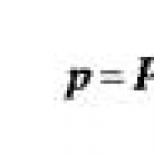Malgenya ankle fracture. Malgenya fractures. The prognosis for this pathology
A Malgenya fracture is a severe form of fracture in the ankle or pelvis. This type of fracture is named after the surgeon and anatomist J. F. Malgaigne. He described its characteristics and method of treatment as early as the eighteenth century.
In this case, the ankle bone breaks, tucking the foot inward. In this case, there is a rupture of the binding material in the joint area. As the process of pressing on the ankle continues and the foot continues to bend inward, the bone breaks at an oblique angle or vertically. Outward subluxation of the foot with this type of fracture is extremely rare.
During the diagnosis of a bone fracture, signs of a tumor in the ankle joint are visually observed. Feeling severe pain when links are broken. During the examination with the help of an X-ray machine, you can see how the fracture was made. The fracture is set by hand and a plaster cast is applied.
With a pelvic fracture, the injury falls on the iliac bones or the pubic and ischial bones. in one and the second cases, the integrity of the continuous bone is broken. Fractures of the pelvic bone are accompanied by large bruises, the occurrence state of shock. In most cases, a fracture is accompanied by a rupture of internal organs.
When diagnosing, deformation in the pelvic region is visible, the navel is significantly shifted to the side. An x-ray shows the location and type of fracture. It is treated with traction, while using a load of six to ten kilograms, which is fixed from the side of the injury. On the other hand, a load of four or six kilograms is attached. Treatment continues for six months.
Causes
The causes of the fracture are injuries of various types. It could be:
- falling from a great height;
- during an injury resulting from a car accident;
- if a person is under the rubble of a destroyed building;
- during accidents.
What type of fracture occurred, you can only determine the field of inspection of the direction of its line and displacement of the bone.
Mechanism of Education
Depending on the mechanism of injury formation, a fracture classification is carried out. The nature of the fracture depends on the direction of the fracture, as well as the force with which the bone was squeezed. There are such types of fractures:
- Stable, during which the bone breaks only at the edges. The pelvic bone remains intact.
- Unstable. In this case, the pelvic ring loses its integrity.
- Fracture, which is accompanied by a dislocation of the joint.
- Fracture of the bottom and acetabulum. In this case, a dislocation in the femoral joint is possible.
With a fracture of Malgenya, the victim loses a large number of blood. In most cases, this loss is about three liters.
Physical rehabilitation in surgery
Pelvic fractures, L-6
Physical rehabilitation for pelvic fractures.
Lecture 6
Classification of pelvic fractures, surgical treatment and stages of physical rehabilitation of such patients
(slide)
Pelvic bone injuries
Causes: falling from a height, compression during car accidents or landslides, falling from a height, divergence of the symphysis - in childbirth.
30% of cases are accompanied by traumatic shock.
Peculiarity:
- severe pain of this due to irritation of the reflexogenic zone,
Always a significant hemorrhage into the intrapelvic tissue.
Possible damage to internal organs: the bladder, urethra and rectum.
(slide) Classification of pelvic fractures (G.S. Yumashev, 1990)
1. Edge- damage to bones not involved in the formation of the pelvic ring: fractures of the spines, ischial tuberosities, coccyx, transverse fracture of the sacrum below the sacroiliac joint, fracture of the ilium.
2. Fractures without breaking the continuity of the pelvic ring. The bearing capacity of the pelvic ring decreases, but the support ability of the pelvic ring remains: 1) one- or two-sided fracture of one branch of the pubic bone; 2) unilateral or bilateral fracture of the ischial bones; 3) a fracture of one of the branches of the pubic bone on one side and the ischium on the other.
3. With a violation of the continuity of the pelvic ring. In this case, each half of the pelvis is connected with the sacrum only on one side; the support of the pelvis is sharply disturbed. Such injuries include: 1) vertical fracture of the sacrum; 2) rupture of the sacroiliac joint; 3) vertical fracture of the ilium; 4) fracture of two branches of the pubic bone on one or both sides; 5) fracture of the pubic ischial bones on one or both sides (butterfly fracture); 6) rupture of the symphysis.
4. Damage with simultaneous violation of the front rear half rings (like Malgenya). With these injuries, the connection of one half of the pelvis with the sacrum is completely lost. There is no pelvic support.
