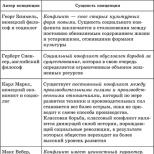
What are medicines and medicines. What is the difference between medicines and medicines. The concept of drug dosage
Medicines
Medicines (drugs, drugs)- substances or their combinations that come into contact with the human or animal body, penetrate into the organs, tissues of the human or animal body, used for prevention, diagnosis (with the exception of substances or their combinations that are not in contact with the human or animal body), treatment of a disease, rehabilitation, for the preservation, prevention or termination of pregnancy and obtained from blood, blood plasma, organs, tissues of the human or animal body, plants, minerals by synthesis methods or using biological technologies. Medicinal products include pharmaceutical substances and drugs.
original medicinal product- a medicinal product containing a pharmaceutical substance obtained for the first time or a new combination of pharmaceutical substances, the efficacy and safety of which have been confirmed by the results of preclinical studies of medicinal products and clinical trials of medicinal products
A source: Federal Law of the Russian Federation of April 12, 2010 N 61-FZ
Medicine, medicinal product, medication, medicine(novolat. praeparatum medicinale, praeparatum pharmaceuticum, medication;) - a substance or mixture of substances of synthetic or natural origin in the form of a dosage form (tablets, capsules, solutions, ointments, etc.) used for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
Before use in medical practice Medicinal products must undergo clinical trials and be approved for use.
Original medicines and generics
An original drug is a drug that was previously unknown and first released to the market by a developer or patent holder. As a rule, the development and marketing of a new drug is a very expensive and time-consuming process. Of the many known compounds, as well as newly synthesized ones, by enumeration, on the basis of databases on their properties and computer modeling of the proposed biological activity, substances with the maximum target activity are identified and synthesized. After animal experiments, in the case positive result, limited clinical trials are being conducted on groups of volunteers. If the effectiveness is confirmed, and side effects insignificant - the drug goes into production, and based on the results of additional tests, the possible features actions, undesirable effects are revealed. Often the most harmful side effects are clarified when clinical application. Currently, almost all new drugs are patented. The patent legislation of most countries provides for patent protection not only for the method of obtaining a new drug, but also for the patent protection of the drug itself.
In the Russian Federation, the term of a patent for an invention related to a medicinal product, the application of which requires obtaining a permit in accordance with the procedure established by law, is extended by the federal executive authority for intellectual property at the request of the patent holder for a period calculated from the date of filing an application for an invention until the date of receipt of the first such permission to use, minus five years. At the same time, the period for which the validity of a patent for an invention is extended cannot exceed five years. After the expiration of the patent, other manufacturers can reproduce and put on the market a similar drug (the so-called generic), if they prove the bioequivalence of the reproduced and original drugs. At the same time, the generic production technology can be any, but not subject to the existing patent protection in the country. Of course, the generic manufacturer cannot use the brand name for this drug, but only the international non-proprietary name (INN), or some new patented by him (synonym). Despite the new name in its own way medicinal action drugs may be similar or very close.
Are original drugs and generics completely equivalent? In terms of chemistry active substance same. But the production technology is different, different degrees of purification are possible. There are other factors as well. For example, it is known that for a long time different firms could not achieve the same efficiency acetylsalicylic acid(for generic), as with Bayer AG - manufacturer original drug"aspirin". It turned out that the matter was not only in the purity of the raw materials, but also in a special method of crystallization, resulting in special, smaller crystals of acetylsalicylic acid. There can be many such nuances. The opposite result is also possible, when the generic is more successful than the original medicine.
Medicines are also created by chemical synthesis without the use of biological technologies, using the activity of microorganisms. Mankind enjoys medicines from time immemorial, but in the history of pharmacotherapy there are periods (horses of the 19th - early 20th centuries) when the positive role of drugs was denied, and this was considered a sign of an advanced way of thinking. The denial of pharmacotherapy was expressed in the punning saying: "Treat with the mind, not with the medicine."
Medicinal preparations - dosed medicinal products, ready for use. They are divided into poisonous, potent and general purpose. When taking, it is important to accurately observe the dose.
Single dose - the amount of the drug, calculated at one time. If the drug is dispensed by prescription, then the doctor determines the single dose. When self-administering drugs, it is important to correctly determine their dose (for example, if you need to take 500 mg of the drug, and the tablet contains 1000 mg, then you need to take 1/2 tablet).
The highest single dose is the maximum amount of the drug calculated per dose.
Higher daily dose- the maximum amount of the drug that can be taken per day.
Medicine is usually called tablets, potions, powders, etc. However, these are only dosage forms of certain therapeutic agents.
Each drug contains an active substance that determines its medicinal properties.
An ordinary tablet may consist entirely of the active substance, but more often it is a mixture of it with excipients, non-drug substances. The fact is that medicinal doses of one or another substance is often milligrams and even fractions of a milligram, and consequently, a tablet consisting entirely of such a substance would have microscopic dimensions. Substances-fillers, in addition, can slow down or, conversely, accelerate the action of the drug. Therefore, even drugs with the same active substance sometimes cause different effects. This should be remembered, and take the remedy only under the supervision of a doctor.
To date, more than 7 thousand drugs have been developed in the world, and most of them appeared in the last 25 years.
Before starting treatment, consult your doctor.
Medicines
Medicinal products are substances or mixtures of substances used for the prevention, diagnosis, treatment of diseases, as well as for the regulation of other conditions (eg prevention of pregnancy, etc.). Medicines are obtained from a wide variety of substances by synthesis, through various chemical reactions, extraction, using biotechnology, and other methods (including from blood, blood plasma, as well as human or animal organs, tissues, plants, minerals).
Thus, medicinal products include substances of plant, animal or synthetic origin that have pharmacological activity and are intended for production and manufacture. dosage forms.
