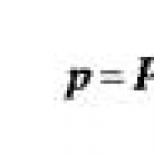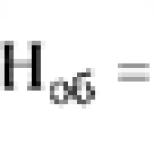Anastrozole time of action. Medicinal reference book geotar. The use of the substance Anastrozole
Recently, more and more "dirty" anabolics have appeared on the black market of anabolic drugs. This is due to the spread and popularization of power sports and the cultivation of artisanal (homemade) preparations that are cooked right in the kitchen. All these prepas cause a number of side effects and a jump in estrogen in the body of an athlete, in order to prevent this, you need to know how to take anastrozole on the course and after the course.
Anastrozole (Anastrozol) is a well-loved anti-estrogen drug. It is presented on the market in tablet form, the first mentions appear in 95, but it came to Russia much later. Initially, the drug was used exclusively by physicians to treat breast cancer, but after that it was also taken in bodybuilding.
If you don’t know how to make a training program, the first course or a diet, then add yourself and write to me in a personal on instagram
Anastrozole is a very strong inhibitor, 1 mg active substance able to reduce the content of estradiol by 85%. You should not put anastrozole and tamoxifen in the same row, the effect of their effects is completely different.
Effects of taking anastrozole
- Effective suppression of aromatization;
- Powerful antiestrogen;
- Strong blocker;
- Able to bring down the level of estradiol concentration right on the course for 2 hours;
- Removes and does not allow to retain water.
How to take
In bodybuilding, anastrozole should be taken on a course for no more than 2 weeks. Reception begins immediately, as the first signs of increased aromatization were discovered. For athletes with low level estradiol in the blood is enough for 0.25 mg of the active substance every other day (this is a quarter of a tablet).
If something went wrong and the level of estrogen goes off scale by 1.5-2 times, carry out prophylaxis 1 tablet every other day for two weeks. At the end, be sure to cancel the drug and check the level of estradiol. Note that there is no difference on the course or after the course you will take the drug.
Reception of anastrozole for women is categorically contraindicated. Failure to comply with this recommendation may lead to a failure of the hormonal system.
Side effects

Side effects are manifested only as a result of individual intolerance or drug overdose. Keep in mind that it's hard to notice an overdose, but if you stick to the prescribed doses, then the risk of side effects is close to zero. If suddenly side effects appear, stop taking the substance immediately.
Main side effects:
- Nausea;
- High blood pressure;
- Headache;
- Diarrhea;
- Vomit;
- Rash on the skin.
Also, the drug should not be used by people with disorders of the cardiovascular system.
ANASTRAZOLE belongs to the group anticancer drugs called "aromatase inhibitors". ANASTRAZOLE is used for the treatment of advanced hormone-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women and as adjuvant therapy for early hormone-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women, including after tamoxifen therapy for 2-3 years.
ANASTRAZOLE reduces the amount of a hormone called estrogen that your body makes by blocking a natural substance (enzyme) in your body called "aromatase".
Do not take Anastrozole if
You are allergic to ANASTRAZOLE or any of the other ingredients of this medicine listed in the "Ingredients" section of this leaflet.
You are pregnant.
You are planning a pregnancy, or you are not using adequate methods of contraception.
You are breastfeeding.
If any of the above apply to you, tell your doctor before starting treatment with ANASTRAZOLE.
ANASTRAZOLE is not recommended for use in children (under 18 years of age).
special instructions and precautions" type="checkbox">
Special instructions and precautions
Tell your doctor before starting treatment with ANASTRAZOLE
- If you are still menstruating and have not yet gone through menopause.
- If you are taking a medicine that contains tamoxifen or medicines containing estrogen (see section "Other medicines and ANASTRAZOLE").
- If you have ever had a condition that affects the strength of your bones (osteoporosis).
- If you have liver or kidney problems.
If any of the above apply to you, tell your doctor immediately.
Always tell your doctor if you are already taking ANASTRAZOLE.
Anastrozole contains lactose.
If your doctor has told you that you have problems with intolerance to any type of sugar, you should not take this medicine.
Talk to your doctor before taking this drug.
Other drugs and Anastrozole
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines. This applies to any herbal preparations or drugs you bought without a prescription.
There are some medicines that can change the effect of ANASTRAZOLE, or their effect can be changed by ANASTRAZOLE. Tell your doctor if you are taking any other medicines.