5. Fractures of the acetabulum. These include: 1) fracture of the edge of the acetabulum; 2) a fracture of the bottom of the acetabulum, which may be accompanied by a central dislocation of the hip - displacement of its head inward towards the pelvic cavity.
(Slide) Treatment of marginal fractures. Symptoms: pain, swelling, pathological mobility in the area of the fracture. With a fracture in the region of the sacrum, pain during defecation, increased pain when trying to sit down are noted.
Treatment: anesthesia at the fracture site; the patient is placed on his back, and the leg on the injured side is placed on the Beler splint. In case of fractures of the sacrum and coccyx, a wide roller is placed under the lumbar spine. It is possible to use a hammock. Operative treatment possible - fixation of a bone fragment with a screw or pin.
(Slide) Fractures without discontinuity of the pelvic ring.
Symptoms : Pain that worsens when you try to move your leg. symptom of "stuck heel") - can not raise the leg.
Treatment : "Frog position": the legs are slightly bent at the knee and hip joints, the knees are apart, the hips are rotated outward, and the feet are brought together. Under the knees - a roller (rice). Bed rest is observed for 4-5 weeks;
Fractures with discontinuity of the pelvic ring. Severe fractures, often shock, organ damage. Symptoms: pain, aggravated by moving the legs; forced "frog position", symptom of "stuck heel".
Treatment: laid on the shield in the "frog position" for 5-6 weeks, with displacement - skeletal traction, hanging in a hammock, surgical treatment.
Fractures with violation of the anterior and posterior semirings (Malgenya type). the most severe injuries of the pelvic bones.
Treatment: lay on a hammock and carry out skeletal traction. bed rest 10-12 weeks.
Fractures of the acetabulum. Symptoms: pain in the hip joint, aggravated by axial load.
Treatment: skeletal traction, surgical treatment with fixation of pelvic fragments with screws and plates.
So, treatment options:
Bed rest on a hard board in the “frog” position, knee roll
Cross Pull Hammock
Hammock, skeletal traction on tires
Skeletal traction
Surgical treatment - MOS, external fixation devices
(Slide 22)- picture "treatment of pelvic fractures"
Methods of treatment and terms of consolidation of pelvic fractures
(reference exercise therapy edited by Epifanov)
THERAPEUTIC PHYSICAL CULTURE FOR FRACTURES OF THE PELVIC BONES
(Slide) Most often found:
Rupture of the pubic symphysis and anterior half ring of the pelvis,
Fractures of the pelvis of the Malgenya type,
Fractures of the bottom of the acetabulum, including those with central hip dislocation (Table).
Start Exercise therapy - after removing the patient from shock
Methodology PH depends on the nature of the fracture and the method of its treatment.
General characteristics: Most often used conservative treatment with a long stay of the patient on bed rest in the supine position.
The general tasks of PH correspond to bed rest and are aimed at preventing complications associated with hypokinesia.
The special tasks change accordingly with the three treatment periods.
First period -
(Slide)1st period (10-12 days) . Until the moment of holding limbs straight on weight.
I.P. - lying on your back, legs bent at the knee and hip joints (this creates conditions for relaxing the muscles of the pelvic girdle, reduces pain and promotes the reposition of fragments).
Relaxation of the muscles of the pelvic girdle (pain reduction, proper consolidation)
Reduction of local eliminate hemorrhage and swelling;
Increased muscle tone of the n. limbs
Influence on the work of the intestines, organs of excretion and blood circulation,
Strengthen the muscles of the shoulder girdle, back;
Prevention of joint contracture and muscle atrophy
Increasing the general tone of the body;
Exercises:
General developmental exercises for the distal sections lower extremities
Breathing exercises. Emphasis on chest type of breathing. With diaphragmatic breathing and tension of the abdominal muscles (increased intra-abdominal pressure), there is an increase in pain associated with retroperitoneal hematoma, which is common with pelvic trauma.
Pelvic lift (for boat training)
Extension in the knee joints from the 4th-6th day (the hips lie on the roller),
With skeletal traction - movement of the free leg without taking the foot off the plane of the bed
Do it yourself 3-4 times a day
Pelvic lift training. The patient takes the Balkan frame with his hands and, bending in the back, raises the pelvis. First - with the help of an instructor, from the 4-6th day - on your own. During immobilization by skeletal traction, when lifting the pelvis, one should lean on the leg bent at the knee, free from immobilization.