Classification of medicines
Prescription and non-prescription medicines
In world practice, there is the concept of "over-the-counter" and "prescription" medicines. The latter suggest a greater potential danger of use without medical advice. There is a constant struggle between the "pharmaceutical" and "medical" lobbies (respectively, for the expansion of the 1st or 2nd group of drugs and the corresponding business).
State regulation is designed to take into account the interests of the population (the dilemma of "availability" and / or "safety" of medicines), without biasing towards the interests of the pharmaceutical or medical business.
Homeopathic medicines
In a number of countries, these drugs are regulated differently - either as a category "Medications", or as " food products and additives", or as "means alternative medicine". Currently, there is no well-established opinion of international organizations on this matter, agreed with national health authorities.
IN Russian Federation Homeopathic medicines are subject to the same legal regulation as conventional medicines.
Legislative regulation
From the point of view of Russian legislation, at the moment (2006), a drug is a drug listed in State Register medicines.
The production of authorized medicines must comply with the international requirements of the GMP standard, however, the introduction of this requirement in the territory of a number of CIS countries is carried out in stages, as the equipment of the main operating enterprises is updated.
The sale of medicines (unlike dietary supplements) is carried out only by specialized stores (pharmacies, pharmacy kiosks) that have the appropriate license.
The circulation of medicines is regulated by law and by-laws, including the regular updating of the list of Vital and Essential Medicines (VED), the List of Narcotic Drugs, etc.
Economic consequences of legislative regulation
VAT on the sale of medicines (Russia, 2006) corresponds to 10% (unlike dietary supplements - 18%).
In Ukraine, there is a practice of returning excise duty for the use of alcohol in the manufacture of medicines - only after they are sold.
Bodies of state control over the quality of medicines
The quality of medicines in Russia is controlled by the Federal Service for Surveillance in Healthcare and social development(Roszdravnadzor), subordinate to the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation.
Centers for quality control of medicines operate in most large cities of Russia. Their main task is to check the organizations selling medicines (compliance with numerous norms for the storage and sale of medicines), as well as selective (and in some regions even total) control of medicines. Based on the data from the regional centers, Roszdravnadzor will make decisions on the rejection of a particular drug.
This is how it should ideally be. In practice, things look a little different.
First, the vast majority of drug quality control centers are more than poorly equipped, and it is difficult to carry out chemical analysis they are not able to use a modern medicine. An even more difficult situation arises with microbiological research, which are either not produced at all or are produced in a very reduced volume. As a result, often all, so to speak, research is limited to assessing appearance medicines (is there any unacceptable sediment, are the tablets cracked, is the packaging correctly designed, the label is crooked, etc.).
Secondly, according to the legislation in force in Russia, it is unacceptable to demand from the seller additional analysis if the medicinal product already has a valid certificate (declaration) of conformity. So everything additional research should be carried out at the expense of the Centers for Quality Control of Medicinal Products. In fact, this translates into additional costs for the seller.
Third, drug quality control centers should produce selective drug control. In many regions of Russia (for example, Stavropol, the Tver region, Tatarstan), the repeated check is of a total nature. In general, this is illegal, and due to the lack of equipment of laboratories, it is simply meaningless, which leads to a significant difficulty in selling not only counterfeit and low-quality drugs, but also drugs in general.
As a result of the above, we can say that most of the regional Centers for Quality Control of Medicines today do not fulfill their tasks, only creating grounds for bribes and unfair competition.
Rejected and counterfeit medicines are subject to withdrawal from the pharmacy network, information about them is available on the following websites:
Original medicines and generics
An original drug is a drug that is first released by the developer. As a rule, the development of a new drug is a very expensive and time-consuming process. Of the many known compounds, as well as newly synthesized ones, by enumeration, on the basis of databases on their properties and computer modeling of the proposed biological activity, substances with the maximum target activity are identified and synthesized. After animal experiments, in the case of a positive result, limited clinical trials are carried out on groups of volunteers. If the effectiveness is confirmed, and side effects are insignificant, the drug goes into production, and based on the results of additional tests, possible features of the action are clarified, undesirable effects are revealed.
At the same time, the manufacturer patents this new drug. All other firms can produce synonyms (so-called generics), but by their own technology, if they prove the bioequivalence of drugs. Of course, they cannot use the brand name for this drug, but only the INN, or some new patented by them. Despite the new name, in their effect, such drugs can be similar, or very close.
Are original drugs and generics completely equivalent? From the point of view of chemistry, the active substance is the same. But the production technology is different, different degrees of purification are possible. There are other factors as well. For example, it is known that for a long time different companies could not achieve the same effectiveness of acetylsalicylic acid (generic) as that of Bayer AG, the manufacturer of the original drug "aspirin". It turned out that the matter was not only in the purity of the raw materials, but also in a special method of crystallization, resulting in special, smaller crystals of acetylsalicylic acid. There can be many such nuances. The opposite result is also possible, when the generic is more successful than the original medicine.
In modern preparations, only one of the isomers (enantiomers) may be biologically active, the other may be weakly active, inactive, or even harmful (see Bioavailability).
Illegal actions in the production and circulation of medicines
Counterfeit drugs, counterfeit drugs
The pharmaceutical business is considered the third most profitable, after the arms and drugs trade. This attracts unscrupulous entrepreneurs to him.
In Russia, until 1991, the problem of falsification of medicines was practically absent.
After the collapse of the USSR, the resulting decrease in the production of its own drugs and a sharp increase in imports, the problem became urgent. Approximately one tenth of all medicines sold on the world market are counterfeit or counterfeit.
- 1998 The first official case of detection of counterfeit drugs in Russia was registered
- 2004 Introduction of the concept of "counterfeit medicines" into the Russian legislation
IN Russian history falsification of drugs can be divided into 3 stages:
A distinction should be made between counterfeit medicines and counterfeit medicines.
