What is a pacemaker, how much does it cost and how is the installation operation performed
The beginning of the 20th century was marked by the rapid development of technology in all areas of human life. Innovative medical research conducted in the 1920s showed the ability of the myocardium to contract under the influence of electric current pulses. The essence of the research was able to revolutionize the treatment of certain heart diseases, which was proved by the external device for maintaining the rhythm created in 1927.
However, due to the large size and relatively small resource of electronic components of that time, the development of pacemakers was frozen for decades. The device in its modern sense was created only in 1958 by Swedish scientists and was named Siemens-Elema. Since then, the design and principle of operation of pacemakers have been improved every year - the devices become more functional, reliable and durable.
Purpose and device of the device
 To understand how a modern pacemaker works, you need to understand what it is. A pacemaker (EX) or, as it is also called, an artificial pacemaker (IVR), is a microprocessor device equipped with an independent power source and located in a sealed metal case, most often made of a titanium alloy.
To understand how a modern pacemaker works, you need to understand what it is. A pacemaker (EX) or, as it is also called, an artificial pacemaker (IVR), is a microprocessor device equipped with an independent power source and located in a sealed metal case, most often made of a titanium alloy.
The design of the device includes:
- Frame- serves to accommodate the internal elements of the pacemaker and isolate them from body tissues.
- Control and communication unit– necessary for coordination of modules operation, exchange of information with control and diagnostic devices.
- memory block– stores statistical information about the operation of the device.
- Sensor block- is able to detect changes in the work of the heart and correct the effects of the pacemaker.
- Working block- generates and transmits electrical impulses to the heart.
- Battery- serves as a power source for the remaining elements of the pacemaker, is equipped with mechanisms to save energy and disable non-basic functions when the charge drops below the threshold level.
The functions of the pacemaker are to perceive the heart's own rhythm, detect pauses and other failures in its work and eliminate these failures by generating impulses and transmitting them to the corresponding chambers of the heart. If the own rhythm is stable and corresponds to the needs of the body, impulses are not generated. An optional feature of some high-tech stimulants is the prevention of arrhythmia, tachycardia and other disorders through special work programs.
What are pacemakers
 At the moment, there are many varieties of pacemakers that differ from each other in design, functionality and other criteria. Classification of devices can be carried out according to various criteria, but the main ones are design features that characterize the specifics of stimulation.
At the moment, there are many varieties of pacemakers that differ from each other in design, functionality and other criteria. Classification of devices can be carried out according to various criteria, but the main ones are design features that characterize the specifics of stimulation.
Depending on them, there are:
- Single chamber pacemakers - affect one atrium or one ventricle;
- Two-chamber - affect the atrium and ventricle at the same time;
- Three-chamber - affect both atria and one of the ventricles;
- Cardioverter-defibrillators (ICD, IKVD) - are used in case of a high risk of complete circulatory arrest.
To understand in which cases a particular pacemaker model should be used, its letter code, which takes into account the design features and functionality of the device, will help.
It includes 3-5 letters of the Latin alphabet, which, depending on the serial number in the marking, indicate:
- Stimulated camera.
- Camera detected by the device.
- The nature of the response of the heart to an impulse.
- Frequency adaptation parameters of the device.
- Type of device response to tachycardia.
The main letters used in the labeling of the pacemaker are the first letters of the English words: Atrium (atrium), Ventricle (ventricle), Dual (two, both), Single (one), Inhibition (suppression), Triggering (stimulation), Rate-adaptive (frequency adaptation). The final code that marks the types of pacemakers may look like this: AAI, VVIR (aka PEX), DDDR, etc.
Considering the classification of IVR, one cannot ignore the temporary pacemaker. It is an external device that is connected to the patient's heart by a resuscitator in the event of a sudden cessation of natural cardiac activity or frequent dangerous fainting.
Indications for installation
The most common heart conditions for which a pacemaker is recommended are:
- Arrhythmia;
- Sick sinus syndrome;
- Atrioventricular block.
 Arrhythmia is a pathological condition that is characterized by a change in the frequency and sequence of stages of excitation and contraction of the heart. With arrhythmia, the normal functioning of the organ is disrupted and a number of serious complications occur.
Arrhythmia is a pathological condition that is characterized by a change in the frequency and sequence of stages of excitation and contraction of the heart. With arrhythmia, the normal functioning of the organ is disrupted and a number of serious complications occur.