(Slide) 2nd period- until the moment of lifting the patient (the end of the process of consolidation of the fracture and lifting the patient).
Special tasks:
Improving blood circulation in the fracture area,
Gradual strengthening of the muscles of the lower extremities and pelvic girdle
Preparation for getting up (a few days before getting up)
Exercises:
General developmental for hands (dynamic free and with weights),
Various breathing exercises
Isometric tension of the back muscles in series of 10-15 repetitions.
1. When I.P. "frog" : flexion of the legs in the knee joints, abduction of the legs, rotation in the hip joints from the 10-12th day are performed along the plane of the roller.
(In case of rupture of the pubic joint, hip extension and rotation in the hip joints are contraindicated, therefore, isometric tension of the muscles of the thighs, buttocks is used, and movements along the plane of the roller - after 3-3.5 weeks)
2. after 3-4 weeks, the roller is removed, I.P. lying on your back on a flat bed - lying on your back - leg exercises with the foot separated from the plane of the bed.
During immobilization by skeletal traction - movements in the knee joint - isometric tension of the muscles of the thighs and buttocks.
3. Preparation for lifting. A few days before lifting and after removing the skeletal traction, the patient is turned over on his stomach. Increase the overall load. Exercises:
For limbs - with weights, static
I.P. lying on the stomach - training the gluteal muscles and thigh muscles: flexion in the knee joints, extension in the hip, holding the raised leg.
I.P. knee-wrist - movement of limbs in dynamic and static modes.
(slide) 3rd period- from the moment of lifting the patient.
Getting up training
Adaptation to vertical position
Strengthening the muscles of the pelvic girdle and lower limbs,
Learning to walk with crutches.
Lifting technique: bypassing a sitting position, from a prone position or standing in a knee-wrist position.
I.P. - any. Exercises:
Movements for all muscle groups of the lower extremities, gluteal muscles, pelvic floor muscles, iliopsoas.
Working out the stereotype of walking movement: use crutches, focus on the correct gait: it is better to walk in small steps and monitor the stability of the pelvis (do not “swing the pelvis”)
Without crutches, you can walk about 2 weeks after getting up, if there is no pain in the area of the fracture
A course of manual massage of the lumbar region, gluteal muscles, muscles of the anterior surface of the thighs is carried out.
FT: magnetotherapy, UHF
After lifting - electrical stimulation
Features of PH in central hip dislocation and acetabular fracture. Morpho-functional features: conditions are created for the development of post-traumatic arthrosis of the hip joint, which is a fairly frequent and unfavorable consequence of a fracture of this localization. This is due to a violation of the blood circulation of the femoral head at the time of injury, the complexity of the reposition of fragments at the level of the acetabulum, leading to a violation of the congruence of the articular surfaces, cartilage injury with its subsequent degeneration. Therefore, it is important for the period of treatment to create conditions conducive to the preservation or increase of diastasis between the articulating surfaces of the joint.
1. During the period of skeletal traction (the period of immobilization), special exercises are aimed at activating blood circulation in the limbs (movements in the ankle joint, isometric short-term tension of the gluteal muscles).
Isometric tensions of the thigh muscles (3-5 s) begin to be performed at a later date - from the 21st day. At the same time, movements in the knee joint are performed. To do this, a removable cloth hammock is put on the horizontal part of the tire. During movements in the knee joint, the instructor must support the patient's leg by the heel area.
2.1. After removing skeletal traction, physical exercises are aimed at restoring mobility in the hip and knee joints, restoration of tone and strength of the gluteal muscles. In the first 5-6 days to restore mobility in hip joint active exercises are used in combination with manual traction along the axis of the limb. For example, the instructor performs traction of the limb, then helps the patient to bend the leg at the hip joint, and when straightened, again conducts traction. To restore the mobility of the knee joint, the prone position is used; bendings are performed actively, with the self-help of a healthy leg and with the help of an instructor. In the absence of pain in the hip joint, exercises to mobilize the latter can be performed in the lying position on the side, on the stomach, in the knee-wrist position. The patient gets up, bypassing the sitting position, and moves with the help of crutches without relying on the injured leg. With good adaptation to the vertical position, exercises are performed in a standing position on a healthy leg with hands resting on the back of a chair or bed. Free, swing movements in the joint are performed in all planes with multiple repetitions. For the convenience of performing the exercises, it is better to stand on a stand (small platform) so that the injured limb hangs freely without touching the floor.
