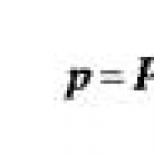Types of herpes in children. Signs, symptoms and treatment options for a herpes infection in a child. Signs of chickenpox in children of different ages
The human pathogen is herpes simplex virus (HSV) types 1 and 2 (DNA viruses).
Allocate:
- primary infection
- recurrent infection: symptomatic recurrent infection (presence of herpetic vesicles due to a previous infection, as well as neutralizing antibodies) and asymptomatic virus isolation.
Although herpes simplex usually affects young people, sometimes this infection is also found in children.
Epidemiology of herpes simplex virus in children
Infection involves close contact with mucous membranes or affected skin.
Infection of the adult population with the herpes simplex virus type 1 is approximately 70-90%. Antibodies to HSV 1 may also have a protective effect against HSV 2.
Primary HSV 2 infection occurs through sexual contact. As a result, in most cases, there is a local herpes genitalis or a latent infection. Approximately 1% of pregnant women have recurrent herpes genitalis.
HSV-associated infections are rare in newborns (1:2000 to 1:3000 among all live births).
- Perinatal infection occurs in approximately 85% of cases.
- Transplacental or ascending prenatal infection (5%), as well as postnatal (10%) infection are rare.
- Postnatal infection in most cases is due to HSV 1. When a nosocomial infection occurs, any person (mother, father, relatives, staff) who has had contact with the patient, for example, herpes labialis, acts as its source.
The risk of infection in a newborn child associated with HSV 2 depends on the stage of the disease of the mother:
- > than in 50% - when a pregnant woman has a primary genital infection in a period of > 32 weeks, since on the one hand there is a high isolation of the virus, and on the other - there are no protective antibodies.
- with recurrent herpes simplex, virus isolation is noted only for 2-5 days, the amount viral bodies significantly lower, in addition, the fetus in this case receives protective antibodies (the risk of neonatal infection< 5 %).
- Least Risk (< 0,5-3 %) заражения существует при бессимптомном выделении вируса организмом матери. Но, поскольку такой статус чаще всего встречается у матерей, инфицированных ВПГ 2, и зачастую это остается неизвестным, то, как правило, именно такая ситуация имеет место при возникновении манифестированных инфекций у новорожденных (60-80 %).
- premature rupture of amniotic fluid increases the risk of infection. Therefore, caesarean section in pregnant women with active genital herpes is performed only if the period from the moment of rupture amniotic sac made up< 4 часов. Во время родов не накладывать электроды на волосистую часть головы и не производить заборы крови у плода.
Symptoms and signs of herpes simplex virus in children
At primary herpetic infection clustered small vesicles or pustules appear. Herpetic rash usually resolves within 2 weeks. Herpes simplex often recurs, and relapses often have a milder course, less pronounced rash and duration of clinical manifestation. If herpes is suspected, a virological examination of the contents of the vesicles and an immunofluorescence reaction are indicated to determine the type of HSV.
Symptoms of perinatal/postiatal infection: there are three flow options:
Disseminated infection(in about 30% of HSV-infected newborns):
- Often after primary maternal infection in the peripartum.
- The dramatic course of the disease (the clinic may very much resemble bacterial sepsis).
- The onset of symptoms, as a rule, is on the 4-5th day of life, the maximum manifestation is on the 9-11th day.
- All organs can be affected: the brain, mucous membranes of the oropharynx, esophagus, intestines (pneumatosis intestinalis). Diffuse interstitial pneumonia, myocarditis with arrhythmias, anxiety of the child, centralization of blood circulation and shock, jaundice associated with biliverdin against the background of high transaminase activity and disorders in the blood coagulation system may occur. Typical vesicular skin lesions occur in about 80% of cases.
Enzefsyi t (in 30% of HSV-infected newborns):
- The onset is usually 2-3 weeks after birth.
- Seizures, drowsiness or restlessness, tremors, sluggish suckling, temperature fluctuations.
- A typical vesicular skin rash occurs in only 50%.
- Encephalitis is not limited to the temporal lobes, but extends to other departments.
- In the cerebrospinal fluid, the number of mononuclear cells and protein is increased, the concentration of glucose is moderately reduced.
HSV infection of the mucous membranes and skin with lesions of the skin, eyes and / or oral cavity(in about 40% of HSV-infected newborns):
- Beginning in most cases on the 11th day of life.
- Typical groups of red vesicles with a cloudy secret are found mainly on the part of the child's body presenting during childbirth, namely: on the head, chest, oral mucosa, in the oropharynx.
- Eye damage manifests itself in the form of keratitis or chorioretinitis, less often cataracts.
- Without treatment, progression to encephalitis is possible.
Symptoms in case of intrauterine infection / congenital infection:
Very severe, unfavorable prognostic intrauterine infections are rare.
Vesicular rash from birth, hydrocephalus, chorioretinitis, microphthalmia.
Subclinical infections: It is still unknown whether subclinical HSV infections exist in newborns. A tactical question arises in a situation where, for example, signs of HSV are detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of absolutely asymptomatic newborns by PCR. Until this situation is clarified, these newborns should be observed and treated as if they had HSV infection.
Diagnosis of the herpes simplex virus in children
Clinical suggestion arises in the event of the onset of symptoms of sepsis with a significant increase in transaminase activity and / or disorders in the blood coagulation system.
Detection of the virus in the contents of the vesicles, buffy coat preparations or smears from the mucous membranes (conjunctiva or nasopharynx), as well as in the cerebrospinal fluid by PCR. The culture of HSV in the cerebrospinal fluid with encephalitis can be obtained only in 40%. PCR is more sensitive than culture. Infection is confirmed by positive PCR or virus culture.
Detection of antibodies by CSC, indirect immunofluorescence, or IgM detection by ELISA at the onset of the disease is of little sensitivity, so these tests are not performed at this stage. In the case of encephalitis, intrathecally formed HSV-specific oligoclonal antibodies are detected after about 10 days.
Imaging studies (ultrasound, MRI): pictures of an isolated lesion of the temporal lobes, typical of older children, cannot be expected, in most cases disseminated encephalitis occurs.
Prevention of herpes simplex virus in children
Delivery by caesarean section:
- If a woman at the time of delivery has Clinical signs obvious genital herpes, and no more than 4-6 hours have passed since the outpouring of amniotic fluid. The protective effect of childbirth has been proven caesarean section with primary infection in the last 6 weeks of pregnancy. In recurrent HSV infection, the effect is less clear, but prophylaxis is strongly recommended.
- Whether delivery by caesarean section is a protective measure in the case when > 4-6 hours have passed since the moment of rupture of the amniotic sac is still unknown.
- Herpes simplex vessels or organs abdominal cavity pregnancy is less of a problem.
It is difficult to make a decision in the case of preterm birth. Possible options:
- Expectant management during acyclovir therapy for a pregnant woman, as well as the introduction of betamethasone to induce maturation of the fetal lungs.
- Rapid delivery by caesarean section with the introduction of a premature newborn surfactant and acyclovir.
Pregnant women with genital HSV infection (primary or secondary) from 36 weeks of gestation should be treated with acyclovir at a dose of 1200 mg / day for 3 injections (a reduction in the frequency of caesarean section is possible against this background).
Asymptomatic shedding of the virus occurs in about 2% of women with recurrent genital herpes, while the risk of infection in newborns is less than 3%. Thus, the overall risk of newborn infection from pregnant women with recurrent genital herpes is< 1:2000. В целом это не является показанием для проведения кесарева сечения.
Isolation of HSV culture in pregnant women is not prognostically significant in terms of labor management, so this technique has fallen into disuse.
HSV-exposed newborns:
- Careful monitoring of newborns for 6 weeks in relation to the occurrence of symptoms of HSV infection.
- Sowing culture of HSV or PCR in swabs from the mucous membrane of the throat, oral cavity and conjunctiva within 14 days, starting from 24 (-48) hours after delivery. Perhaps, in order to assess perinatal exposure to HSV, it is rational to obtain a culture of the virus from the mother's vaginal discharge. If HSV is detected in a newborn, then acyclovir therapy is recommended in the absence of symptoms of infection.
- Prophylactic administration of acyclovir to newborns from mothers with primary or recurrent symptomatic HSV infection.
Mothers shedding the virus, as well as infected newborns, are isolated.
In the case of recurrent infections (Herpes labialis, Herpes genitalis), the spread of the virus must be prevented by preventive measures such as hand disinfection, protection of affected skin areas (face mask). Breastfeeding of the mother is allowed with all precautions, provided that she does not have lesions of the nipples of the mammary glands.
Treatment of herpes simplex virus in children
Treatment is with valaciclovir or famciclovir given orally.
Of fundamental importance is the immediate initiation of therapy in case of any suspicion of HSV infection (this improves the prognosis).
Acyclovir or vidarabine can be used. Both substances are equally effective. Due to the lower toxicity and volume of the solution, preference is given to acyclovir.
Dose of acyclovir: 60 mg / kg / day for 3 injections, duration of therapy 14-21 days (21 in case of HSV sepsis). Premature infants with limited renal function: 40 mg/kg/day for 2 doses (60 mg/kg/day, one landmark study found better than 30 mg/kg/day for HSV sepsis and HSV encephalitis ).
Forecast of herpes simplex virus in children
With disseminated HSV infection, mortality decreases from more than 90% without treatment to almost 40% with therapy. Long-term results, however, are not yet known. High risk of delayed psychomotor development.
Without treatment, 2/3 of newborns with HSV encephalitis die. Surviving children have severe psychomotor damage with microcephaly, tetraspastic paresis, chorioretinitis, hearing loss. Against the background of therapy with acyclovir or vidarabine, 90% of newborns survive, 30-40% of these children subsequently develop normally. However, in the long term, the symptoms may worsen progressively.
Isolated lesions of the skin, eyes, or oral cavity are more prognostic in terms of prognosis.
Despite adequate therapy, relapses of vesicular rash during the first year of life are very common. At the same time, only the course of outwardly manifested local HSV infections is known, the lethality in which is low (about 7%), but the relatively long-term prognosis seems doubtful, since many of these children, especially with frequent relapses, at the age of 6 months, there is a delay psychomotor development. If necessary, these infants are treated with acyclovir 900 mg/m 2 /day for 6 months.
Relapses similar to acute progressive infectious encephalitis of the CNS are known, the treatment of which is always carried out with acyclovir. The effectiveness of adjuvant therapy with glucocorticosteroids is currently under debate.
The body of a child is more often affected by pathogens of herpes simplex type 1 (HSV-I). Outwardly, a herpetic infection in children is manifested by the growth of vesicles with watery contents on the lips, nostrils, and in the oral cavity. Therapy is recommended for immunomodulatory and antiviral drugs, folk remedies. It is important for parents and other adults to remember that viruses can easily spread between people, so it is advisable to limit the social circle of a sick child during the period of illness.
About 8 types of herpesviruses cause human disease, five of them are better studied, research is ongoing on the next three. Clinical manifestations of herpes viral infection in children, they depend on the age of small patients, the immune status, the site of penetration of the pathogen and its typology. Primary infection is accompanied by more severe symptoms than relapses.
A child can be infected with any of the following virus genotypes:
- HSV-I, II - causative agents of herpes simplex.
- Varicella zoster causes chickenpox, shingles (herpes zoster).
- Epstein-Barr virus - the causative agent of infectious mononucleosis (rarely).
- Cytomegalovirus - the cause of infectious mononucleosis, hepatitis (rarely).
- Causative agents of sudden exanthema or "pseudo-rubella" (rare).
Primary infection almost always leads to the appearance of pronounced symptoms, a higher incidence of complications.
Various lesions of the skin, including the appearance of rashes on the face, provoke HSV-I and Varicella zoster. Herpetic stomatogingivitis and tonsillitis are caused by viruses of the first three types. HSV-I infection usually results in mucosal changes in the throat and mouth. HSV-II usually causes genital infections, a serious illness in newborns. The most common ways of infection with herpesviruses of the first and second types are contact-household.