Do not take ANASTRAZOLE if you are already taking any of the following medicines:
- Medicines used to treat breast cancer (selective estrogen receptor modulators), such as medicines containing tamoxifen. These medicines may affect ANASTRAZOLE.
- Preparations containing estrogen as a replacement hormone therapy(HRT).
- Drugs known as "luteinizing releasing hormone analogue". For example, gonadorelin, buserelin, goserelin, leuprorelin and triptorelin. These medicines are used to treat breast cancer, certain women's health conditions (gynecological conditions), and infertility.
If any of the above apply to you, please consult your physician.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility
Do not take ANASTRAZOLE if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
If you think you are pregnant or planning to have a baby, check with your doctor before taking this medicine.
vehicles and work with mechanisms" type="checkbox">
Driving vehicles and working with mechanisms
ANASTRAZOLE is unlikely to affect your ability to drive or use machines. However, some people may occasionally feel weak or drowsy while taking ANASTRAZOLE. If you have any symptom, seek help from your doctor.
Application of the drug
Always take this medicine exactly as directed by your doctor. If in doubt, consult your doctor.
The recommended dose is one tablet once a day.
Try to take the pill at the same time each day.
Swallow the tablet whole with drinking water.
It does not matter if you take ANASTRAZOLE before, with or after a meal.
Continue taking ANASTRAZOLE for as long as your doctor has recommended. This is a long term treatment and you may need to take ANASTRAZOLE for several years. If you have questions, please consult with your doctor.
Use in children and adolescents
ANASTRAZOLE is not used in children and adolescents.
If taken more than prescribed
If you have taken more than the prescribed dose, contact your doctor immediately.
If you forget to take Anastrozole
If you forget to take ANASTRAZOLE, take your next dose as usual.
Do not take a double dose (two doses at the same time) to make up for a missed dose.
If you stop using Anastrozole
Do not stop taking the tablets unless your doctor tells you to.
If you have any further questions about using this drug, contact your doctor.
Possible adverse reactions
Like all medicines, ANASTRAZOLE can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
Stop taking ANASTRAZOLE and seek medical attention immediately medical care if you experience the following serious, but very rare, side effects:
- If you have an extremely severe skin reaction with sores or blisters on the skin. The reaction is called Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
- If you have allergic reaction(hypersensitivity), which is manifested by swelling of the throat and can cause difficulty in breathing and swallowing. The reaction is called angioedema or angioedema.
Often(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Headache.
- Tides.
- Feeling of nausea.
- Skin rash.
- Pain or stiffness in the joints.
- Inflammation of the joints (arthritis).
- Feeling of weakness.
- Loss of bone mass (osteoporosis).
Often(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Loss of appetite.
- An increase in the level of cholesterol in the blood, which is determined by a blood test.
- Drowsiness.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (tingling, pain, coldness, weakness in parts of the hand).
- Tickling sensation, tingling or numbness of the skin, loss/lack of taste.
- Diarrhea.
- Feeling unwell (vomiting).
- Changes in blood tests that show the condition of your liver.
- Thinning hair (hair loss).
- Allergic (hypersensitivity) reactions, including the face, lips or tongue.
- Pain in the bones.
- Dryness of the vagina.
- Bleeding from the vagina (usually in the first few weeks of treatment, if the bleeding does not stop, consult a doctor).
- Pain in the muscles.
Infrequently(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Changes in blood tests that determine the state of the liver (gamma-glutamyl transferase, bilirubin).
- Inflammation of the liver (hepatitis).
- Rash or nettle fever.
- Trigger finger syndrome (a condition where the fingers are in a forced flexion position).
- Increasing the level of calcium in the blood. If you feel nauseous, vomiting or thirsty, tell your doctor immediately as blood tests are required.
Rarely(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- Inflammation on the skin, which may include red patches or blisters.
- Skin rash caused by hypersensitivity (which may be an allergic or anaphylactoid reaction).
- Inflammation of small blood vessels causing a red or purple discoloration of the skin. Very rarely, symptoms of pain in the joints, stomach and kidneys (“Schonlein-Henoch purpura”) may occur.
Effect on mineral density bone tissue
Since ANASTRAZOLE lowers the level of estrogen in the blood, this can lead to a decrease in bone mineral density with a possible subsequent increase in the risk of fractures.