Fake
Counterfeit is a deliberate change in the formulation of the production of a medicinal product. Replacing expensive components with cheaper ones, or reducing the content (and in the worst case, completely absent) of the necessary component of the drug. For example, replacing the more expensive cefazolin with cheaper (and less effective) penicillin. In addition, other violations in production are possible: violation of the time and sequence of the technological process, underestimation of the degree of purification, poor-quality packaging materials, etc.
counterfeit
Counterfeit drugs are drugs produced without the permission of the patent holder - the developer company.
The effectiveness of a drug is primarily determined by the active substance (but not only by it, see bioequivalence). According to regulations international law, the formula or composition of the active substance cannot be a company secret. But for some time (about several years) this information is closed to other manufacturers, who, even under a different name, cannot produce this medicine without the permission of the patent holder's company.
Even at the end of the allotted time, other companies cannot use the name of the drug (Brand) registered by the company - the patent holder (the so-called patent form).
There is a temptation for drug manufacturers, knowing the formula, to release drugs bypassing the patent owner. An example is the drug No-Shpa® (registered brand name). In fact, this is a fairly simple synthesized drug, the active substance of which has generic name"drotaverine". However, for several generations people have used No-Shpa and know nothing about some drotaverine. Accordingly, the price of a branded drug is 10 (!) Times higher than the price of exactly the same in composition, manufacturing technology and action, the drug drotaverine. It is not surprising that at some factories that produce cheap domestic drugs during the day, at night the same drugs are packed in foreign, branded packages. It should be added that this usually does not affect the quality of the drug, since the counterfeit manufacturer is afraid to arouse even the slightest suspicion from the inspection authorities.
Illicit drug trafficking
Narcotic substances are subject to stricter rules of circulation than other drugs. However, due to the increased demand for them, there are situations in which officials neglect the proper performance of official duties.
- The flip side of the tightening of requirements for the circulation of narcotic drugs is the unreasonably difficult obtaining by persons with direct indications for use (oncological diseases, etc.).
5. Medicinal substance, medicinal product, medicinal product, dosage form
A drug is any substance or product used to modify or alter physiological systems or pathological conditions for the benefit of the recipient (according to WHO, 1966); individual substances, mixtures of substances or compositions of unknown composition, with proven medicinal properties.
Medicinal substance - individual chemical compound used as a medicine.
The dosage form is convenient for practical application the form given to the drug to obtain the desired therapeutic or prophylactic effect.
Medicinal product – a medicinal product in a specific dosage form approved by a government agency.
6. Names of drugs, generic drugs.
a) complete chemical name: para-acetaminophenol
b) international (non-proprietary, officially approved in the pharmacopoeia): "Paracetamol"
c) trade (proprietary): "Panadol"
Generic drugs (generic drugs) - drugs that have chemical, biological and clinical equivalence with known drugs for which patent protection has expired.
7. Concepts of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Pharmacokinetics - everything that the body does with drugs: it studies absorption, distribution, metabolism (biotransformation), binding to plasma proteins and other tissues, and elimination of drugs.
Pharmacodynamics is everything that drugs do with the body: it studies the localization, mechanism of action, biochemical, physiological, side effects, toxic effects of drugs, their strength and duration.
8. The main components of pharmacokinetics:
Association with plasma proteins and other tissues
Metabolism (biotransformation) of drugs
Elimination of drugs from the body
9. Ways of introducing drugs into the body. Presystemic elimination of drugs.
Ways of introducing drugs into the body:
1. For systemic action
but. Enteral route of administration:
Inside (peros) - orally
Through a probe (for example, into the 12th duodenum)
b. Parenteral route of administration: intravenous, subcutaneous, intramuscular, inhalation, subarachnoid, transdermal.
2. For local exposure:
In the cavity (abdominal, pleural, articular)
In tissue (infiltration)
Presystemic elimination of drugs - loss of drugs before entering the common system circulation (i.e. into the systemic circulation) - losses during the first passage (through the liver).
10. Transfer of drugs through biological barriers: main mechanisms and determinants.
The main mechanisms of drug transfer:
a) filtration through the water channels of the membranes (pore diameter of the order of 4 Ắ), characteristic of water, some ions, small hydrophilic molecules (urea).
b) diffusion in lipids is the main mechanism of drug transfer, drugs diffuse passively along the concentration gradient.
2) active (i.e., flowing with energy consumption):
a) active transfer - the transfer of drugs, regardless of the concentration gradient using the energy of ATP, is characteristic of hydrophilic polar molecules, a number of inorganic ions, sugars, amino acids, pyrimidines.
b) microvesicular transport (pinocytosis) - invagination of the cell membrane and subsequent capture of the drug with the formation of a vacuole (absorption of vitamin B 12 in combination with the intrinsic factor of Castle and some protein molecules).
To continue downloading, you need to collect the image:
What is a drug
A medicinal product (MP) is a special substance or a combination of several substances of natural, synthetic or biotechnological origin that has pharmacological activity and is used in a certain dosage form for the prevention and diagnosis of diseases, treatment and medical rehabilitation patients, preventing pregnancy by internal or external use.
Classification of medicines (basic criteria):
1. According to the state of aggregation (dosage form):
Solid (tablets, dragees, granules, powders, collections, hard gelatin capsules, films);
Soft (ointments, gels, creams, suppositories, soft gelatin capsules);
Liquid (solutions, tinctures, extracts, suspensions, emulsions, syrups);
2. According to the dosing method:
Dosed (powders, solutions, tablets, capsules and others, divided into separate doses);
Undosed (ointments, gels, powders, bath powders, etc.);
3. According to the method and route of introduction into the body:
Enteral - introduced into the body through gastrointestinal tract(through the mouth - orally, under the tongue - sublingually, through the rectum - rectally);
Parenteral - administered bypassing the gastrointestinal tract (by injection into the vascular bed (artery, vein), under the skin or into the muscle, by application to the skin and mucous membranes of the body, by inhalation).
