the patient as a whole.
Contraindications
Indapamide has a number of fairly strict contraindications. This drug should not be used in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. In case of violations of the functions of these organs, a diuretic is taken exclusively under the strict supervision of a doctor, constantly monitoring the situation and the dynamics of changes.
- Also, this drug should not be used in case of intolerance to the components of the composition, primarily the diuretic itself, as well as other substances included in the drug.
- In particular, you should not use the remedy for lactose intolerance, since it is part of the tablet itself.
- A strict contraindication is children's age. Before the age of eighteen, this medicine for high blood pressure should not be used, as there is no evidence of its safety in children.
- Indapamide should not be used during pregnancy either: childbearing and breastfeeding are quite strict contraindications to taking the medicine.
Side effects
This diuretic has quite a few possible side effects. They do not appear so often if you take Indapamide according to the instructions. Usually, the following groups of side effects are distinguished:
- dizziness, headaches, sleep disturbances, asthenia, other disorders of the nervous system;
- hypotension, rhythm disturbances, other side effects from the circulatory system;
- severe cough, pharyngitis, sinusitis;
- various infections from the excretory system;
- violations of hematopoiesis, changes in blood tests;
- all kinds of allergic reactions, skin rashes, urticaria.
These side effects are most common with indapamide. but with the right reception, the likelihood of their occurrence is quite small.
Compatibility with other drugs
Consider which drug can replace Indapamide and which one is better.
Concor and Indapamide: compatibility
Concor and Indapamide have good compatibility, they are often prescribed as joint complex therapy. Indapamide may also combine well with other beta-blockers.
Lorista and Indapamide: can they be taken together?
Lorista (an angiotensin receptor antagonist) and Indapamide can be combined together with your doctor's permission. Quite often, these two drugs are prescribed simultaneously for complex therapy.
Prestarium and Indapamide: joint use
Prestarium is a medicine used for hypertension and heart failure. It happens that it is prescribed together with diuretics, in particular - with Indapamide. These drugs work well together.
Lisinopril and Indapamide: Can I take it at the same time?
The combination of Lisinopril and Indapamide allows you to quickly and effectively lower blood pressure, while they remain within the normal range for a long time, and hypertension recedes. Lisinopril is an ACE inhibitor. In this case, you should not start taking such a combination of funds on your own - you must first consult with a specialist.
Analogues and their comparison
Direct analogues of Indapamide are other diuretics based on the same active substance. They primarily include Arifon. You can also use other diuretics aimed at lowering blood pressure. Before using the analog, you must definitely read the instructions for use.
In terms of effects, only drugs of the same group can be compared - diuretics, which include Indapamide. It is difficult to say which is better: Indapamide or Concor. These drugs are different types of drugs and affect the body in different ways. It is also impossible to say which is better: Indapamide or Enalapril. This is a completely different tool with a different effect on the body. However, it is worth noting that diuretics should first of all be paid attention to if hypertension is accompanied by swelling.
Arifon Retard or Indapamide
Arifon Retard is also based on the action of the substance Indapamide, but the price of this analogue is higher. One pack of medicine costs up to 300-350 rubles. At the same time, these tools practically do not differ in action.
Nevertheless, it should be borne in mind that Arifon has fewer contraindications. At an older age and in the presence of liver and kidney diseases, it is better to choose it. Indapamide has a more negative effect on the body.
Indapamide or Veroshpiron
Veroshpiron is also a fairly effective diuretic for arterial hypertension. However, it is worth noting that this drug can be used for a number of other diseases, while it has fewer contraindications than Indapamide. Therefore, when choosing drugs, it is worth paying attention to it as well.
Hypothiazide or Indapamide
Hypothiazide is also an effective diuretic for hypertension, which is often prescribed for this disease. At the same time, it has a wider range of applicability. According to contraindications, these drugs are very similar.