The following factors contribute to the activity of herpes infection in the body:
- hypothermia and overheating;
- hypo- and beriberi;
- poor digestion;
- weak immunity;
- frequent colds;
- stress.
After infection, a herpes infection in a child manifests itself or passes into a latent form and remains in sensory neurons. Relapses of the disease are associated with both adverse external and internal changes. Type 1 hepatitis virus reactivation may follow oral trauma, unsuccessful dental procedures.
Causes and danger of children with herpes simplex
Infection of the fetus occurs during fetal development through the placenta. A newborn becomes infected when passing through the birth canal, after childbirth - through contact with the mother, medical staff. HSV-I is found in saliva, is transmitted through shared utensils and other items. Diseases of children are often noted after the age of one year, by which time the effect of mother's antibodies ends in the body of babies. If the child already attends a preschool institution, then it becomes infected through toys, hygiene items.
The virus remains in the human body forever, treatment is mainly aimed at getting rid of the symptoms of the disease, preventing complications and relapses.
Often, the primary infection with HSV-I is asymptomatic, but the virus "sleeps" in the child's nerve cells - it is in a latent form (latent). From time to time, it reactivates in response to hypothermia, overheating, fever, or other factors. A recurrence of HSV-I often begins with a tingling, itching sensation in the area where the blisters used to be.


The development of primary herpes infection of the second type in newborns is observed in the first weeks of life. The virus infects the central nervous system, skin, eyes and oropharynx. The generalized form of HSV-II often causes the development of herpes pneumonia in the newborn. The addition of a bacterial and fungal infection to it leaves little hope for the recovery of the baby. Such forms of herpes require hospitalization of the patient. If relapses occur and they are less dangerous, then treatment is carried out at home.
HSV-II reactivation is manifested by the growth of vesicles on the genitals and adjacent areas of the body - in the vagina, on the cervix, vulva, penis, buttocks and thighs.
Early age, lack of treatment, reduced immunity- the main causes of serious complications of herpes simplex in a child. Then stomatitis or tonsillitis proceed in a severe form, the herpes virus causes eye damage - conjunctivitis, keratitis. The most severe cases lead to joint disease, internal organs, to herpetic encephalitis or meningitis.
Signs of herpes type 1
When a primary HSV-I infection develops, inflammation of the oral mucosa begins, the gums swell, the lymph nodes swell, and the temperature rises. There are bubbles in the mouth, as in the photo. They then turn into ulcers and heal slowly over 7 to 14 days. During a recurrence of herpes, sores around the mouth may develop.