4. According to anatomical-therapeutic-chemical groups ( international classification) :
According to the nosology of the disease for which the drug is intended
By pharmacological action LS,
Its chemical structure
Group L: Anticancer drugs and immunomodulators
L 01 Anticancer drugs
L 01 C Alkaloids plant origin
L 01 SA Vinca alkaloids and analogues
L 01 CA01 Vinblastine
L 01 CA02 Vincristine
L 01 CA04 Vinorelbine
L 01 CD Taxoids
L 01 CD01 Paclitaxel
L 01 CD02 Docetaxel
Dosage form - the form given to the medicinal product, which determines its state, dosage, packaging and method of application.
Types of dosage forms of medicines:
Solid (tablets, hard gelatin capsules, powders, granules);
Liquid (solutions, suspensions, emulsions);
Soft (ointments, creams, gels, suppositories, soft gelatin capsules);
2. Pharmacy and pharmaceuticals: history of origin and development. « | » 4. The composition of medicines | pharmaceutical ingredient, excipient.
CHAIN OF PHARMACIES "I'M HEALTHY"
- ANY DRUGS TO ORDER
Medicines - what is it? Classifications
Pharmacology is the science that studies how drugs act on human body how new drugs are made. Even the ancient Greeks and Indians, the inhabitants of the tundra and the southern edge of Africa, tried to defeat diseases, looked for ways to deal with them. People have always strived for this, making their obsession the main dream.
A little about pharmacological terminology
Drugs are substances or a combination of substances used by people to treat diseases or for preventive purposes.
Medicinal products are drugs that are ready to use. Medicines may have various forms, which makes their use convenient and creates the possibility of an individual approach to the treatment of each patient. A variety of forms of drug release allows you to deliver them to the body different ways, which helps to work with unconscious patients and treat patients who have been injured or burned.
The concept of lists: A and B
There is a division of all drugs into three main groups:
- List A includes poisonous drugs.
- To list B - potent drugs and analgesics.
- To medicines available without a doctor's prescription - all the rest.
To obtain medicines of classes A and B in pharmacy chains, a special prescription is required. They demand that they be treated with increased attention: they know how to take it correctly, as well as the conditions for the proper storage of these medicines. Some of them decompose in sunlight or become toxic if stored in the light.
In addition, there is strict reporting on the use of certain drugs (such drugs include morphine). In this case, the drugs are handed over by ampoules by nurses after the shift, which must be confirmed by an appropriate entry in the journal. Medicines that are considered antipsychotics, vaccines, and drugs for anesthesia are also subject to accounting.
What is a recipe?
A prescription is a special note by a doctor to pharmacists or pharmacists, which indicates a request to allow the patient to purchase a medicine. The prescription indicates the form, dose, method and frequency of use of the drug.
The prescription form is both a medical, legal and monetary document in the case when the medicine is given free of charge and on a discount. Based on the existing legislative act regulating the rules for issuing prescriptions, this can be done by a doctor of any specialty and position.
A drug can not only eliminate or prevent diseases. It can also be poisonous, so the doctor must be careful when writing a prescription: the dosage must be accurate and correct.
The concept of drug dosage
Filling out the prescription form, the doctor writes down, using Arabic numerals, the amount medicinal substance, indicating mass or volume units in the decimal system, separating grams with a comma (1.5). The drops that make up the medicinal substance are indicated by Roman numerals. The calculation of the composition of some antibiotics is made only in international or biological units, denoted by IU or ED.
There are various forms of medicinal substances: solid, liquid, gaseous. To indicate the amount of liquids and gases in the prescription, milliliters are used, and for inhalation, doctors sometimes note doses of a dry medicinal substance. At the bottom of the prescription, the doctor puts his signature and personal seal. Also in the prescription it is necessary to indicate the surname, initials, age of the patient, put the date and expiration date of the prescription.
Prescriptions are written on special forms for the purchase of subsidized drugs, narcotic substances, sleeping pills, antipsychotics and painkillers. Such prescriptions are signed by the attending physician, the chief physician of the hospital, certifying with a seal. A round seal of the medical institution is also put.
It is forbidden in outpatient clinics to extract ether for anesthesia, fentanyl, chloroethane, ketamine and other sleeping substances. Doctors in most countries use Latin for writing prescriptions. Medication recommendations are written in language that patients can understand.
Permission to sell narcotic and poisonous drugs is issued for five days, medical alcohol for ten days, and prescriptions for other medicines have a validity period of two months after issuance
What is the general classification?
Today there are many unusual drugs, so they need to be classified for proper orientation. There are the following conditional classification guides:
- Therapeutic action - a group of drugs that are used in the treatment of one disease.
- Pharmacological action - the effect produced by the drug.
- Chemical structure.
- Nosological principle, which is similar to the therapeutic, but with a narrow distinction.
The division of drugs into groups
The development of medicine has led to the fact that doctors had to deal with the systematization of medicines. The classification was made by chemists and pharmacists, using the principle of the application point. It consisted of the following categories:
- Psychotropic drugs and drugs that have a therapeutic effect on the cells of the central nervous system (tranxilizers, neuroleptics, sedatives, antidepressants, antiepileptic, anti-inflammatory drugs).
- Medicines for the treatment of the peripheral nervous system (ganglion blockers, anticholinergics).
- Local anesthetics.
- Drugs that change vascular tone.
- Diuretic and choleretic agents.