Indapamide or Furosemide
With arterial hypertension, it is better to choose the first diuretic, since this drug is intended for the treatment of this disease. Furosemide is commonly used for other conditions.
hydrochlorothiazide or indapamide
Hydrochlorothiazide is also a thiazide diuretic, like Hypothiazide. In action, these drugs are more similar. The most appropriate group of drugs should be chosen depending on the indications, the course of the disease, and comorbidities.
Diuver or Indapamide
Diuver is more similar in effect to Furosemide, while it is also quite often prescribed for arterial hypertension. This remedy is especially helpful with increased edema formation. It has more contraindications, so before using it, you must definitely read the instructions for use.
Valsartan tablets: instructions for use, price and reviews
The drug Valsartan is in the drug reference book of the RLS. This is a modern drug, the therapeutic effect of which is to bring blood pressure back to normal and improve the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
In 2008, Valsartan received the title of the most popular remedy for arterial hypertension. The advantages of the drug include the absence of a negative effect on total cholesterol, uric acid and plasma glucose, as evidenced by the reviews of doctors.
Valsartan is a tablet for oral use. The drug is covered with a protective pink shell and contains the main active ingredient valsartan in volumes of 40.80 or 160 mg. Tablets also contain such auxiliary components:
- microcrystalline cellulose,
- magnesium sterate,
- pink dye,
- aerosil.
The instruction reports that Valsartan nan contains:
- valsartan - 80 mg or 160 mg,
- gossypin,
- maize starch,
- croscarmellose sodium,
- povidone,
- silicon dioxide,
- magnesium stearate,
- disaccharide monohydrate,
- hydroxypropyl methylcellulose,
- titanium dioxide,
- copovidone,
- polydextrose,
- polyethylene glycol,
- medium chain triglycerides,
- scarlet iron oxide.
Pharmacological characteristics
Valsartan tablets are taken orally, the medicine immediately enters the digestive canal. Its main active ingredients are quickly absorbed through the mucous membranes into the bloodstream.
The drug and its analogues act on the AT 1 anti-ongesin 2 receptors located in:
- vascular endothelium,
- heart muscle,
- kidney tissue,
- lung tissue,
- brain,
- adrenal cortex.
The active ingredients of the drug reduce the hypertrophy of the heart muscle, which can develop as a result of a steady increase in blood pressure.
Feedback from patients suggests that after about three weeks there is a significant improvement in the condition. In particular, blood pressure indicators are normalized, and with physical activity, and at rest.
In people with chronic heart failure, swelling of the face and legs is reduced, and the risk of post-infarction complications is also reduced.
Amlodipine + Valsartan
Amlodipine + Valsartan is a combined antihypertensive drug. Valsartan acts as an AT1 angiotensin II receptor blocker. Amlodipine is a third generation calcium channel blocker.
For the treatment of hypertension, our readers have successfully used ReCardio. Seeing the popularity of this tool, we decided to bring it to your attention.
Read more here…
It inhibits the flow of calcium ions through the membrane in vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiomyocytes, relaxing them.
Amlodipine reduces peripheral total vascular resistance, which helps to reduce pressure in the supine and standing positions. Amlodipine is 90% metabolized in the liver. Amlodipine is excreted by the kidneys in two phases.
Absorption of the drug Amplodipine + Valtarsan corresponds to the bioavailability of each drug separately. The maximum concentration of the drug Amlodipine is reached after 6-8 hours, and the drug Valsartan - after 3 hours.
Instructions for use informs that the drug should be taken orally with water, regardless of the meal. The medicine is taken once, 1 tablet per day. The drug received favorable reviews from doctors and patients.
Valsartan tablets should not be chewed. Tablets should be taken with a sufficient amount of liquid. The dosage of the drug and the duration of use is determined by the doctor, depending on the diagnosis and individual characteristics.
Instructions for use informs that patients with an increase in pressure should take 80 mg of the drug per day. If necessary, daily dose may increase, but this should occur gradually and only in the absence of a therapeutic effect from the minimum dose.
After suffering a myocardial infarction, the patient is prescribed 40 mg of the drug twice a day in the first hours. For three months, this dose is gradually increased to 320 mg per day.