In most cases, rashes during HSV-I infection are localized in children in the oral cavity and in the oropharynx. The virus of the first type causes herpetic stomatitis, affects the red border of the lips and the area around, other parts of the face. But only 10–30% of HSV-I carriers develop symptoms that persist for 5–14 days. Virus shedding lasts approximately 3 weeks.
Clinical signs and symptoms of herpes infection in children:
- Sudden onset of illness, lethargy or irritability, fever.
- Increased salivation in infants, pain on sucking and swallowing.
- Redness, swelling of the gums, their bleeding.
- Vesicles on the tongue, palate, gums, sometimes on the lips.
- Reluctance to eat and/or drink.
Common clinical manifestation HSV-I in a child aged 6 months to 5 years is considered acute herpetic stomatitis. Herpes in children 2-3 years old is manifested by lethargy, malaise, redness and pain in the throat, temperature. Symptoms of a herpes infection in the throat in children of primary school age and adolescents resemble pharyngotonsillitis. Lesions can spread to areas of the mucosa or skin if they get infected saliva. Complications often develop in the case of a primary infection, in the subsequent immunity usually copes with the virus.
Genital herpetic infection. Diagnosis of HSV
The second type of virus mainly affects the organs of the reproductive system, although this pathogen also causes oral herpes. If the infection occurred in utero or during the passage of the child through the birth canal, then the weakened baby begins to hurt immediately after birth. Incubation period averages 6 to 8 days.
Generalized herpes of newborns leads to lesions the most important organs and systems - nervous, digestive, cardiovascular.
The most severe disease occurs with intrauterine infection, infection of the child immediately before childbirth. Already a few days after birth, there are characteristic symptoms- fever develops, rashes appear on the body. Signs of herpes are complemented by yellowing of the skin, urine darkens, and the child's stool becomes discolored. The external genitalia are covered with vesicles. With the development of herpesvirus pneumonia, a fatal outcome is possible.
The doctor prescribes general analysis blood to determine changes in its composition. Swabs are taken from the mucous membranes to detect the virus. Diagnosis is most facilitated by blood tests using enzyme immunoassay or polymerase chain reaction (ELISA and PCR, respectively).
The final diagnosis is confirmed by virus isolation in tissue cultures. For adequate treatment, it is important to identify its genotype.
In the case of a generalized infection, the medical staff performs scrapings from the affected areas. Doctors prescribe lumbar puncture to examine the cerebrospinal fluid for signs of disease. In addition, it helps to identify the degree of damage to individual organs. electroencephalogram, ultrasound and other studies (MRI, CT).
Drug treatment of herpes infection
Children with a generalized form of herpes need hospitalization, intensive care. It is necessary to contact the pediatrician if the newborn, after being discharged from the maternity hospital, develops a fever, rashes, redness and inflammation of the eyelids and mucous membranes of the eyes. When children older than a year develop superficial lesions of the mouth, pharynx, and skin, home treatment may suffice. During this period, it is necessary to prevent combing of the bubbles, scratching of the crusts.


Children who experience discomfort due to sores in the mouth or on the lips are given paracetamol (acetaminophen). When a viral herpes infection develops in children in the oropharynx, the use of medications accelerates the healing of ulcers, reduces the risk of complications and relapses. Antiviral therapy is more often used in the case of a generalized infection of newborns, genital herpes, a weakened immune system, and severe brain damage.
Doctors prescribe drugs and select dosages in accordance with the age, body weight and condition of the child.
How to treat herpes of the first and second type in children:
- Treatment of affected areas with antiseptic and anesthetic fluids (chlorhexidine, lidocaine).
- Lotions with solutions of proteolytic enzymes to dissolve dead tissue (lysozyme).
- Immunomodulatory medicines based on interferon - suppositories, gel and ointment "Viferon".
- Antiviral agent acyclovir - tablets inside, cream - externally.
- Desensitizing therapy (fenkarol, pipolfen).
- Applications from oil solutions tocopherol and vitamin A, sea buckthorn oil.
- Antiherpetic vaccination between relapses of the disease.
It is recommended to include in the diet of sick children dairy products, veal, poultry, rabbit, fish, vegetables, dried fruits, nuts. It is necessary to avoid foods and drinks that irritate the inflamed epithelium. You can not allow dehydration of the body, so give Apple juice, mineral water without gas.
Folk remedies
Alternative medicine suggests using medicinal plants and natural substances to treat herpes in children. Simple home procedures - compresses, baths, lotions - alleviate the condition and speed up recovery. Separate dishes and towels should be given to the patient to prevent the spread of infection in the family. The child can attend school, but in case of primary infection, pediatricians recommend leaving children at home.
A viral disease poses a threat to the health of the child. Treatment of herpes in children 3 years of age begins after the diagnosis is established, the results of additional research methods are obtained.
Treatment infectious disease carried out using medicines:
- chemotherapeutic agents;
- interferon inducers;
- immunotropic substances;
- recombinant vaccines.
For the specific prevention of relapses, drugs that restore immunity are used:
- Polyoxidonium;
- Ridostatin;
- Tromantadine;
- Khelepin-D;
- Likopid.
A protracted pathological process requires long-term use of immunomodulators. Course therapy is designed for 60 days.
During the period of remission, the child is prescribed herbal adaptogens:
- Immunal;
- Eleutherococcus tincture;
- decoction of the herb echinacea purpurea.
Vitamins for children with herpes will help strengthen the immune system and alleviate the course of the disease.
Manifestations and treatment of acute stomatitis in preschool children
Illness in a child early age begins with complaints of feeling unwell, headache, loss of appetite. The temperature rises to 39°C.
The patient notes the appearance of dizziness, drowsiness, rashes appear in the oral cavity, salivation increases. In a child, the submandibular lymph nodes increase, the gums become inflamed and bleed.
In the oral cavity, the bubbles merge with each other. In severe cases, the child's body does not tolerate high temperature, there is a runny nose, coughing, edematous conjunctiva of a bright red color. The soft palate is affected, the gums are covered with necrotic plaque. To maintain immunity, the child is prescribed interferons:
- Viferon;
- Kipferon;
- Ingaron.
Antivirals affect cellular and humoral immunity. The convenient form of release of Kipferon suppositories allows them to be used to treat children younger age. In the case of a severe course of the disease, several courses of therapy are carried out.
With a recurrent form of herpes stomatitis, Viferon suppositories are prescribed to the child. The effect can be achieved if treatment is started in the prodromal (initial) period of the disease. The doctor determines the one-time and daily dose drug to eliminate itching, burning and rashes in the oral cavity.
Labial form of infection
Three years. An acute viral disease is accompanied by itching, the appearance of a small edema in the places of future rashes. The child has symptoms of intoxication:
- chills;
- headache;
- irritability;
- weakness.
The patient has bubbles in the corners of the mouth, filled with transparent contents.
A severe course of the disease is observed in children suffering from chronic tonsillitis, blood diseases. subfebrile temperature lasts for several days, an unpleasant odor is felt from the mouth.
Among note the appearance of a specific rash in a child, which is covered with a crust after opening the bubbles.
To ensure the normal functioning of the immune system, the patient is prescribed drugs containing zinc. The use of the drug prevents the development of complications. For regular treatment of rashes, antiseptic preparations are used:
- camphor or 70% ethyl alcohol;
- 3% oxolinic ointment;
- Hyporamine tablets.
The child is recommended to take beneficial bifidobacteria that affect the temperature, eliminating signs of intoxication. Vitamin C shortens the duration of the disease, makes it easier for the patient to endure the "cold" on the lips.
Genital herpes in a child
A viral disease is dangerous for a small person. The patient complains of a burning sensation in places of future rashes. The child suffers from high fever, headache, irritability, insomnia.
Lesions in the genital area are extensive weeping areas. The patient is showing signs of toxicity. With an unfavorable course of herpes in the affected area, it is felt strong pain, pulse quickens, dry mouth, urination disorders appear.
Treatment of inflammation is carried out under the supervision of a physician. To stabilize the patient's condition and increase T-lymphocytes in the blood, drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect are prescribed. To strengthen the immune system, natural remedies are recommended:
- flower pollen;
- cranberries;
- natural honey;
- carrot;
- tea with echinacea purpurea herb;
- broccoli;
- turnip;
- oat flakes.