- Medicines for the treatment of organs internal secretion and metabolism.
- Antibiotics and antiseptics.
- Anticancer drugs.
- Diagnostic tools (dyes, contrast agents, radionuclides).
With the help of this and similar divisions, young doctors study the medicines that exist today. With the help of classification into groups, doctors intuitively understand how a particular drug works and remember the doses.
Medicines are classified according to their chemical structure.
By given feature antiseptic and antimicrobial preparations are classified. Medicinal substances are bactericidal and bacteriostatic, and differ in their chemical structure, which underlies the mechanism of action of the drug on the body and names.
- Halides. They are based on elements belonging to the halogen group (chlorine, fluorine, bromine, iodine).
- Oxidizers. The mechanism of their action is the ability to form free oxygen in in large numbers(hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, hydroperite).
- Acids. IN medical purposes various acids are used, but salicylic and boric acids are most often used.
- alkalis. These include sodium borate, ammonia.
- Aldehydes that remove fluid from tissues (formalin, ethanol and others).
- Salts of heavy metals.
- Phenols, characterized by the provision of an irritating and cauterizing effect on the body (carbolic acid, lysol).
- Dyes. Used for diagnostics, as well as a local irritant and antibacterial agent (methylene blue, brilliant green, and others).
- Tars and resins in the form of Vishnevsky's balm, Wilkinson's ointment, ichthyol and others. They are used to improve local blood supply to tissues.
Solid drugs are drugs that are produced in the form of:
- Tablets obtained by shaping a powder under pressure, which contains active and excipients.
- Dragee - arranged in layers of active and auxiliary substances, which are pressed around the granules.
- powder. They are used as powders for wounds, for intramuscular or intravenous injections(Saline solution is used to dilute the powder). Powders are undosed and dosed, simple and complex.
- A capsule in a gelatin shell contains a medicine that can be liquid, granular, powder or paste.
- The granules most commonly used for the manufacture of homeopathic medicines are small particles, the size of which does not exceed half a millimeter.
Medicines are available in liquid form
This method is used to prepare solutions, galenic and novogalenic preparations, balms, collodions and other liquid and semi-liquid preparations.
- To form solutions, the drug substance is mixed with a solvent.
- To obtain galenical preparations, plant extracts are heated.
- For the preparation of infusions and decoctions, dry medicinal plants. Their composition is indicated in the prescription, and the solvent and its amount are also indicated so that the pharmacist correctly prepares the drug.
- Infusions and extracts are liquids that contain alcohol. They can prepare for pure form, and there are also alcohol-water or alcohol-ether.
- For the preparation of novogalenic preparations, raw materials and the finished product are subjected to a high degree of purification.
Medicines of special forms
These include balms. Balm is an oily liquid that has deodorizing and antiseptic properties.
Collodion is obtained by dissolving nitrocellulose in alcohol and ether. A combination of one to six. Used for external use.
Any cream has a semi-liquid consistency and consists of plant extracts that are mixed with a base in the form of glycerin, wax, paraffin.
It is better for children to give medicines in the form of lemonades and syrups. Little patients take them with pleasure and they like this treatment process.
Injections are made with sterile aqueous and oily solutions, which are simple and complex. When writing a prescription, the doctor must indicate the dose of the medicinal substance and its volume, which contains one ampoule, and recommend the place of administration of the drug.
Soft drugs
A mild form of the drug is obtained by using a fatty or fat-like substance as a base. They are defined, classified, manufactured by chemists and pharmacists. The doctor should only specify the dose and indication for use in the prescription.
Medicinal ointments should contain at least twenty-five percent of solids. The appropriate consistency can be achieved by mixing the powder and animal fat, wax, vegetable oils, petroleum jelly or polyethylene glycol.
The same conditions are used when making pastes, with the difference that they are more viscous. The consistency of the liniments, on the contrary, should be more liquid. In addition, they are shaken before use in order to allow the settled powder to be evenly distributed in the solvent.
Suppositories or suppositories have a solid form, however, when they enter the human body, they quickly melt and turn into liquid.
The patches have a solid form while they are in a room at room temperature. Once on the skin, they melt and stick to it, which contributes to the formation of a tight contact.
Most medicines are substances of plant origin, which are subjected to chemical or physical treatment in order to better assimilate them into the body of an unhealthy person.
Pharmacology is a science that studies the effect of drugs on the human body, methods for obtaining new drugs. Also in Ancient Greece and in India, in the tundra and on the southernmost tip of Africa, people tried to find a way to fight the disease. It became, in a sense, their obsession, a dream worth striving for.
Pharmacological terminology
Medicines are substances or combinations thereof that are used to treat a disease or as a preventive measure.
A medicinal product is a medicinal product that is ready for use.
There are various forms of medicines. This is done for ease of use and the possibility of an individual approach to the treatment of patients. In addition, due to the variety of forms of release, it is possible to deliver the drug to the body in several ways. This makes it easier to work with unconscious patients, as well as with people who have received injuries and burns.
List A and B
All drugs are divided into three groups:
List A (poisons);
List B (strong drugs, including analgesics);
Medicines available without a prescription.
Class A and B drugs require heightened attention, therefore, a special prescription is required to obtain them in the pharmacy network. In addition, you need to know where and how to properly store these medicines. Since they may well decompose in sunlight or acquire additional toxic properties. And some drugs, such as morphine, are subject to strict accountability. Therefore, each ampoule is handed over by nurses at the end of the work shift with an entry in the appropriate journal. Some other medicines are also registered: neuroleptics, drugs for anesthesia, vaccines.
Recipes

A prescription is a written request from a doctor to a pharmacist or pharmacist to sell a drug to a patient, indicating the form, dose and method and frequency of use. The form immediately performs the functions of a medical, legal and financial document if the medicines are given to the patient on a preferential basis or without payment.