Valsartan tablets are not intended for use by pregnant women. If a woman used the drug and pregnancy began during this period, then it is necessary to stop treatment as soon as possible and consult a doctor. In some cases, the pregnancy is terminated.
Possible side effects
When using this drug in humans, in some cases, the following negative phenomena may appear:
- lethargy,
- weakness and dizziness,
- decreased sex drive,
- fainting
- muscle pain,
- development of renal failure with the wrong dosage,
- insomnia,
- the formation of angioedema,
- stool disorder,
- joint discomfort,
- increased sensitivity,
- skin rashes,
- nausea, epigastric pain,
- pressure drop,
- viral infections: sinusitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis,
- change in clinical picture blood: anemia, thrombocytopenia.
With a significant increase in the recommended dosages, the patient may develop severe hypertension, up to fainting, collapse, and then coma. Overdose therapy consists of gastric lavage and oral intake of enterosorbents.
Instructions for the drug Amlodipine + Valsartan indicate such restrictions for use:
- aortic or mitral stenosis,
- chronic renal failure,
- hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy,
- decrease in the amount of circulating blood.
In case of an overdose of Amlodipine + Valsartan, symptoms may appear:
- a strong decrease in blood pressure,
- dizziness,
- reflex tachycardia,
- a pronounced decrease in pressure up to shock with a fatal outcome.
To normalize blood pressure indicators, you can enter an isotonic sodium solution. With the simultaneous administration of the drug with diuretics in humans, the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases significantly. A similar process occurs with the simultaneous use of potassium preparations.
If Valsartan is used together with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, then patients may experience a decrease in the therapeutic effect of Valsartan and deterioration in kidney function. At simultaneous use with other drugs that lower blood pressure, the risk of syncope and hypotension is significantly increased.
Since at first, during treatment with the drug, a person has drowsiness and dizziness, driving should be avoided. Vehicle and control of dangerous mechanisms that require reaction speed and concentration.
Instructions for using the drug
Valsartan tablets are prescribed to people in the treatment and prevention of such conditions:
- the initial stage of hypertension with a persistent increase in blood pressure,
- myocardial infarction,
- heart failure in congestive processes.
This drug, based on the instructions for use, is not recommended for patients for treatment if there are such conditions:
- severe liver damage
- childhood,
- pregnancy and lactation,
- individual intolerance to the components that make up the product.
With caution, Valsartan should be prescribed to people in the presence of the following pathologies:
- stenosis of the renal arteries,
- dehydration,
- kidney failure,
- obstruction of the bile ducts, which are caused by stones or a tumor,
- hyposodium diet.
Additional Information
Valsartan, like Amlodipine, is available from a pharmacy on prescription. The medicine must be stored in an inaccessible place at a temperature not exceeding 30 degrees.
The average price of the drug Valsartan in tablet form is 200 rubles. The price of Valsartan is in the range of 300-900 rubles, depending on the amount of the active substance. The cost of the drug Amlodipine + Valsartan is within 250 rubles.
The drug Valsartan has analogues that have this active ingredient:
If Valsartan and these drugs cannot be purchased, you can buy the following analogues:
Enap consists of enalapril, which has similar characteristics to Valsartan and positive reviews. Corinfar treats heart diseases, its active ingredient is Nifedipine.
Sakura has a narrow application - the treatment of arterial hypertension, so the drug and its analogues replace Valsartan. The active ingredient in Sakura is lacidipine.
Cardura is used as a first-line drug for the treatment of hypertension. The main task is to control pressure. The drug receives positive reviews because it has a small number of side effects.
Tonusin has a complex effect and is used as a general tonic. Tonusin normalizes blood pressure and improves coronary circulation. How else can you deal with pressure, the video in this article will tell.
on the
Indapamide is an affordable and effective drug for arterial hypertension.
Have you struggled with HYPERTENSION for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure hypertension by taking it every day.