In severe cases of herpes in children, immunostimulants, such as Likopid, are included in therapy.
It is necessary to treat genital herpes with the help of creams that have an antiviral effect. The child is assigned antihistamines that prevent the development allergic reaction reducing itching and burning:
- Suprastin;
- Diazolin;
- Zyrtec;
- Claritin.
How to treat shingles
A viral disease in a child of the third year of life is rare. Infection can occur from a sick person. In children, the disease manifests itself acutely, characterized by high fever. The child is naughty, refuses to eat, cries a lot.
He complains of numbness in the fingers, the appearance of blisters, which dry up and crust over after a week. In some cases, there are no rashes, the skin becomes bright red, and painful spots form. , proceeding in a severe form, are hospitalized. For therapy, antiviral agents are prescribed:
- Acyclovir;
- Metisazon.
For local treatment use salicylic alcohol, 1% oxolinic ointment, 1% alcohol solution brilliant green. To reduce pain and discomfort the patient is prescribed drugs:
- ibuprofen;
- Nise;
- Panadol Solutab.

Claritin and other antihistamines for children are available in the form of syrups.
Cytomegalovirus - signs and treatment
The acute form of the disease is manifested by severe symptoms:
- headache;
- fatigue;
- malaise;
- fever.
Herpetic conjunctivitis occurs with inflammation that provokes simultaneous damage to the upper respiratory tract. Some symptoms of herpes may persist for 2-3 months. In this case, the kids need the help of a pediatrician.
The correct approach to the treatment of the disease is to take measures aimed at increasing the body's defenses. The child must be given drugs that reduce body temperature, physical and psychological rest should be ensured. It is necessary to be afraid of joining a bacterial infection.
The illness in a child is chickenpox, infectious mononucleosis, herpes zoster, or stomatitis caused by HSV types 1 or 2.
Severe complications develop in children with disorders in the immune system, suffering from diabetes, kidney disease. If the infection is severe, the patient is prescribed the drug Ganciclovir. In the event of a cough with sputum, the child takes expectorant drugs:
- marshmallow root syrup;
- Mukaltin;
- Lazolvan.
If there are rashes
Herpesvirus type 7 (HHV-7) causes an acute viral infection in a child preschool age. Sudden exanthema is manifested by the following symptoms:
- elevated temperature;
- runny nose;
- itching;
- lacrimation;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- decreased visual acuity;
- punctate rash on the upper palate.
The temperature drops on the fourth day of illness. The lesions are located on the neck, torso, disappear after 3 days without a trace. Herpesviruses type 6 cause the development of hepatitis, allergies, thrombocytopenic purpura. If a child falls ill suddenly, it is necessary to limit his contact with other children.
Convulsive syndrome is treated with drugs:
- Phenobarbital;
- Depakine;
- Difenin;
- Finlepsin;
- Seduxen.
During periods of exacerbation, treatment is carried out with antiviral agents that are taken for a long time. The doctor prescribes drugs:
- Pharmaciclovir;
- Valaciclovir.
With atypical exanthema ( infectious mononucleosis) drugs are used for treatment:
- Viferon;
- Cycloferon;
- Isoprinosine.
The drug Ergoferon has an anti-inflammatory effect, quickly eliminates the main symptoms of the disease.
Pink lichen is a sign of a herpes infection
At the initial stage, the patient complains of malaise, fever, pain and aching joints as with the flu.
on the chest and upper limbs plaques the size of a ruble coin appear. They have a bright color, uneven edges, rise above the level of the skin. There are no rashes on the neck and face. The patient complains of itching and burning in places where light red oval or round blisters appear.
For the treatment of herpes in a child at 3 years old, the doctor prescribes antihistamines:
- Fenistil;
- Claritin;
- Diazolin.
It is useful to take general strengthening agents:
- Askorutin;
- pantothenic acid;
- B vitamins.
Sharp and spicy foods are excluded from the diet. Do not wet the rashes with water, rub them with a washcloth. Traditional medicine recommends treating the affected areas 2-3 times a day with cranberry or lingonberry juice.

Severe illnesses caused by the herpes virus are highly contagious and require isolation of the sick child from other children. Bed rest is required.
If the temperature rises, malaise or chills appear, the doctor prescribes antipyretics:
- Paracetamol;
- Analgin;
- Nurofen.
Particular attention is paid to the regime of the day and the state of the nervous system.
Epstein-Barr virus treatment
One of the representatives of the family of herpes pathogens causes the following diseases:
- infectious mononucleosis;
- Burkitt's lymphoma;
- respiratory infections.
The child complains of fever, sore throat, runny nose, discomfort in the right iliac region. In the case of the development of a severe form of mononucleosis, indigestion, nausea, and vomiting appear.
A rare complication of the disease is rupture of the spleen. The patient complains of abdominal discomfort, palpitations, muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall, fainting is noted. With an erased form of the disease, the symptoms are mild.
Do not give medicine to a young child unless advised by a doctor. Antiviral agents are used at an early stage of the disease. The drug Inosine Pranobex does not cause the development of adverse reactions, therefore, it is prescribed to patients from 3 years of age. The child is given complex therapy using hepatoprotectors and antipyretic drugs. If mononucleosis occurs against the background of a fungal infection of the internal organs, it is recommended to take Fluconazole, Nystatin.

Increasingly, doctors register in babies various forms herpetic infections. These diseases have chronic course, which requires mandatory monitoring by parents and physicians. Not everyone knows what are the symptoms and treatment of herpes in children.

Virus types
Currently, scientists have discovered 8 types of viral herpes species. These harmful microorganisms very easily cause a herpes infection in young children. The structure of only three of the eight subtypes has been well studied. They are the most detailed and studied. These infectious agents most often cause manifestations of “colds” on the lips and in the intimate area in babies.
Literally translated, herpetic lesion means "creeping disease." Doctors gave this name to the disease several centuries ago. The peculiarity of this virus is that the favorite places for its occurrence are various mucous membranes. Microbes render toxic effect on epithelial cells, which leads to the appearance of various adverse symptoms.