Your doctor will take these risks into account and prescribe treatment according to protocols for treating bone and joint problems in menopausal women. You should talk to your doctor about the risks and treatment options.
Reporting adverse reactions
If you experience any adverse reactions, please consult your physician. This also applies to any side effects not listed in this package insert. You can also report adverse reactions to the information database on adverse reactions (actions) to medicines, including reports of ineffectiveness medicines, identified on the territory of the state (UE Center for Expertise and Testing in Public Health M3 RB, rceth.by). By reporting adverse reactions, you help to get more information about the safety of the drug.
Trade name:
anastrozole.
International non-proprietary name:
anastrozole.
Dosage form:
coated tablets film sheath.
Composition per tablet:
active substance: anastrozole - 1 mg;
Excipients
- sodium carboxymethyl starch (type A), povidone K-25, calcium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, lactose monohydrate; opadra II white (85 F);
shell composition (Opadry II white (85 F)): polyvinyl alcohol, partially hydrolyzed, macrogol (polyethylene glycol), talc, titanium dioxide.
Description:
film-coated tablets, white or almost white, round, biconvex. On the surface of the tablets, the roughness of the film coating is allowed.
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
antitumor agent - estrogen synthesis inhibitor.
ATC code:
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Anastrozole is a highly selective non-steroidal inhibitor of the aromatase enzyme, which in the body of postmenopausal women converts androstenedione in peripheral tissues to estrone and then to estradiol. The therapeutic effect in patients with breast cancer is achieved by reducing the level of circulating estradiol. In postmenopausal women, anastrozole at a daily dose of 1 mg causes a decrease in estradiol levels by 80%.
He has progestogenic, androgenic and estrogenic activity. A daily dose of up to 10 mg has no effect on the secretion of cortisol and aldosterone. Replacement corticosteroids are not required. Anastrozole may cause a decrease in bone mineral density in patients with hormone-positive postmenopausal early breast cancer. Anastrozole alone, as well as in combination with bisphosphonates, does not change plasma lipid levels.
Pharmacokinetics
It is rapidly absorbed, the maximum plasma concentration is reached within 2 hours after ingestion on an empty stomach. Food slightly reduces the rate of absorption. The degree of reduction does not have a clinically significant effect on the equilibrium concentration of the drug in plasma with a single dose. daily dose. Approximately 90-95% of the equilibrium concentration of anastrozole is achieved after 7 days of taking the drug. There are no data on the dependence of pharmacokinetic parameters on time and dose. The age of postmenopausal women does not affect the pharmacokinetics. Communication with plasma proteins - 40%.
Anastrozole is excreted from the body slowly. The plasma half-life is 40-50 hours. Extensively metabolized in postmenopausal women. 10% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine within 72 hours after ingestion. Metabolized by N-dealkylation, hydroxylation and glucuronidation. The main metabolite triazole has no activity. Excretion of metabolites occurs in the urine.
Cirrhosis of the liver or impaired renal function does not change the clearance of anastrozole after oral administration.
The pharmacokinetics of anastrozole in children has not been studied.
Indications for use
- adjuvant therapy early cancer of the breast, with positive hormone receptors in postmenopausal women, including after adjuvant therapy with tamoxifen for 2-3 years.
- First-line therapy for locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer with positive or unknown hormone receptors in postmenopausal women.
- Second-line therapy for advanced breast cancer progressing after tamoxifen treatment in postmenopausal women.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to anastrozole or other components of the drug.
- Pregnancy and lactation period;
- Contraindicated in premenopausal women.
- Expressed kidney failure(creatinine clearance less than 20 ml/min).
- moderate or severe liver failure(safety and efficacy not established).
- Concomitant therapy with tamoxifen or drugs containing estrogen.
- Childhood(safety and efficacy in children have not been established).
Carefully
Osteoporosis, hypercholesterolemia, coronary heart disease, liver dysfunction, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Use during pregnancy and during breastfeeding
Use during pregnancy and during breastfeeding contraindicated.
Dosage and administration
Inside, the tablet is swallowed whole with water. It is recommended to use at the same time.
Adults, including the elderly: 1 mg 1 time per day, long-term. If signs of disease progression appear, the drug should be discontinued.
As adjuvant therapy, the recommended duration of treatment is 5 years.
In case of impaired renal function mild to moderate dose adjustment is not required.