There is a legislative act that regulates doctors of different specialties and positions.
A drug is not only a substance that can eliminate a disease or its manifestations, but also a poison, so the doctor must correctly indicate the dosage when issuing a prescription.
Doses
On the prescription form, the amount of the medicinal substance is written in Arabic numerals in mass or volume units of the decimal system. Whole grams are separated by a comma, such as 1.0. If the medicine contains drops, then their number is indicated by Roman numerals. Some antibiotics are calculated in international (IU) or biological units (U).
Medicines are substances that can be in solid, liquid or gaseous form. Liquids and gases in prescriptions are indicated in milliliters, in the case of inhalation, the doctor can only note the dose of dry medicine.
At the end of the prescription, the signature and personal seal of the doctor is put. In addition, the patient's passport data is indicated, such as surname, initials, age. Be sure to include the date of issue of the prescription and its expiration date. There are special forms for recording prescriptions for subsidized medicines, narcotic substances sleeping pills, antipsychotics and painkillers. They are signed not only by the attending physician, but also chief physician hospital, certifies with his seal, and puts a round seal of the medical institution on top.
It is forbidden in the outpatient clinic to prescribe ether for anesthesia, fentanyl, chloroethane, ketamine and other sleeping substances. In most countries, prescriptions are written in Latin, and only recommendations for admission are written in a language that the patient understands. For narcotic and poisonous substances, the period of validity of the marketing authorization is limited to five days, for medical alcohol - ten, the rest can be bought within two months from the date of issuing the prescription.
General classification

In modern realities, when there are the most unusual drugs, classification is simply necessary in order to navigate in their diversity. To do this, several conditional guides are used:
- Therapeutic use - groups of drugs used to treat a single disease are formed.
- Pharmacological action - the effect that the drug produces in the body.
- Chemical structure.
- nosological principle. It is similar to therapy, only the distinction is even narrower.
Group classification
At the dawn of the development of medicine, doctors tried to systematize medicines themselves. Classification as such appeared through the efforts of chemists and pharmacists, compiled according to the principle of the application point. It included the following categories:
1. Psychotropic drugs and those acting on the central nervous system means (tranquilizers, neuroleptics, sedatives, antidepressants, antiepileptic, anti-inflammatory).
2. Drugs acting on the peripheral nervous system (ganglioblockers, anticholinergics)
3. Local anesthetics.
4. Drugs that change vascular tone.
5. Diuretic and choleretic agents.
6. Drugs that affect the organs of internal secretion and metabolism.
7. Antibiotics and antiseptics.
8. Anticancer drugs.
9. Means for diagnostics (dyes, contrast agents, radionuclides).
This and similar separation helps young doctors to better understand the drugs that are already available. Classification into groups helps to intuitively understand the mechanism of action of a particular drug and remember dosages.
Classification by chemical structure
This feature is most suitable for the classification of antiseptic and antimicrobial drugs. There are bactericidal and bacteriostatic drugs. The classification by covers both of these groups. The chemical structure of a substance reflects the mechanism of action of the drug and its name.
- Halides. They are based on a chemical element of the halogen group: chlorine, fluorine, bromine, iodine. For example, antiformin, chloramine, pantocid, iodoform and others.
- Oxidizers. It is easy to guess that their mechanism of action is aimed at the formation of a large amount of free oxygen. These include hydrogen peroxide, hydroperite, potassium permanganate crystals.
- Acids. They are used in medicine in large quantities. The most famous of them are salicylic and boric.
- Alkalis: sodium borate, bicarmint, ammonia.
- Aldehydes. The mechanism of action is based on the ability to remove water from tissues, making them more rigid. Representatives - formalin, formidron, lysoform, urotropin, urosal, ethyl alcohol.
- Heavy metal salts: sublimate, mercury ointment, calomel, lapis, collargol, lead plaster, zinc oxide, Lassar paste, etc.
- Phenols. They have an irritating and cauterizing effect. The most common of them are carbolic acid, lysol.
- Dyes. They are used in diagnostic manipulations and as a local irritant and antibacterial agent. These include methylene blue, brilliant green, fucorcin.
- Tars and resins, for example, Vishnevsky balm, ichthyol, paraffin, naphthalene, sulsen. Improve local blood supply to tissues.
solid drugs

These drugs have the following representatives: tablets, dragees, powders, capsules and granules and other drugs. Determining the release form is not difficult, since you can determine with the naked eye what exactly is in front of you.
Tablets are obtained by shaping the powder, consisting of the active substance and the excipient. This is usually done under pressure.
Dragees are active and auxiliary substances arranged in layers, pressed around the granules.
Powders have several uses. They can be drunk, sprinkled on wounds, diluted with saline and injected intramuscularly or intravenously. There are undosed and dosed powders, which, in turn, are simple and complex.
Capsules are a gelatin shell that contains a liquid, granular, powder or paste medicine.
Granules are most often found in homeopathic preparations, they look like small particles (no more than half a millimeter in size).
liquid forms

This method of preparing the drug includes solutions, galenic and novogalenic preparations, balms, collodions and other liquid and semi-liquid options.
Solutions are formed after mixing the drug and a solvent, such as water or alcohol.
They consist only of plant extracts obtained by heating.
Infusions and decoctions are prepared from dry plants. Each of them signs the prescription, including the amount of diluent that the pharmacist must use.
Infusion and extract - on the contrary, alcohol-containing liquids. They can be either pure or alcoholic or ethereal. Novogalenic preparations differ from conventional, galenic, high degree of purification of raw materials and the finished product.