In pediatric practice, the most common are 8 subspecies of viruses that cause various damage to the baby:
- Type 1. More often contribute to the development in the child of various rashes on the mucous membranes of the lips.
- Type 2. Causes a rash on the mucous membranes of the genital organs.
- Type 3. Refers to a subspecies of the virus that can cause chickenpox or shingles in a baby.
- Type 4. Doctors call it the Epstein-Barr herpes virus. These microorganisms can cause manifestations of infectious mononucleosis in a baby.
- Type 5. It is the culprit in the development of cytomegalovirus infection.
- Type 6 . A fairly new subspecies of the virus. Scientists conduct a large number of different studies to study in detail the infectious and virulent properties of this microorganism. This type of herpes can cause manifestations of multiple sclerosis or the development of a sudden exanthema.
- Type 7. Not described in detail. Currently, researchers are studying the properties of this microorganism. There is scientific evidence that it is this subspecies that is responsible for the development of sudden skin rashes and leads to chronic fatigue.
- Type 8. A rather unfavorable subspecies of the virus. Can help develop malignant neoplasms on the skin. Exist Scientific research, indicating that it is this virus that contributes to the development of Kaposi's sarcoma.

Incubation period
Majority viral diseases is highly contagious (contagious). Herpes is no exception. A sick person who has a high concentration of viruses in the blood is contagious. Focusing on statistics, it can be noted that the largest number of cases of the disease is caused by a subtype of herpes simplex. It contributes to the development of adverse symptoms of herpes infection in 90% of children.
For a long time, the child may not suspect that he is already infected with herpes. In this case, the infection proceeds in a latent form. With this variant of the disease, there are no symptoms. The latent form occurs in about 5% of babies.
Usually, infection with the herpes virus occurs through primary contact with an infected person. The incubation period for different subtypes of the virus may be different. The first symptoms of the disease can appear both a couple of days after the pathogen enters the child's body, and after a few months.

The duration of the incubation period depends on many factors and initial data. The level of the immune system plays an important role in this. If the baby's immunity is strong, then the symptoms of the disease can be expressed slightly (or absent altogether) - for a long period of time. Usually they appear only when the immune system is not working properly.


The incubation period for type 1 herpes usually ranges from a few days to a couple of weeks. In this case, the first rashes appear on the mucous membranes of the lips and in the mouth. Genital herpes, which causes a rash in the intimate area, causes uncomfortable symptoms, usually after 6-7 days. Shingles variants of the disease have a longer incubation period. In some cases, it can be several months (or even years).

Main symptoms
Different subtypes of viruses can settle on different mucous membranes. This leads to a wide variety of localizations. Each type of herpes has its own clinical features. This is due to the properties of the viral particles themselves. Infection manifests itself in children in different ways.
Herpes can cause the following clinical manifestations in a child:
- Increase in body temperature. Usually it increases to febrile values. The peak of fever falls on the first 3-4 days from the onset of the acute period of the disease. The temperature usually drops quickly. Normalization requires the appointment of anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs.
- The appearance of a rash. It is represented by a set of numerous formations, inside of which there is a liquid. These rashes look like bubbles filled with contents. The localization of the rash is determined by the type of virus that caused the disease.
- Increase lymph nodes. Regional lymph collectors are usually affected. If the virus causes rashes on the upper half of the body, then the cervical, parotid, submandibular and subclavian lymph nodes will be involved in the process. They increase in size, become tightly soldered to the skin. When they are felt, the child may experience soreness.

- Severe symptoms of intoxication. The abundance of viral toxins has a toxic effect on the entire body. The child feels “broken”, becomes very lethargic. In babies, appetite and sleep are disturbed. Babies often refuse breastfeeding.
- Behavior change. Toddlers become more capricious. Children of the first years of life do not make good contact. More severe forms of the course of the disease lead to an increase in drowsiness. Unbearable itching of skin rashes contributes to increased anxiety and nervousness in the baby.
- Soreness in places of herpetic vesicles. Herpes rash is usually very itchy. With the herpes zoster, pain spreads along the damaged nerve. After the rash disappears pain syndrome passes.


In the mouth
Most often, this variant is caused by the herpes virus type 1. The child has all the symptoms described above. Herpetic rash has several features. With the herpes simplex virus, it can occur on the tonsils, cheek, and tongue. The rash is represented by various diverse vesicles, inside of which there is a liquid.
The liquid component usually has a grayish or reddish color. Herpetic vesicles protrude a couple of millimeters above the surface of the skin. In severe cases, they can be numerous and quite large in size. Such rashes on the tonsils present a certain difficulty. They can easily break through and be injured during meals.

This type of herpes is also characterized by an increase in the parotid and group of cervical lymph nodes. In some cases, they even become visible from the naked eye. The body temperature of the baby rises to 38-38.5 degrees. The abundance of rashes leads to severe pain when swallowing. This contributes to the deterioration of appetite.
Eruptions on the lips
Most common when infected with a simple virus. Usually, subtype 1 contributes to the development of this herpetic rash. The disease is characterized by the appearance of numerous vesicles filled from the inside with a serous-bloody fluid. These formations are easily injured. Even a minor injury can cause capillary bleeding.
The danger also lies in the fact that if such bubbles are damaged, open wounds appear. Secondary bacterial infection. This leads to the development of viral-bacterial conditions. You can also notice these changes at home. When bacteria enter, the bubbles begin to suppurate.
The red border of the lips is the most favorite localization for herpes simplex viruses. The rash does not appear immediately. First, the damaged area begins to itch strongly. After a couple of hours or by the end of the first day from the moment of the onset of severe itching, bubbles are already beginning to appear. When they appear, itching increases several times.

Bubbles usually remain on the skin for 6-12 days. After an acute period of illness, they completely disappear from the skin. In their place, a dry crust appears, which after a while disappears on its own. In some cases, there is a persistence of moderate itching and redness of the damaged areas of the skin.
Herpetic eruptions on the face
Such localization is not the most common. Typically, this form of herpes infection occurs in weakened and often ill babies, as well as children with various forms of immunodeficiency. With this variant of the disease, red itchy vesicles appear on the nose, chin, forehead, and eyelids. severe forms diseases are accompanied by the occurrence of herpetic eruptions on almost the entire surface of the skin of the face.
Each subspecies of herpes has its own favorite localization and some features of the development of adverse symptoms. So, with the herpes virus type 1, the vesicles appear mainly in the zone of the nasolabial triangle. With the shingles variant, rashes cover not only the face, they occur throughout the body. Chickenpox is characterized by a stepped rash. In some cases, it also appears on the head, in the hair area.