2.2.. After removing the traction is assigned manual massage of the gluteal muscles and thighs on the side of the injury, the lumbar region.
Underwater massage and exercise in the aquatic environment.
3. Strengthening of the periarticular muscles begins in parallel with the mobilization of the joint according to the method described for coxarthrosis. It should be emphasized that, while strengthening the muscles, it is impossible to increase the pressure on the articular surfaces, which happens, for example, when lifting a straight leg with weights in the prone position. Therefore, it is better to strengthen the stabilizers of the hip joint (gluteal muscles and hip flexors) while standing on a healthy leg. A dosed load on the leg should be started after 4-5 months, and a full load - after 5-6 months from the moment of injury. To prevent the development of coxarthrosis with such damage, further treatment is required on an outpatient basis and adherence to the orthopedic load regimen on the limb
Big Medical Encyclopedia
Malgen's fractures - complex types ankle and pelvic fractures. They are described by the French surgeon J. Malgen in 1847-1855.
J. Malgen described a pelvic fracture in 6 places:
- fracture of both iliac bones parallel to the sacroiliac joints,
- bilateral fracture of the pubic and ischial bones.
This type of fracture is extremely rare. Unilateral fractures or dislocation fractures in the posterior pelvis are much more common in combination with unilateral or bilateral fractures in the anterior pelvis or with a rupture of the pubic symphysis. Common to these types of damage to the pelvic ring is the simultaneous disruption of its continuity in the posterior and anterior sections.
All such injuries, in contrast to injuries only in the anterior or posterior sections of the pelvic ring, are called fractures or fracture-dislocations of the Malgen type. With a fracture of the anterior and posterior sections of the pelvic ring on the one hand, they speak of vertical fracture pelvis Malgenya. With a fracture in the posterior part of the pelvic ring on one side, and in the anterior part with opposite side- about diagonal fracture.
Fractures of the anterior and posterior sections on both sides are called bilateral fractures pelvis Malgenya. If there is not a fracture, but a rupture of the ligaments of the sacroiliac joint or pubic symphysis with a displacement of half of the pelvis, they speak of fracture-dislocation.
Malgenya pelvic fractures are the most severe injuries, as they are always accompanied by extensive retroperitoneal hematomas, the development of severe shock, and often damage to the pelvic organs.
Diagnostics
In the diagnosis of these fractures, examination and palpation of the pelvis are important, which reveal:
- asymmetry of the halves of the pelvis,
- displacement of the navel from the midline,
- "reversal" of one of the halves of the pelvis with external rotation of the leg of the same side.
With bilateral fractures, a kind of “flattening” of the pelvis is visible - a significant expansion of it in diameter. When radiography in one anteroposterior projection, attention is paid to fractures of the pubic and ischial bones, rupture of the pubic symphysis, longitudinal fracture of the ilium, or rupture of the sacroiliac joint.
The height of the displacement of half of the pelvis is determined. X-ray studies also play a leading role in monitoring the correctness of reposition.
Treatment
The main treatment for Malgenya pelvic fractures is bilateral skeletal traction behind the tuberosities tibia and condyles of the femur. Load on the displacement side 6-10 kg, on the opposite side 4-5 kg. Traction is often supplemented by hanging the patient's pelvis in a hammock.
Traction is continued for up to 2.5-4 months, depending on the magnitude of the displacement and the time of onset of reposition. Immobilization by skeletal traction for torn ligaments of the sacroiliac joint or pubic symphysis lasts longer than for fractures.
Forecast
Ability to work after fractures of the pelvis of Malgenya is restored on average after 4-6 months. after injury.
Malgenya fracture is one of the types of damage to the pelvic bones.
All fractures of the pelvic bones are classified according to their severity, and the amount of damage received is also taken into account. This injury is one of the most severe fractures and, according to the classification of pelvic injuries, belongs to type C. In the absence of timely medical care injury is almost always fatal.