Special Forms of Medicines

Balms are oily liquids with deodorizing and antiseptic properties. Collodion is a solution of nitrocellulose with alcohol and ether in a combination of one to six. They are used exclusively externally. Creams have a semi-liquid consistency and contain plant extracts mixed with a base such as glycerin, wax, paraffin, etc. Lemonades and syrups are designed to make it easier for children to take medicines. This helps, without additional effort, to interest little patient the treatment process.
Suitable for injection are sterile aqueous and oil solutions. They can be as simple as they are complex. When writing a prescription, they always indicate the dose of the substance and the volume in one ampoule, as well as recommendations on where exactly the drug should be injected.
soft forms

If fatty or fat-like substances are used as a base, soft drugs are obtained. The definition, classification, manufacturing process of these - all these issues are studied by chemists and pharmacists to perfection, while the doctor only needs to know the dose and indications for the appointment.
So, ointments should contain at least twenty-five percent of the dry matter. Appropriate consistency can be achieved by mixing the powders with animal fat, wax, vegetable oils, petroleum jelly or polyethylene glycol. The same criteria apply to pastes, but they must be more viscous. Liniments, on the contrary, should be more liquid, and before use they need to be shaken so that the settled powder is evenly distributed inside the solvent. Candles or suppositories have a solid form, but when ingested, they quickly melt and become liquid. The patches are also solid at room temperature, but on the skin they melt and stick, forming a tight contact.
Medicinal products are substances of predominantly plant origin that have undergone chemical or physical processing so that the patient's body absorbs them better.
Most people mistakenly believe that a drug and a drug are the same thing. In fact, there is a slight difference between these two things.
Features of the drug
A drug is a substance or mixture of substances that is used for disease prevention, diagnosis and treatment. Medicines are created from various substances using synthesis, a variety of chemical reactions and biological technologies. It is worth noting that this tool can be not only a synthetic product, but also a substance of plant or animal origin. Presented as food additives.
To date, medicines are divided into the following:
- Those that are sold strictly by prescription.
- Those that are sold without the consent of a doctor.
Despite the fact that these substances in our country belong to the group of medicines, in Europe they are a group of food additives or a group of alternative medicine.
According to the Russian law, which came out in 2006, all substances listed in the state register of medicines are such.
The manufacture of medicines must be carried out strictly in accordance with international requirements, otherwise such products are not tested and cannot be sold to people. 
You can sell these substances only in pharmacies that have the appropriate license. The sale of medicines in cosmetic stores is strictly prohibited.
Features of drugs
A medicinal product is a substance or a mixture of certain substances that for disease prevention, diagnosis and treatment. Such drugs can be created from synthetic and natural substances. Such drugs are presented in the form of tablets, capsules, ointments, solutions and more.
Before using drugs, you need to make sure that they have passed all the necessary studies and do not have dangerous side effects.
Used to create medicines the following types raw materials:
- Plant substances (grass, flowers, roots), as well as products related to their processing (juice, resin, oil).
- Animal substances - fat, fat.
- Organic fossil raw materials - oil and products of its distillation.
- Inorganic fossil raw materials - products of processing of mineral rocks.
- Various products from the chemical industry.
As a rule, drugs are taken directly by mouth through the mouth.
As well as drugs, these drugs are divided into the following:
- Those sold by prescription only;
- Those sold without a doctor's prescription.
It is worth noting that doctors prefer drugs, not drugs. 
What is common between drug and drug?
It is important to highlight the point that medicines and drugs are very similar to each other and they have a lot in common, which makes people confuse them:
- A drug, like a drug, is a substance or a mixture of substances that was created for the prevention of a disease, its diagnosis and further treatment.
- In both cases, synthetic substances are used, as well as substances of animal and vegetable origin.
- Both types of substances are divided into those that are sold only by prescription and those that are sold without a doctor's prescription.
- Before going on sale, both types of substances are thoroughly tested and tested on volunteers.
In order not to confuse these substances, you should always remember that a drug is only a food supplement, but a drug can be an ointment, a solution, and, of course, a tablet.
Main Differences Between Drug and Drug Product
Differences between drugs and medicines are as follows:
- The drug is presented in the form of some food additives, and the drug is presented in the form of tablets, ointments, solutions.
- In European countries, it is believed that a drug is part of alternative medicine, but a drug is already part of modern medicine.
- IN modern medicine Preference is given to drugs, as there is much less confidence in drugs.
- And there is also another slight difference, it lies in the fact that drugs are directly related to food intake (presented in the form of food supplements), but drugs can be taken regardless of food.
These are all the differences between drug and drug product. If we analyze everything in detail, it can be noted that these substances have much more and larger similarities than differences, so the best option would be to combine them into one group.
In addition, there is also Nosological classification.
Prescription and non-prescription medicines
In world practice, there is the concept of "over-the-counter" and "prescription" medicines. The latter suggest a greater potential danger of over-the-counter use. There is a constant struggle between the "pharmaceutical" and "medical" lobbies (respectively, for the expansion of the 1st or 2nd group of drugs and the corresponding business).
State regulation is designed to take into account the interests of the population (the dilemma of "availability" and / or "safety" of medicines), without biasing towards the interests of the pharmaceutical or medical business.
Homeopathic medicines
In a number of countries, these drugs are regulated in different ways - either as a category "Medications", or as "Food and supplements", or as "alternative medicine". Currently, there is no well-established opinion of international organizations on this matter, agreed with national health authorities.
In the Russian Federation, homeopathic medicines are subject to the same legislative regulation as conventional medicines.
Legislative regulation
The circulation of medicines is regulated by law and by-laws, including the regular updating of the list of Vital and Essential Medicines (VED), the List of Narcotic Drugs, etc.
Economic consequences of legislative regulation
In Ukraine, there is a practice of returning excise duty for the use of alcohol in the manufacture of medicines - only after they are sold.