After the disappearance of the bubbles, crusts remain on the skin. They usually differ in color from the surrounding skin. The crusts are reddish or red-brown in color. After a couple of days, they completely disappear, and the skin again becomes pale pink and clean. Itching usually disappears after 5-6 days from the moment the first rash appears on the face.
What does the encircling option look like?
The herpes virus type 3 leads to the development of this disease. This viral subtype is quite virulent. The risk of infection is quite high. Usually, babies who visit Kindergarten and preschool institutions. The herpes virus can stay in the environment for a long time. Only prolonged exposure to high temperatures and ultraviolet radiation leads to its destruction.
Most often, doctors note the disease with a shingles form of infection in babies who have recently had chickenpox. This is largely due to the peculiarities of the immune system. Weakened immunity cannot cope with the attack of pathogenic viruses. Often ill children and toddlers with immunodeficiencies are also at increased risk.

Once in the child's body, viruses can be in a "sleepy" state for quite a long time. Usually, with the bloodstream, they enter the nerve ganglia, where they can long time maintain their viability without loss of virulent properties. Under adverse conditions, they begin to actively multiply and cause the baby to experience the classic symptoms of a herpes infection.

With the encircling form, herpetic vesicles appear on almost the entire body. Their location depends on the affected nerve. They can be located on the leg, arm, back, front surface chest. The rarest localization for the herpes zoster is the location on the palms and feet. In such cases, painful vesicles mainly appear on the skin of the fingers.
The development of rashes goes through several successive stages. The first to appear is intense redness. After a couple of hours, a moderate itching appears, which becomes unbearable over time. The next stage is the appearance of bubbles. Inside them is a serous fluid. Herpetic vesicles remain on the skin for three to four weeks.
Then they disappear, and ulcers form in their place. If at this time the secondary bacterial flora does not enter the damaged areas, they heal and crusts form. Crusts may persist for up to a week. Itching at this time is noticeably reduced. A week later, the crusts begin to fall off on their own.


After an illness, only areas of depigmented skin may remain on the skin. This is a temporary phenomenon. Usually, over time, this symptom disappears completely. In the future, the skin of the child becomes clean, without traces of a herpes infection.
Skin rashes also accompany other symptoms. These include an increase in temperature to febrile values, soreness and enlargement of the cervical and axillary lymph nodes, increasing headache and great weakness. Usually they persist during the entire acute period of the disease. To eliminate them, the appointment of anti-inflammatory drugs and plentiful warm drinking is required.
Usually, doctors note that the severity of the disease depends on the age of the patient. The younger the child, the easier it is to tolerate this form of herpes infection. At an older age, the disease is tolerated quite hard. Some patients with severe herpes zoster are even admitted to the hospital. They are shown intensive treatment.

In the intimate area
The defeat of the genital organs with herpes infection is a fairly common pathology encountered in pediatric medical practice. This disease is caused by the herpes virus type 2. It is distinguished by its peculiarity to affect the mucous membranes of the genital organs. The severity of the disease depends on the age of the child, the presence of concomitant chronic diseases, as well as the state of his immunity.
This variant of herpes infection is usually transmitted sexually. However, in children there are some features of the transmission of the disease. They can also become infected during fetal development - transcervically. In this case, the viruses enter the blood along with the amniotic fluid. The transplacental method promotes the transfer of microorganisms through the blood vessels of the placenta.
Scientists also note a variant of infection through the fallopian tubes- transovarially. A fairly common way of infection is during childbirth. Even minor damage contribute to the easy entry of viruses into the child's body. This option is also called contact. Doctors note that children are usually very easily infected with a herpes infection at the time of birth.
The most significant susceptibility to infection with type 2 herpes viruses is in babies aged six months to three years. The immune system of children at this age is not yet fully functional. This contributes to the fact that the child's body cannot cope with the destruction of viruses on its own. Usually after initial contact clinical symptoms appear only in 10% of cases. The rest of the infection remains in a latent form.

Most cases of herpesvirus type 2 infection occur during adolescence. The variant of infection in this case is sexual or contact-household. After 5-7 days, the first adverse symptoms of the disease appear in children. They can keep for several weeks. The subsidence of the acute period of the disease does not mean complete recovery. Very often the course is chronic.
The classic symptom of "sexual" herpes are numerous vesicles. They are located on the external genitalia. These skin elements are quite itchy. In some cases, itching can be unbearable. The time of day doesn't matter. Itching can disturb the child both during the day and at night.
After the disappearance of the bubbles, erosion and wounds remain on the skin. It will take some time for epithelialization. It usually takes 5-6 days. Then the mucosa is completely restored and heals. There are no traces of the disease.

The child is severely impaired general well-being. The kid feels bad, his nervousness grows. Small children are more often naughty, babies can often ask for pens. Body temperature usually rises to 38-39 degrees. Against the background of febrile condition, the child may develop chills, as well as fever.


Symptoms of intoxication are also significantly pronounced. With these forms of the disease, headache, sleep and appetite disturbances, as well as rapid fatigue quite often occur. It is important to note that this subtype of the virus contributes to the development of relapses. Any condition that leads to a decrease in immunity leads to the appearance of new skin rashes in the child. Such relapses can occur even several years after the first exacerbation.
Mild forms of genital herpes occur in 90-95% of children. In other cases, the disease proceeds with a severe course. This condition requires emergency hospitalization of the child in a hospital. There, for the baby, they will carry out the entire necessary complex of antiviral and anti-inflammatory treatment.

Genital disease in a newborn and a one-year-old child
Every day, doctors began to note an increasing number of cases of infection with this particular form of herpes infection. Babies are predominantly infected during childbirth. Pregnancy pathologies also contribute to the development of intrauterine infection of the unborn fetus. Violation of the integrity of the placenta and feeding blood vessels leads to easier penetration of viruses to the baby.

Children under the age of 1 year suffer herpes quite hard. However, there are also exceptions. The severity of the disease depends on the state of immunity of the baby, his weight at birth, as well as the presence of concomitant chronic diseases. If a child becomes infected with the virus during childbirth, then the first symptoms appear, as a rule, after 10-14 days.
Doctors identify several options for the course of infection in babies in the first months of life:
- Localized. It usually occurs in every 2-4 children who become infected with genital herpes during childbirth. Herpetic eruptions appear on the skin, mucous membranes of the oral cavity, as well as in the eye area. Usually they are single, other options are found only in severe cases of the disease. The most dangerous localization is the eye area, since dangerous complications can occur in the form of optic nerve atrophy and the development of visual impairment.
- Generalized. Usually occurs in 25-40% of cases. The first symptoms appear in the baby after 5-7 days from the moment the viruses enter the bloodstream. It is characterized by a rather severe course. Herpetic eruptions cover almost the entire surface of the skin.
- Penetration into the brain. Approximately 30% of newborns infected with the herpes virus type 2 are registered. The first clinical signs appear after 2-3 weeks from the moment the microorganisms enter the child's body. The course of the disease is unfavorable: the symptoms increase rapidly - over a short period of time. The danger of the condition is that a fatal outcome may occur.


Treatment
To date, the treatment of herpes infections is diverse. It includes a large number of different drugs and medicines. Unfortunately, it is not possible to completely cure herpes in some cases. Some forms of the disease (for example, chickenpox) go away on their own. After suffering chickenpox, the baby develops a stable lifelong immunity.