Anatomical features of the pelvic bones
The pelvis is formed by two bones: nameless or those. Each of these bones, in turn, is formed by three bones fused together - the ilium, ischium, and pubis. These bones fuse during adolescence.
The bones of the pelvis are connected to each other, forming a ring. The walls of this ring are a protection for the organs located inside it, in addition, it is a support element for the entire human body.
On both sides, the pelvic ring is divided into two half rings by the acetabulum:
- The posterior half ring is located behind the acetabulum. It includes the back of the ilium, the cross-iliac joints, the sacrum.
- The anterior half ring is located in front of the acetabulum. It is formed by the symphysis and branches of the pubic bones.
The stability of the pelvis is provided, first of all, by a semi-ring located behind. With a Malgenya fracture, two pelvic semirings are damaged. Damage can be unilateral or bilateral, accompanied by ligament rupture. With such an injury, the pelvis turns back or forward and shifts upward.

Causes of pathology
A Malgenya fracture can occur as a result of an extremely intense impact of a damaging force that is directed to the lateral surfaces of the pelvic bones.
This can happen in the following cases:
- when under a blockage resulting from the collapse of residential premises, an avalanche;
- major rail or road accidents;
- falling from a very great height.
That is, it is an uncommon injury, but it is characterized by severe manifestations and a high frequency of deaths.
Symptoms

In most cases, with a Malgenya fracture, the patient is in an extremely serious condition. The victim has symptoms of pain, hemorrhagic shock:
- Significant drop blood pressure.
- Thready or rapid pulse.
- Oppression of consciousness.
- Discharge of cold clammy sweat.
- Paleness of the skin.
Among characteristic features similar injury to the pelvic bones are as follows:
- Severe pain on palpation of the pelvic region.
- Puffiness, the occurrence of growing hematoma in the sacrum and perineum.
- Asymmetric arrangement of bony pelvic protrusions.
Fracture of the pelvis of Malgenya is accompanied by the formation of a large retroperitoneal hematoma. The spilled blood can reach the level of perirenal fiber. As a result of this phenomenon, palpation of the abdomen makes it possible to detect symptoms of peritoneal irritation - a positive symptom of Shchetkin, board-like muscle tension.
A characteristic sign of such an injury is a pronounced dysfunction of the lower extremities. Fragments of bones can damage organs located in the pelvis - the uterus in women, the rectum, bladder. As a result of damage, pelvioperitonitis may develop, which is inflammatory process in the pelvic peritoneum.

Fracture diagnosis
To clarify the diagnosis of a fracture of the Malgen type, the traumatologist prescribes an X-ray examination. The picture is taken when the patient lies on his back, while his legs should be extended. This position allows you to provide an overview of all pelvic structures. A more accurate study is carried out by computed or magnetic resonance imaging.
Methods of therapy for this pathology
How to treat a pelvic fracture like Malgenya? Therapeutic measures for such an injury are divided as follows:
- prehospital;
- basic;
- rehabilitation.
Each stage has a specific instruction for carrying out medical measures.
Prehospital care
A double fracture of the pelvic bones is accompanied by pain shock and massive bleeding. That's why prehospital care is to minimize all movements of the victim. The patient is transported using a wooden shield or a rigid stretcher.
To immobilize the patient, traumatologists use special suits or transport tires. During transportation, intensive hemostatic and anti-shock therapy is carried out.

Treatment of a Malgenya pelvic fracture in a hospital
The main therapy begins with the elimination of conditions that threaten the patient's life. It is necessary to stabilize hemodynamics, compensate for blood loss, anesthetize the injured part of the body.
To eliminate the pain shock, an intrapelvic blockade according to Shkolnikov is shown. The doctor, using a long needle, injects Novocaine into the iliac fossa. This technique allows not only to fully anesthetize the injured area, but also to stop the bleeding.
The main method of therapy for a pelvic fracture of the Malgenya type is the repositioning of displaced pelvic semirings. For this purpose, the patient is placed in a hammock, and then, using a Behler splint, a skeletal traction of the pelvis is carried out by the condyles. thigh bones. A sixteen-kilogram load is suspended on one side, and a load weighing up to 6 kilograms is suspended on the other. Traction takes an average of 8-9 weeks. It is allowed to give a full load on the lower limbs no earlier than after 4.5 months.
