Heart pacemaker: contraindications. Rules of conduct for a patient with a pacemaker
Cardiovascular diseases are the most common worldwide. The most dangerous are the consequences of improper treatment of hypertension. A stroke or heart attack develops, which have a very high mortality rate.
In the occurrence of such terrible consequences, arrhythmia plays an important role. Incorrect asynchronous contraction of the heart muscle not only leads to a decrease in blood supply to vital organs, but also provokes the formation of blood clots. Patients with dangerous forms of arrhythmias are usually treated with various pharmaceuticals, but a pacemaker is an effective and reliable option for their relief. Any center of modern cardiology in Russia performs operations to install it.
What is a pacemaker
The pacemaker is an electronic device that is designed for monitoring and correction. The device itself consists of a conventional battery and several electrodes that are connected to the heart muscle. The essence of the work of the pacemaker is to detect arrhythmia and correct it due to electrical signals that reach the heart. An electromagnetic stimulus affects the heart muscle and causes the wrong rhythm to "switch" to the right one. Therefore, the installed pacemaker will help to effectively eliminate dangerous arrhythmia. There are no contraindications to its implantation.
What are the types of pacemakers
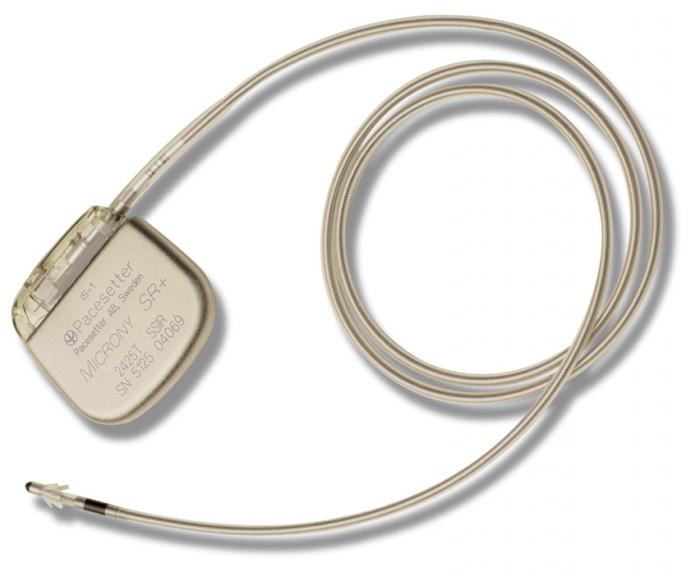

The division of devices is based on the number of heart chambers to which electrodes from the device fit. Therefore, almost every cardiac surgeon will offer you a one-, two-, or three-chamber pacemaker. The photo shows the appearance of a single-chamber device that has only one electrode. It is usually located in the ventricle. Such models are practically not used now, due to the limited range of the electric charge. The dual chamber device has one electrode in the atrium and another in the ventricle, which provides both better monitoring and correction of the heart. Such devices are used more often. A three-chamber pacemaker has three electrodes, and one of them can act as a defibrillator, which is especially desirable for patients with or ventricles. The cost of a pacemaker depends on the manufacturer and the pricing policy of the medical institution.
When is the pacemaker installed?
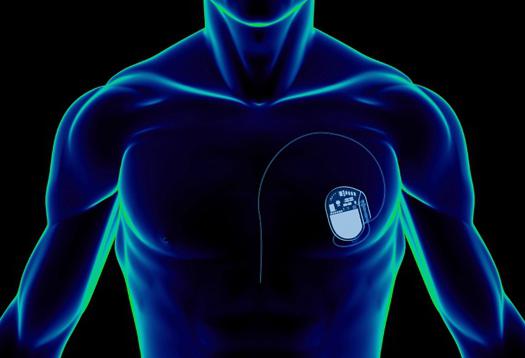
Pacemaker implantation is aimed at restoring the correct rhythm. To combat brady- and tachyarrhythmias, a heart pacemaker is installed. The operation is used only in the presence of certain types of arrhythmia. In particular, the group of bradyarrhythmias includes bradycardia with a pulse rate of less than 40 beats per minute, Morgagni-Edems-Stokes syndrome, II-III degree AV blockade, incomplete blockade, weakness of the sinus node and carotid sinus. Morgagni-Edems-Stokes syndrome is manifested by loss of consciousness, convulsions, which is associated with complete AV blockade. As for tachyarrhythmias, rhythm disturbances that are associated with physical activity are also indications.
The Center for Modern Cardiology can offer you the appointment of a pacemaker on a temporary or permanent basis. Temporary implantation of the device is rarely used and serves to correct certain ones (for example, paroxysmal tachyarrhythmia).
Cardiac pacemaker, contraindications