In violation of liver function mild degree dose adjustment is not required.
Side effect
Development frequency side effects is given in the following gradation: very often (≥1/10); often (≥1/100,<1/10); нечасто (≥1/1000, <1/100); редко (≥1/10000, <1/1000); очень редко (<1/10000), в том числе отдельные сообщения.
From the side of the cardiovascular system: very often - hot flashes.
From the musculoskeletal system: very often - arthralgia, joint stiffness, arthritis; often - bone pain; infrequently - trigger finger.
From the reproductive system: often - dryness of the vaginal mucosa, vaginal bleeding (mainly during the first weeks after the abolition or change of previous hormonal therapy to anastrozole).
From the side of the skin: very often - skin rash; often - thinning hair, alopecia, allergic reactions; infrequently - urticaria; rarely - erythema multiforme, anaphylactoid reaction, skin vasculitis (including isolated cases of purpura (Schonlein-Genoch syndrome)); very rarely - Stevens-Johnson syndrome, angioedema.
From the digestive system: very often - nausea; often - diarrhea, vomiting.
From the hepatobiliary system: often - increased activity of alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase; infrequently - increased activity of gamma-glutamyl transferase and bilirubin concentration, hepatitis.
From the nervous system: very often - headache; often - drowsiness, carpal tunnel syndrome (mainly observed in patients with risk factors for this disease), sensitivity disorders (including paresthesia, loss or perversion of taste sensations).
From the side of metabolism: often - anorexia, hypercholesterolemia; infrequently - hypercalcemia (with / without an increase in the concentration of parathyroid hormone). Taking the drug can cause a decrease in bone mineral density due to a decrease in the concentration of circulating estradiol, thereby increasing the risk of osteoporosis and bone fractures.
Others: very often - asthenia of mild and moderate severity.
Adverse events noted in the course of clinical studies, not associated with taking anastrozole: anemia, constipation, dyspepsia, back pain, abdominal pain, increased blood pressure, weight gain, depression, insomnia, dizziness, anxiety, paresthesia.
Overdose
Cases of overdose are isolated and accidental. A single dose of the drug, which could lead to life-threatening symptoms, has not been established.
Treatment: there is no specific antidote. Treatment is symptomatic. Induction of vomiting (if the patient is conscious). Dialysis. General supportive care, monitoring the patient and monitoring the function of vital organs and systems.
Interaction with other drugs
Drug interaction studies with phenazone (Antipyrine) and cimetidine indicate that co-administration of anastrozole with other drugs is unlikely to result in a clinically significant cytochrome P450-mediated drug interaction. There is no clinically significant drug interaction when taking anastrozole concomitantly with other commonly prescribed drugs. At the moment, there is no information on the use of anastrozole in combination with other anticancer drugs. Preparations containing estrogens reduce the pharmacological action of anastrozole, and therefore, they should not be administered simultaneously with anastrozole. Tamoxifen should not be administered concomitantly with anastrozole, as it may weaken the pharmacological action of the latter.
special instructions
Safety and efficacy in children have not been established.
In women with an estrogen receptor-negative tumor, the effectiveness of anastrozole has not been demonstrated, except in cases where there was a previous positive clinical response to tamoxifen.
In case of doubt in the hormonal status of the patient, menopause should be confirmed by the determination of sex hormones in the blood serum.
There are no data on the use of the drug in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency and in patients with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 20 ml / min).
In the case of persistent uterine bleeding while taking anastrozole, consultation and observation of a gynecologist is necessary.
Estrogen-containing drugs should not be administered simultaneously.
A decrease in circulating estradiol levels can cause a decrease in bone mineral density with a subsequent increase in the risk of fracture. Patients with such a high risk should be treated according to the guidelines for the treatment of these complications. The combined use of bisphosphonates in patients with an average and high risk of fractures helps to prevent changes in the skeletal system. Supportive treatment with vitamin D and calcium in low-risk patients prevents changes in bone structure.
In patients with osteoporosis or at risk of developing osteoporosis, bone mineral density should be assessed by densitometry, such as DEXA scanning (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry - dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry), at the beginning of treatment and over time. If necessary, treatment or prevention of osteoporosis should be started, under close medical supervision.
There are no data on the simultaneous use of anastrozole and analogues of luteinizing hormone releasing hormone. It is not known whether anastrozole improves treatment outcomes when used in combination with chemotherapy.