Bodies of state control over the quality of medicines
The quality of medicines in Russia is controlled by the Federal Service for Supervision of Health and Social Development (Roszdravnadzor), subordinate to the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation.
Centers for quality control of medicines operate in most large cities of Russia. Their main task is to check the organizations selling medicines (compliance with numerous norms for the storage and sale of medicines), as well as selective (and in some regions even total) control of medicines. Based on the data from the regional centers, Roszdravnadzor will make decisions on the rejection of a particular drug.
This is how it should ideally be. In practice, things look a little different.
Firstly, the vast majority of drug quality control centers are more than poorly equipped, and they are not able to carry out a complex chemical analysis of a modern drug. An even more difficult situation arises with microbiological studies, which are either not carried out at all or are carried out in a very reduced volume. As a result, often all, so to speak, studies are limited to assessing the appearance of the drug (is there any unacceptable sediment, are the tablets cracked, are the packaging correctly designed, the label is crooked, etc.).
Secondly, according to the legislation in force in Russia, it is unacceptable to require additional analysis from the seller if the medicinal product already has a valid certificate (declaration) of conformity. Thus, all additional studies should be carried out at the expense of the Centers for Quality Control of Medicines. In fact, this translates into additional costs for the seller.
Third, drug quality control centers should produce selective drug control. In many regions of Russia (for example, Stavropol, Tver region, Tatarstan), the re-check is of a total nature. In general, this is illegal, and due to the lack of equipment of laboratories, it is simply meaningless, which leads to a significant difficulty in selling not only counterfeit and low-quality drugs, but also drugs in general.
As a result of the above, we can say that most of the regional Centers for Quality Control of Medicines today do not fulfill their tasks, only creating grounds for bribes and unfair competition.
Rejected and counterfeit medicines are subject to withdrawal from the pharmacy network, information about them is available on the following websites:
Original medicines and generics
An original drug is a drug that is first released by the developer. As a rule, the development and marketing of a new drug is a very expensive and time-consuming process. Of the many known compounds, as well as newly synthesized ones, by enumeration, on the basis of databases on their properties and computer modeling of the proposed biological activity, substances with the maximum target activity are identified and synthesized. After animal experiments, in the case of a positive result, limited clinical trials are carried out on groups of volunteers. If the effectiveness is confirmed, and side effects are insignificant, the drug goes into production, and based on the results of additional tests, possible features of the action are clarified, undesirable effects are revealed. Often the most harmful side effects are found in clinical use.
At the same time, the manufacturer patents this new drug. All other firms can produce synonyms (so-called generics), but according to their own technology, if they prove the bioequivalence of drugs. Of course, they cannot use the brand name for this drug, but only the INN, or some new one patented by them. Despite the new name, these drugs can be similar or very close in their effects.
Are original drugs and generics completely equivalent? From the point of view of chemistry, the active substance is the same. But the production technology is different, different degrees of purification are possible. There are other factors as well. For example, it is known that for a long time different companies could not achieve the same effectiveness of acetylsalicylic acid (generic) as that of Bayer AG, the manufacturer of the original drug "Aspirin". It turned out that the matter was not only in the purity of the raw materials, but also in a special method of crystallization, resulting in special, smaller crystals of acetylsalicylic acid. There can be many such nuances. The opposite result is also possible, when the generic is more successful than the original medicine.
In modern preparations, only one of the isomers (enantiomers) may be biologically active, the other may be weakly active, inactive, or even harmful (see Bioavailability).
Illegal actions in the production and circulation of medicines
Counterfeit drugs, counterfeit drugs
The pharmaceutical business is considered the third most profitable, after the arms and drugs trade. This attracts unscrupulous entrepreneurs to him.
In Russia, until 1991, the problem of falsification of medicines was practically absent.
Fake
Counterfeit is a deliberate change in the formulation of the production of a medicinal product. Replacing expensive components with cheaper ones, or reducing the content (and in the worst case, completely absent) of the necessary component of the drug. For example, replacing the more expensive cefazolin with cheaper (and less effective) penicillin. In addition, other violations in production are possible: violation of the time and sequence of the technological process, underestimation of the degree of purification, poor-quality packaging materials, etc.
counterfeit
Counterfeit drugs are drugs produced without the permission of the patent holder - the developer company.
The effectiveness of a drug is primarily determined by the active substance (but not only by it, see bioequivalence). According to international law, the formula or composition of the active substance cannot be a company secret. But for some time (about several years) this information is closed to other manufacturers, who, even under a different name, cannot produce this medicine without the permission of the patent holder's company.
Even at the end of the allotted time, other companies cannot use the name of the drug (Brand) registered by the company - the patent holder (the so-called patent form).
There is a temptation for drug manufacturers, knowing the formula, to release drugs bypassing the patent owner. An example is the drug No-Shpa® (registered brand name). In fact, this is a fairly simple synthesized drug, the active substance of which has the generic name "drotaverine". However, for several generations people have used No-Shpa and know nothing about some drotaverine. Accordingly, the price of a branded drug is 10 (!) Times higher than the price of a drug that is exactly the same in composition, manufacturing technology and action, drotaverine. It is not surprising that at some factories that produce cheap domestic drugs during the day, at night the same drugs are packed in foreign, branded packages. It should be added that this usually does not affect the quality of the drug, since the counterfeit manufacturer is afraid to arouse even the slightest suspicion from the inspection authorities.
Illicit drug trafficking
Narcotic substances are subject to stricter rules of circulation than other drugs. However, due to the increased demand for them, there are situations in which officials neglect the proper performance of official duties.
- The flip side of the tightening of requirements for the circulation of narcotic drugs is the unreasonably difficult obtaining by persons with direct indications for use (oncological diseases, etc.).
see also
Links
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010 .