Arterial hypertension is a formidable disease that shortens the life of many people. modern medicine offers a variety of drugs to combat this disease. The main task of these drugs is to lower blood pressure in humans and prevent sudden pressure surges in humans that cause strokes and heart attacks.
For the treatment of hypertension, our readers have successfully used ReCardio. Seeing the popularity of this tool, we decided to bring it to your attention.
Read more here…
Indapamide instructions for use
In pharmacology, this medicine is referred to as diuretics, chemicals enhancing the process of urine formation and removal of excess salts with it from the body.
Action of Indapamide
This medicine changes the balance of Na and Cl in the body, from excess makes it negative. In addition to Na and Cl ions, it removes K and Mg ions somewhat less. The excretion of ions of these salts is accompanied by increased excretion of urine, which leads to a decrease in blood pressure.
This drug increases the elasticity of large arteries, reduces the resistance of the vascular system to the ejected blood flow by the human heart. It also reduces the rate of hypertension.
The maximum effect occurs after 6-7 days of administration by establishing an individual dose of the drug for each patient.
Pharmacokinetics
When ingested in the form of tablets or capsules, the drug is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) within 2 minutes, while the bioavailability of the drug reaches 93%, 7% of the drug is removed unchanged with feces. When taking the drug during meals, bioavailability does not change, but the duration of absorption in the gastrointestinal tract increases.
Indapamide indications for use or what Indapamide is prescribed for
The drug is aimed at the treatment of arterial hypertension. And in complex treatment it is used to relieve edema that occurs in chronic heart failure.
Indapamide: release forms and dosage
The drug is sold in standard tablets, tablets with controlled release of the main substance and tablets of prolonged action.
Standard white tablets film sheath hemispherical shape. Each contains 2.5 mg of the active substance. The composition also includes excipients.
Tablets with controlled release and tablets of prolonged action and contain 1.5 mg of indapamide and excipients.
Tablets are prescribed to be taken in the morning every day, without chewing, swallowing it, drinking water.
Indapamide: side effects
With prolonged treatment with the drug may appear side effects as an effect on:
- nervous system increased nervousness, depression, insomnia;
- Hematopoiesis, increasing thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic and hemolytic anemia;
- The digestive system in the form of vomiting, nausea, constipation, diarrhea, dry mouth and much less often pancreatitis;
- Respiratory organs in the form of a dry cough, manifestations of pharyngitis or sinusitis;
- Cardiovascular system in the form of arrhythmia or pronounced hypotension;
- The genitourinary system by weakening the resistance to infections, a decrease in potency;
- Skin possible appearance allergies (itching, redness, rash);
- Laboratory indicators for the appearance of hypokalemia, very rarely hypercalcemia and hyponatremia, as well as for growth
- The concentration of uric acid and glucose in the blood.
Contraindications to the use of the drug
- Indapamide is not taken with severe renal failure and severe liver dysfunction;
- Contraindicated in hypokalemia;
- It is unacceptable to take this medicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding, be wary of children under 18 years of age;
- The drug should not be used in case of hypersensitivity to indapamide and its components;
- With diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2, with gout;
- Caution should be used in the elderly, under the mandatory control of creatinine levels;
- It should not be taken concomitantly with drugs that increase the QT interval on the ECG and other antiarrhythmic drugs.
Indapamide analogs
An analogue of Indapamide is Indapamide Retard, produced in the form of prolonged-release tablets. This analog increases the duration of the drug when its dose is reduced from 2.5 mg to 1.5 mg. This is precisely the answer to frequently asked question which is better Indapamide or Indapamide Retard. Therefore, the price of Indapamide Retard is higher than that of Indapamide.
Other analogues of indapamide are mostly associated with the name of the drug manufacturer. For example, Indapamid-Teva is a manufacturer of Teva Israel, Indapamid MV Stada is a manufacturer of Stada Arzneimittel Germany. This list also includes Arifon Retard, produced in France, the period of prolonged action of which remains 24 hours.
In addition to the above indapamide preparations, there are analogues under other names.