There are no safety data for long-term treatment with anastrozole.
With the use of anastrozole, ischemic diseases were observed more often than with tamoxifen therapy, but there was no statistical significance.
The efficacy and safety of anastrozole and tamoxifen when used simultaneously, regardless of the status of hormone receptors, are comparable to those when using tamoxifen alone. The exact mechanism of this phenomenon is still unknown.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles, mechanisms
Care should be taken when driving vehicles and potentially dangerous mechanisms, since anastrozole can cause asthenia and drowsiness.
Release form
Film-coated tablets 1 mg.
10 tablets in a blister pack made of PVC film and aluminum foil. One or three blisters, together with instructions for use, are placed in a cardboard pack.
Storage conditions
Store in a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
2 years.
Do not use after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
Holiday conditions
On prescription.
Name and address of the legal entity in whose name the registration certificate is issued / Organization accepting consumer claims
RUE "Belmedpreparaty", Republic of Belarus
220007, Minsk, st. Fabricius, 30,
Manufacturer
RUE "Belmedpreparaty"
Production site address:
Republic of Belarus, 220006 Minsk, st. Mayakovsky, 1/5.
Anastrozole (anastrozole)
Composition and form of release of the drug
Coated tablets white or almost white, round, biconvex; on the surface of the tablets, the roughness of the film coating is allowed.
Excipients: sodium starch glycolate type A, K25, calcium stearate, sodium lauryl sulfate, lactose monohydrate.
Shell composition: Opadry II white (85F): polyvinyl alcohol, partially hydrolyzed; macrogol/polyethylene glycol; talc (E553b); titanium dioxide (E171).
10 pieces. - cellular contour packings (1) - packs of cardboard.
10 pieces. - cellular contour packings (3) - packs of cardboard.
pharmachologic effect
Antitumor agent. It is a selective non-steroidal aromatase inhibitor. In postmenopausal women, estradiol is mainly formed from estrone, which is produced in peripheral tissues by conversion from androstenedione (with the participation of the aromatase enzyme). A decrease in the level of circulating estradiol has a therapeutic effect in women with. In postmenopausal women, anastrozole at a daily dose of 1 mg causes a decrease in estradiol levels by 80%. Anastrozole does not have progestogenic, androgenic and estrogenic activity; in therapeutic doses does not affect the secretion of cortisol and aldosterone.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, anastrozole is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. C max in is achieved within 2 hours (on an empty stomach). Food somewhat reduces the rate, but not the degree of absorption. Plasma protein binding is 40%. There is no information about cumulation.
The metabolism of anastrozole is carried out by N-dealkylation, hydroxylation and glucuronization. Triazole, the major metabolite found in plasma and urine, does not inhibit aromatase.
Anastrozole and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine (less than 10% unchanged), within 72 hours after a single dose. T 1/2 from plasma - 40-50 hours.
The clearance of anastrozole after oral administration in volunteers with stabilized or impaired renal function does not differ from the clearance determined in healthy volunteers.
The pharmacokinetics of anastrozole in postmenopausal women does not change.
Indications
Postmenopausal breast cancer.
Contraindications
Premenopausal period, severe (CC less than 20 ml / min), moderate and severe liver failure, pregnancy, lactation, childhood, hypersensitivity to anastrozole.
Dosage
Inside - 1 mg 1 time / day.
Side effects
From the endocrine system: hot flashes, vaginal dryness and thinning hair.
From the digestive system: anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. In patients with advanced breast cancer, in most cases with liver metastases, there was an increase in the level of GGT, less often - ALP.
From the side of the central nervous system: asthenia, drowsiness, headache.
From the side of metabolism: slight rise in total cholesterol.
Allergic reactions: skin rash.
drug interaction
Anastrozole reduces the effectiveness of estrogens.
Clinical studies have shown that with the simultaneous use of anastrozole with antipyrine, drug interactions due to the induction of microsomal liver enzymes are unlikely.
special instructions
In case of uncertainty of the hormonal status of the patient, the state of menopause must be confirmed by additional biochemical studies.
Formula: C17H19N5, chemical name: alpha,alpha,alpha",alpha"-Tetramethyl-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1ylmethyl)-m-benzenediacetonitrile.