All treatment of herpetic infections can be divided into several sections:
- Use of antiviral therapy. Medicines can be prescribed in the form of tablets, injections and ointments. In mild forms of the disease, topical preparations are predominantly used. To eliminate severe symptoms, the appointment of tablets is already required. Among the most commonly used drugs are Acyclovir, Zovirax, Valtrex, Vectavir, Famvir and others.
- Restoration of the immune system. Immunotherapy is carried out mainly during remission. The use of interferon preparations and immunoglobulins helps to strengthen the immune system. Medications are prescribed for a course appointment. The scheme is selected by a pediatrician or an immunologist - taking into account the age of the child and the characteristics of his anamnesis, as well as the presence of concomitant chronic diseases.
- Bed rest in acute period. The time when the baby has a high temperature is best spent in bed. This will contribute to a faster recovery and prevention dangerous complications. Usually bed rest is prescribed for 3-5 days. In severe cases, it can be extended for a week or more.



- A complete meal with a fairly high calorie content. Prolonged development of the disease leads to physical exhaustion of the baby. To compensate for this condition, more intensive nutrition is required. If a child has herpetic eruptions in the mouth, then you should choose dishes that are more liquid and soft consistency. After the subsidence inflammatory process in the oral cavity, the baby's menu can be expanded.
- Reception of multivitamin complexes. To cope with the consequences of viral intoxication, additional enrichment of the diet with vitamins and useful microelements is required. The good functioning of the immune system is helped by multivitamin complexes enriched with antioxidants. Selenium, vitamin C and retinol will be great helpers in the fight against a dangerous viral infection.
- Warm plentiful drink. Helps eliminate all toxic products from the body. As drinks, various fruit drinks and compotes made from berries and fruits are perfect. Too sweet drinks should not be given to the baby. It is better to pre-dilute them with boiled water. During the day, a sick baby should drink 1.5 liters of fluid.
- If a child develops chickenpox, it is very important to observe quarantine. The entire acute period of the disease, the baby should be at home. This will help prevent mass outbreaks of the disease in educational institutions. After normalization of health, the child can continue attending kindergarten.
- Strengthening the immune system is an important component of the treatment of herpes infection. regular hardening, proper nutrition, optimal physical exercise, as well as good rest and sleep contribute to the good functioning of the immune system. Any overload leads to physical and mental exhaustion of the baby, which contributes to the development of immunodeficiency in him.


At home
For many centuries, people have been treating herpes on their own, without resorting to medicines. Doctors recommend such treatment only for mild forms of the disease. Use for newborns and infants home therapy folk remedies medicine is quite dangerous. Before any use medicinal plants Be sure to consult with your doctor.
To eliminate the adverse symptoms of herpes are used:
- Lotions made from lemon balm or mint. These products do an excellent job of eliminating itching and redness of damaged areas of the skin. To prepare the infusion, take 1 tablespoon of raw materials and pour a glass of boiling water over it, leave for about an hour. After that, cool the solution to a comfortable temperature. Lotions with lemon balm infusion can be used up to 3-6 times a day - until the rash completely disappears.
- Propolis. This bee product has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect and helps to eliminate itching, as well as any redness. You can use propolis to treat herpetic vesicles several times a day. This remedy is prohibited for use for babies who are allergic to honey.
- Eucalyptus oil. It helps to eliminate redness and itching in the affected area. Eucalyptus oil has excellent antiseptic properties. Applying this remedy to herpetic eruptions will help prevent the ingress of pathogenic bacteria and the development of suppuration.
- Decoction of calendula. This tool is often used in the form of lotions. For cooking, it is enough to take 1-1.5 tablespoons of crushed calendula flowers and pour 200 ml of boiling water. You need to insist for 40-50 minutes. Lotions with calendula are applied to damaged areas 3-4 times a day.
- Sea buckthorn oil. Promotes rapid healing of inflamed skin. You can treat rashes several times a day. Sea buckthorn oil is well applied to wound surfaces, which are formed after rupture of herpetic vesicles. It's simple and available remedy helps to effectively cope with redness and reduces the severity of skin itching.