Most effective method therapy, which allows to reduce the period of immobilization, is bone osteosynthesis using metal plates. After such surgical intervention patients are allowed to get up after a couple of weeks.
What is the rehabilitation period?
Rehabilitation measures should begin in the hospital. Their main goal is to alleviate the well-being of the victim, speeding up his recovery.
The main directions of rehabilitation are physiotherapy procedures, physiotherapy and massage.
In addition, patients with fractures of the pelvic bones need to eat well, and the diet should be enriched with minerals, vitamins, calcium. Every day the patient should consume dairy products.
Additional calcium can be obtained using medicines, as "Calcium-D3", "Calcemin". In addition to the named element, they contain vitamin D, which contributes to better absorption of calcium in bone tissue.

The prognosis for this pathology
The prognosis of the outcome of such an injury strongly depends on the correctness and timeliness of the provision of medical care. With a fracture of Malgenya, cases of death of the patient were also noted, but most of the injuries have a favorable outcome.
After an injury, the patient may develop some complications. These include:
- Complications during pregnancy and childbirth in women.
- Pathology of the activity of the pelvic organs.
- neurodystrophic disorders.
- Gait disorders.
- Chronic form pain syndrome.
Thus, a Malgenya fracture requires urgent hospitalization and intensive care.
- (fractura) damage to the bone with a violation of its integrity. Fracture obstetric (f. obstetrica), see Fracture generic. Barton's fracture, see Barton's fracture. Bennett's fracture, see Bennett's fracture. Bush fracture see Bush fracture. Depressed fracture (f. cum ... ... Medical Encyclopedia
FRACTURE OF PELVIC BONES- honey. Pelvic fractures account for 47% of all fractures. Classification Marginal fracture: fractures of the iliac spines, ischial tubercles, coccyx, transverse fracture of the sacrum below the sacroiliac joint, ilium ... ... Disease Handbook
MALGENIA FRACTURES- - described by the French surgeon J. F. Malgaigne (1806–1865). 1. Fracture of the base of the olecranon, characterized by dislocation of the head of the beam and displacement of the distal fragment of the ulna. The diagnosis is confirmed radiographically. Fracture and dislocation ... ... encyclopedic Dictionary in psychology and pedagogy
- (J. F. Malgaigne) bilateral fracture of the anterior and posterior part of the pelvic ring, in which the fracture line passes in front through the pubic and ischial bones, and behind through the right and left iliac bones ... Big medical dictionary
- (J. F. Malgaigne, 1806 1865, French surgeon) the general name for ankle fractures with excessive supination of the foot, more often in the form of tearing off the end of the lateral malleolus and fracture of the medial with rupture of the tibiofibular ligaments, less often in the form of an isolated ... ... Big Medical Dictionary
TAZ- TAZ. Contents: I. Anatomy of the pelvis .................. 267 II. Pathology of the pelvis .................... 278 III. female pelvis................... 293 IV. Clinic of a narrow pelvis .............. 306 I. Anatomy of the pelvis. Pelvis (pelvis), part of the skeleton that forms the so-called ...
I (pelvis) a bone ring formed by two symmetrical pelvic bones, the sacrum and coccyx, forming the sacroiliac and pubic articulation. The pelvis forms a belt of the lower extremities, is a support for the body, forms an arch, ... ... Medical Encyclopedia
I Ankle joint(articulatio talocruralis) is formed by the distal epiphyses of the bones of the lower leg and the talus. The distal ends of the bones of the lower leg are interconnected by the tibiofibular syndesmosis (anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments) and ... ... Medical Encyclopedia
dislocations- DISTRUCTIONS. Contents: I. Traumatic dislocations. origin mechanism. diagnostic signs. Flow. Prediction. Treatment .............. . . Dislocations of the shoulder................ Dislocations of the elbow................ Dislocations of the wrist............. Dislocations... Big Medical Encyclopedia
PATELLA- PATELLA. Anatomy N. Patella, patella, patella, a flat rounded bone, laid in the form of a self-shaped bone in the tendon of the quadriceps muscle in front of the lower end of the thigh. The anterior surface of N. is convex, rough, with many ... ... Big Medical Encyclopedia