Pharmacological group: antitumor agents/antitumor hormonal agents and hormone antagonists.
Pharmachologic effect: antitumor, inhibits the synthesis of estrogens.
Pharmacological properties
Anastrozole is active against estrogen-dependent breast tumors in postmenopausal women. Androstenedione is the main source of circulating estrogens in postmenopausal women, in peripheral tissues it is converted to estrone, and then to estradiol, this whole process takes place with the participation of the aromatase enzyme. And anastrozole inhibits this enzyme (it is a selective non-steroidal inhibitor) in peripheral tissues, including adipose tissue, which, accordingly, leads to a decrease in the level of estradiol. With anastrozole therapy at a dose of 1 mg per day, the concentration of estradiol decreases by 70% for the first day, by 80% after 2 weeks. The decrease in the level of estradiol is maintained for 6 days after stopping taking 1 g of anastrozole daily. This decrease in estradiol levels has a therapeutic effect in postmenopausal women with breast tumors. With daily intake of anastrozole at doses of 3, 5 and 10 mg, there is no effect on the production of aldosterone and cortisol. Also, anastrozole did not show direct androgenic, progestogenic and estrogenic activity in animals, but changed the levels of circulating androgens, progesterone and estrogens. After oral administration, 83-85% of the dose is absorbed, food reduces the absorption of the drug. On an empty stomach, the maximum concentration of the drug in the blood is reached after 2 hours. Anastrozole binds to plasma proteins up to 40%. With daily use, the equilibrium concentration in the blood will be reached in about a week, its value will be 3-4 times greater than with a single dose. Anastrozole is extensively metabolized in postmenopausal women, less than 10% is excreted unchanged in the urine within 3 days after administration, 60% is excreted as metabolites. Biotransformation in the liver occurs by hydroxylation, N-dealkylation and glucuronization, and inactive metabolites are formed, the main one being triazole. The terminal half-life is about 50 hours. The age of women (range 50 - 80 years) does not affect the pharmacokinetics of anastrozole. Acute toxicity in animals. An acute toxicity study in rodents (rats) has shown that a single oral lethal dose exceeds 100 mg/kg/day (this is about 800 times the recommended human dose, in mg/m2) and causes severe gastric irritation (necrosis ulceration, gastritis, hemorrhage). When administered to dogs, the median lethal dose exceeded 45 mg/kg/day.
Mutagenicity. Anastrozole did not show clastogenic and mutagenic properties in a number of in vivo and in vitro tests, including the Ames test, the micronucleus test in rats and the test for chromosomal aberrations on human lymphocytes.
Reproductive toxicology. Oral administration of anastrozole to female rats from 2 weeks before mating to day 7 of gestation caused a strong increase in infertility and a decrease in the number of successful pregnancies at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 10 times the MRHD in mg/m2 and 9 times the AUC0 -24 postmenopausal female volunteers at recommended doses). At doses ≥0.02 mg/kg/day (approximately 1/5 MRDH in mg/m2), pre-implantation egg loss or fetal loss has been reported. Fertility was restored 5 weeks after discontinuation of the drug after a 3-week intake. It is not known whether the observed effects of such disorders in rats indicate the possibility of human fertility disorders.
Carcinogenicity. Studies in rats with oral anastrozole at doses of 1.0 to 25 mg/kg/day (10-243 times the MRHD in mg/m2) have shown an increase in the incidence of hepatocellular adenoma and carcinoma, as well as uterine stromal polyps in females, adenoma thyroid gland in males with the introduction of anastrozole in high doses (25 mg / kg / day). There was a dose-dependent increase in the incidence of uterine and ovarian hyperplasia in females. At a dose of 25 mg/kg/day, plasma levels of AUC0-24 in rats were 110-125 times higher than those in postmenopausal female volunteers receiving therapeutic doses of anastrozole. Studies in mice with oral anastrozole at doses of 5 to 50 mg/kg/day (approximately 24 to 243 times the MRDH in mg/m2) found an increase in the occurrence of benign tumors (stromal, epithelial, granular) of the ovary at all studied doses . Dose-dependent ovarian hyperplasia was also noted in female mice. These changes in the ovaries are regarded as a specific consequence of aromatase inhibition in rodents and are not considered clinically significant in humans. The frequency of detection of lymphosarcomas was increased in female and male mice at high doses. At a dose of 50 mg/kg/day, plasma levels of AUC0-24 in mice were 35-40 times higher than those in postmenopausal female volunteers at therapeutic doses.