You can learn more about herpes in the next video.
The children's body is more susceptible to infections and viruses, especially those that it encounters for the first time. In view of this, the symptoms are more pronounced, and the course of the disease can be severe.
The most common viral pathologies include herpes, which has a large number of varieties. The consequences of entering the body of its pathogens can be a cold on the lips, chickenpox, shingles, sudden exanthema.
Herpes is a widespread virus that has many varieties, the simplest of which is a rash on the lips.What is the herpes virus?
The herpes virus belongs to a group of opportunistic infections that can cause harm to health if the body's immune system is weakened by illness, severe overexertion or medication. It has a large number of varieties, but only 8 of them pose a serious danger to humans.
From Greek, the word "herpes" is translated as "creeping skin disease". Manifestations of the disease are observed on the skin and mucous membranes. Depending on the type of herpetic infection, the lesion is localized in different places on the body, for example, on the head, abdomen or legs, the pathology has a different incubation period and provokes other diseases.
About 90% of people are carriers of the virus. In almost any person, its pathogens are present in the body in a latent state, until some factor provokes an exacerbation. Any organ is susceptible to infection. Another distinguishing feature of the disease is a high probability of infection.
Does a child have an innate immunity to herpes?
Young children are much more likely to get herpes due to the lack of immunity to this infection. From the moment of primary infection in the blood of the child, the production of antibodies begins. There is a formation of immunity to a specific type of herpetic pathogen that has entered the body. However, this is not a 100% guarantee that the disease will not return.
After recovery, the herpesvirus infection remains in the nerve cells. Under certain conditions, it can begin to multiply again. As a result, herpes gets sick many times throughout life. Factors contributing to its reappearance:
- colds, acute respiratory infections or SARS;
- not good nutrition and lack of vitamins;
- overheat;
- severe stress;
- entry into the body a large number active pathogens of the virus.
About 5% of children are born with innate immunity to herpes infection. It is laid down genetically and goes to the child from the parents by inheritance. However, this does not completely exclude the possibility of getting sick. Activation of the virus can occur when exposed to a significant amount.
Ways of infection with herpes
 Herpes is easily contracted through close contact with an infected person.
Herpes is easily contracted through close contact with an infected person. Being highly contagious, the herpes virus can be transmitted in several ways. 5 main routes of infection:
- Airborne. The spread of the virus through the air occurs when the herpetic cells are released from the mucous membranes. For this reason, if one of the relatives, people from close circle is a carrier or is sick, the risk of getting infected is quite high.
- Household or direct contact. Don't hug, kiss, or shake hands with someone who has been diagnosed with herpes. Sharing common household items such as towels, utensils, doorknobs, and toys can lead to any type of infection, from simple to cytomegalovirus and other types.
- With blood transfusion or transplantation of internal organs. Such procedures are always accompanied by the possibility of infection.
- Perinatal. Infection occurs during the passage of the fetus through the birth canal. Most often, herpes No. 6 is transmitted this way (we recommend reading:).
- Transplacental. The route of transmission is the placenta. If the mother's blood does not produce antibodies to herpesvirus infections, then the baby may be born infected.
Varieties and symptoms of herpes
The age when herpes on the child's body begins to appear most often is 3-5 years. This period marks the beginning of independent movements, knowledge of the world and active communication with other children. The incubation period for herpes infection ranges from 1 day to a month.
 Exanthema on the baby's body - herpes virus type 6
Exanthema on the baby's body - herpes virus type 6 For all dangerous types herpes is characterized by its own symptoms, but there are a number of common features indicating infection:
- high body temperature, reaching 38–39 degrees;
- weakness;
- excessive irritability;
- aches in the joints of the limbs;
- headache;
- poor appetite;
- rash on the skin on different parts of the body, for example, on the head, around the mouth, on the abdomen, legs, arms (we recommend reading:).
 herpes virus type 1
herpes virus type 1 The table shows the 6 main types of herpes and their characteristic symptoms:
| type of herpes | What diseases does it cause | Symptoms |
| First, or simple | A cold on the lips that lasts 5-12 days (we recommend reading:) |
|
| Second, or genetic | Rashes on the genitals that disappear from 10 days to a month |
|
| The third | Chickenpox (duration - 7 days), shingles (3-4 weeks) (we recommend reading:) |
|
| Fourth, or Epstein-Barr virus | Infectious mononucleosis (rare but lasts up to 2 months) |
|
| Fifth, or cytomegalovirus (we recommend reading:) | Cytomegalovirus infection (1-1.5 months) (we recommend reading:) |
|
| Sixth | Exanthema in children (up to 7 days), multiple sclerosis in adults |
|
 Chickenpox is a herpes infection (virus of the third type)
Chickenpox is a herpes infection (virus of the third type) Diagnosis of the disease in children
As a rule, if bubbles filled with liquid appear on the skin of a child all over the body, then upon examination, a qualified specialist is able to make a diagnosis and prescribe a therapeutic course without additional laboratory research. However, this does not apply to inexperienced parents trying to compare rashes with photos from the Internet.
To assign the most effective treatment, a number of auxiliary manipulations will be required to properly treat herpes in children. More detailed diagnostics include:
- General inspection. It consists in collecting information about the condition of the baby, living conditions and external symptoms of the disease.
- Delivery of analyses. The patient's blood, feces, urine, and secretions from the mucous membranes are examined for the presence of the virus.
- Histological examination of tissue samples. It is carried out with suspicion of oncology.
- Ultrasound and MRI. These procedures help determine the degree of damage to the brain and other internal organs.
- Immunofluorescent study to study the liquid component of the vesicles.
- Consultation of narrow specialists. It is necessary to find out the causes of a malfunction in the immune system.
 It is important to conduct an analysis for the presence of herpes in the blood of a child - the result of the study will show how seriously disease hit the children's body (we recommend reading:)
It is important to conduct an analysis for the presence of herpes in the blood of a child - the result of the study will show how seriously disease hit the children's body (we recommend reading:) Methods of treatment
The peculiarity of herpes is that it is impossible to completely cure the disease. After the initial infection, a person will be forced to periodically face relapses of the disease throughout his life.
However, in order to avoid complications, one should always treat and eliminate the existing symptoms in a timely manner. For this reason, you should not resort to self-treatment, based on the advice of friends, photos from the Internet and other sources. The regimen of taking drugs with dosages and duration of the therapeutic course should be prescribed by a doctor.
Medications
The essence of the treatment of herpes simplex, like any other of its varieties, comes down to complex therapy, which includes the reception:
- Antiviral drugs. There is no separate group of medicines against herpes for young children. Regardless of the age at which the infection occurred - be it an infant under one year old, a 2-year-old baby or a child of 7 years old, the same drugs are used. Among them: Acyclovir, Zovirax and Famvir. They are available in the form of tablets or ointments. Tablets are prescribed to achieve a stronger effect. Usually, for the first three types of herpes, ointments are used, which are applied in a thin layer to the rash.
- Immunomodulators. Restoration of protective functions of an organism is required. Viferon, Cycloferon and Immunal are suitable for this.
- Drugs that relieve external symptoms. To eliminate itching, burning and an allergic reaction, antihistamines are used, for example, Suprastin, Zirtek or Tavegil. Antipyretics such as Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol for children should be given to bring down the high temperature and relieve pain in the muscles and joints.

Traditional medicine
With the help of traditional medicine, you can also alleviate the condition of a patient with herpes and speed up his recovery. For this, lotions, baths, compresses are made using various medicinal plants. The most popular recipes for ointments, decoctions and other remedies are:
- Compress with garlic, apple and potato to relieve discomfort. To do this, you need to crush the garlic, take the pulp of an apple and grate the potatoes, wrap everything together in a bandage and apply to the affected area.
- Tincture of lemon balm leaves or lemon mint for oral administration. 2 tsp mixture pour boiling water. Used in 3 doses.
- Tincture of celandine. It will take 1 tsp. celandine, a glass of boiling water. With this tincture, ulcers and vesicles are washed.
- Fresh juice or oil extract from celandine grass. This natural remedy lubricate damaged skin areas several times a day.
- Tincture of calendula flowers. Used for lotions.
- Propolis tincture. She rubs her skin. Dilute with water before use.
 Alcohol tincture of calendula flowers is very effective for external use in herpetic eruptions.
Alcohol tincture of calendula flowers is very effective for external use in herpetic eruptions. Diet
Diet plays an important role in the treatment of herpes. It has been scientifically proven that arginine proteins contribute to the activation of the virus, while lysine proteins, on the contrary, prevent this. As a result, the patient's diet should be enriched with products with lysine and those containing arginine should be excluded. The first ones include:
- shrimps;
- sea fish;
- milk or natural yogurt.
Reduce consumption of foods such as:
- chocolate;
- nuts and seeds;
- cereals and legumes.
It is also important to support immune system. To do this, include in the diet:
- ginger;
- lemon;
- garlic.
 It is necessary to constantly monitor the health of the baby and give him natural immunostimulants in small quantities.
It is necessary to constantly monitor the health of the baby and give him natural immunostimulants in small quantities. Complications after herpes
Herpes rash is a very unpleasant phenomenon that causes discomfort to the patient. However, most often it passes quickly and does not pose a health risk. The threat lies in the development of complications after herpes. Although they occur rarely, without proper treatment, the child may experience such consequences of the virus as:
- damage to internal organs (liver, heart, intestines, spleen);
- functional disorders of the nervous system;
- angina;
- inflammation of the tonsils;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- cerebral palsy;
- pneumonia;
- encephalitis;
- hepatitis;
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- problems with blood clotting due to the formation of blood clots in small vessels;
- miscarriage or pathological changes in the development of the fetus in case of infection of a pregnant woman, especially in the first trimester and during primary infection.
Preventive measures
Prevention of the disease directly depends on the type of herpes infection. For example, to prevent chickenpox and other aggressive varieties of the disease in children, vaccination is carried out.
It is also very important to maintain the immunity of the child, because. it is with its weakening that there is a risk of infection or reactivation of herpes. For this you should:
- provide a nutritious diet rich in vitamins and minerals;
- spend more time outdoors
- play sports and hardening;
- observe personal hygiene;
- once a year, additionally drink a course of a vitamin complex;
- go to the sea, because such climatic conditions contribute to the restoration of the protective functions of the body.
The same goes for pregnant women. Infection of the fetus during the intrauterine period is a danger to the health of the unborn child, especially if future mom I have never had a problem with herpes before.