Installing a pacemaker has no contraindications. The only caveat is the validity of the device installation, which depends both on the life expectancy of the patient with arrhythmia, and the form. Before implantation of the pacemaker, the patient must undergo Holter monitoring. This is a round-the-clock monitoring and analysis of the rhythm and pulse rate, which allows you to find out the type of arrhythmia and when it occurs most often.
How is the pacemaker implantation procedure performed?
The operation is considered minimally invasive, as it is made from small incisions. First, the surgeon inserts a catheter into the subclavian vein and, under X-ray control, places electrodes in the desired area of the heart. After the introduction of sensors into the formed bed in the projection, a heart pacemaker is installed. The operation ends with several stitches on the skin.
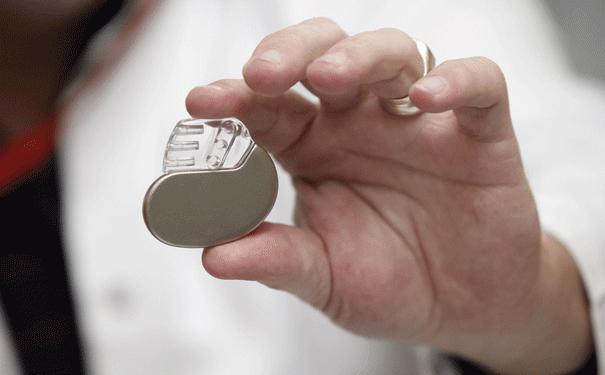
After that, the device starts to work and generates impulses depending on the correctness of the rhythm. To minimize the likelihood of arrhythmias, a heart pacemaker will help, which has no contraindications.
Patient's lifestyle after surgery
Life with a pacemaker imposes certain limitations on the patient, which, although not serious, are important for the correct and long-term operation of the device.
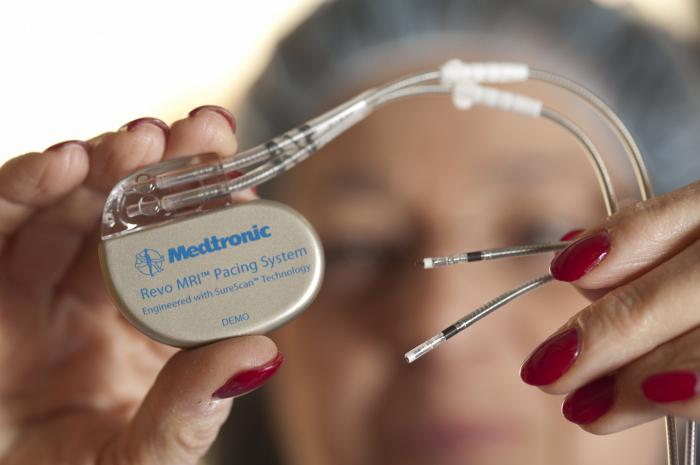

First of all, one should remember about the methods of examination of the body, the principle of which is based on the action of an electromagnetic field or current. It is recommended to use computed tomography or ultrasound for a patient who has a pacemaker. Contraindications relate to magnetic resonance imaging and external defibrillation, lithotripsy and radiation therapy. When performing echocardiography, you should warn the doctor about the installed device, as a direct hit can cause interruptions.
Each patient is given a specific document-passport of the patient who has a pacemaker implanted. This document contains information about the model of the installed device, the date of implantation, and the approximate date of replacement of the battery. For persons who are traveling abroad, such documentation will be required when passing through airports.
The dosage of physical activity should be gradual, but regular. During the first month, light housework, morning hygienic exercises, small walks in the fresh air are recommended. In the future, the mode of increasing tolerance to loads is gradually expanding. If the patient was engaged in swimming or tennis before the operation, then approximately in six months he can gradually restore his level of training. In this case, it is necessary to monitor the heart rate and blood pressure. If you notice interruptions, shortness of breath, dizziness or general weakness, consult your doctor.
Postoperative wound and follow-up
The most critical period is the first 7 days after the operation. This
concerns primarily the state of the postoperative wound. The first 5-7 days the patient is in the hospital to monitor the operation of the pacemaker. Bandaging and toilet of the wound are performed every day. The sutures are removed on the 6th - 7th day. After removing the sutures, the patient must limit the load on the upper limb from the side of the implanted device for another 7 days. Such activities are carried out in order to create a mature scar that can withstand the usual work.
![]()
Diet
For patients, such dietary nutrition is provided, as in atherosclerosis. Diet number 10 recommends limiting animal fats and replacing them with vegetable oils (sunflower, linseed, olive), a diet that is enriched with fiber and vegetable proteins. It is undesirable to use rich broths, salty meats and fish, limit flour dishes. You should also limit the intake of coffee and strong tea, as these drinks are stimulants of the nervous system and can provoke arrhythmias. For the correct selection of the diet, you should seek the help of a nutritionist or, as an alternative, completely eliminate forbidden foods.
Doctor's examinations
Provided that you do not have any complaints, the first examination by a doctor should be carried out in a month. The medical specialist prescribes a blood test, a coagulogram and an ECG, which are basic examinations. In the future, you should visit a doctor after 3 months and then 1 time in six months. These visits are essential and allow for better control of both your pacemaker and your heart muscle.