Indications
Adjuvant treatment of early hormone-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women; treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women; adjuvant treatment of early hormone-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women after treatment with tamoxifen for 2–3 years.
Dosing and Administration of Anastrozole
Anastrozole is used 2 to 3 hours after (or before) meals, 1 mg 1 time per day. The course of therapy depends on the severity and form of the disease.
If you miss the next dose of anastrozole, you must take the drug as you remember, the next dose should be taken in a day.
Efficacy of anastrozole has not been obtained in patients with estrogen receptor-negative tumors, except in those cases where there was previously a positive clinical reaction to tamoxifen. The safety and efficacy of tamoxifen and anastrozole when used together, regardless of the status of hormone receptors, are comparable to those when using tamoxifen alone (the mechanisms of this phenomenon are not known). If there are doubts about the hormonal status of the patient, then menopause must be confirmed (or refuted) by determining the sex hormones (their level) in the blood serum. If uterine bleeding persists while taking anastrozole, then observations and periodic consultations with a gynecologist are necessary. Medicines that contain estrogens should not be given together with anastrozole because these drugs will reduce the pharmacological effects of anastrozole. Anastrozole may lower bone mineral density. Patients who suffer from osteoporosis or are at risk of developing it should assess bone mineral density by densitometry at the beginning of therapy and over time. If necessary, the treatment of osteoporosis or its prevention under the supervision of a physician should be prescribed. There is no data that said anything about the combined use of analogues of LHRH (luteinizing hormone releasing hormone) and anastrozole. It is also unknown whether the results of treatment improve when anastrozole is used together with chemotherapy. Such side effects of anastrozole as drowsiness, asthenia can adversely affect the ability to perform activities that require rapid psychomotor reactions and a high level of attention.
Contraindications and restrictions for use
Hypersensitivity, joint treatment with drugs that contain estrogens, or tamoxifen, premenopausal period; severe renal failure (when creatinine clearance is less than 20 ml / min), liver failure (efficacy and safety have not been established), breast-feeding, pregnancy. Limit the use of anastrozole for hypercholesterolemia, osteoporosis, coronary heart disease.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
The use of anastrozole during pregnancy and lactation is contraindicated.
Side effects of anastrozole
Circulatory and blood system: hypertension (severe dizziness, prolonged headache), anemia, thrombophlebitis, leukopenia with/without infection, thromboembolism;
nervous system: asthenic syndrome, drowsiness, insomnia, depression, anxiety, headache, paresthesia, dizziness;
digestive system: loss of appetite, constipation/diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, dry mouth;
allergic reactions: rash, erythema multiforme, itching, Stevens-Johnson syndrome;
respiratory system: dyspnea, rhinitis, sinusitis, bronchitis, pharyngitis;
others: hot flashes, vaginal bleeding, vaginal dryness, arthralgia, myalgia, chest and back pain, sweating, decreased joint mobility, peripheral edema, influenza-like syndrome, alopecia and thinning hair, increased levels of AST and ALT, alkaline phosphatase (in patients with liver metastases) , hypercholesterolemia, weight gain.
Interaction of anastrozole with other substances
Preparations that contain estrogens reduce the pharmacological effect of anastrozole, so they should not be administered together with anastrozole. Tamoxifen should not be administered together with anastrozole, as it can also weaken the pharmacological effects of anastrozole. When using anastrozole together with tamoxifen in patients with breast cancer, the level of anastrozole in the blood plasma decreased by 27% compared to that without the use of tomoxifen, while such a joint intake of 2 drugs did not affect tamoxifen and its metabolites at all. No therapeutically important effects of the influence of anastrozole on anticoagulant activity, as well as the pharmacokinetics of warfarin, have been obtained. The studies involved 16 male volunteers, and they showed no effect of anastrozole on exposure (which was estimated by AUC and maximum concentration) and anticoagulant activity (which was measured by APTT, PT and thrombin time) of warfarin.
Overdose
There are only isolated cases of anastrozole overdose. A single dose that may cause life-threatening symptoms has not been established. Treatment: induce vomiting (if the patient is conscious), symptomatic treatment, control and monitoring of vital organs and systems. Dialysis is possible. No specific antidote has been found.