Arrhythmias can be caused by a variety of reasons, but the most common are:
- Ischemic heart disease;
- Heart failure;
- Cardiomyopathy and myocarditis;
- Heart defects (both congenital and acquired);
- Mitral valve prolapse;
- Toxic effects, including smoking, alcoholism, drug use;
- Mixed effects, manifested by atrial fibrillation or ventricular fibrillation (heart rate increases to 250 beats / min. or more).
A pacemaker is not implanted in all of these cases. Some violations allow you to do without surgical intervention, affecting the source of the problem with medications or other factors.
Sick sinus syndrome (SSS) reflects disturbances in the functioning of the sinoatrial mechanism for controlling the rhythm of heart contractions.
Arrhythmias and blocks associated with SSS include:
- The drop in the minimum heart rate to 40 beats / min. and below, and heart rate under load - up to 90 beats / min. and below;
- Pauses between contractions exceeding 2.5 seconds;
- Alternating bradycardia and tachycardia;
- Severe sinus bradycardia;
- Bradysystolic mitral arrhythmia;
- "Migration" of the atrial driver;
- Sinoauricular blockade, etc.
According to various sources, SSSU occurs in 6%-25% of people who seek help from cardiologists. Most of them recommend the installation of a pacemaker.
Atrioventricular block (AVB) indicates a violation of the conduction of impulses from the atria to the ventricles, which leads to a violation of the heart rhythm and hemodynamics.
There are three degrees of atrioventricular blockade:

Contraindications
We have considered the indications of the installation of the stimulator, it remains to figure out in which cases pacing can be dangerous.
The device is not installed:
- Patients with problems with blood clotting;
- overweight patients;
- Patients who constantly take certain types of medications;
- Persons suffering from mental disorders;
- People who have bad habits and do not get rid of them.
A few years ago, there were also contraindications for age, but today the device can be installed for both a child and an elderly person.
Features of the operation
The operation to install a pacemaker refers to minor surgical interventions and is performed in an X-ray operating room. The first step is to determine the installation location.
The most common options are:
- Left subclavian region - for right-handers, left-handers with tissue damage on the right side of the chest;
- Right subclavian region - for left-handers, right-handers with tissue damage on the left side of the chest;
- Other places connected by veins to the chambers of the heart - if the classic options are not possible for any reason.
Let's see how the operation goes. The algorithm usually includes the following sequence of actions:
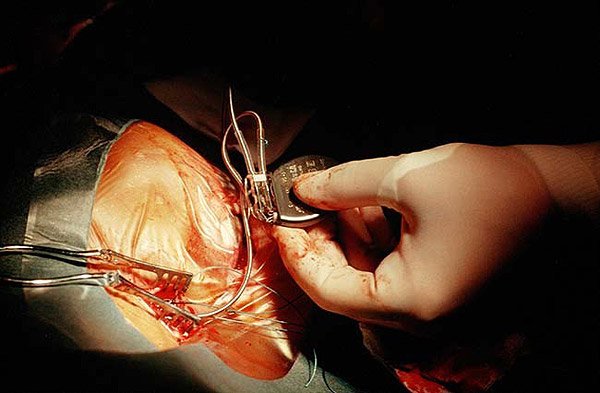
For an experienced surgeon, 20-30 minutes is enough for all this, however, with an atypical installation site or connecting several cameras at once, the time for surgical intervention may increase.
Device installation cost
There is no definite answer to the question of how much such an operation costs - it all depends on the reputation and prices of the clinic, the features of the technologies used in it. In Moscow heart health clinics, the cost of the operation will be from 100 to 600 thousand rubles, in St. Petersburg the price fluctuates - from 60 to 300 thousand. Provincial clinics are ready to do the work for 25-100 thousand rubles.
But it is important to understand that these amounts take into account only the installation of the device. For the pacemaker itself, you will need to pay another 2,500-10,000 dollars.
Patients who are treated under the quota can receive a full range of services for 3500-5000 dollars.
This amount includes:
- Accommodation and maintenance in the clinic;
- The cost of a pacemaker;
- The cost of consumables;
- Payment for the work of doctors and medical staff.
Patients with serious cardiac arrhythmias who have general health insurance are provided with a pacemaker free of charge.
How to live with a pacemaker?
 Despite the possibility of returning, in fact, to the old life, a patient with a pacemaker should still adhere to some rules. The first and main thing is to regularly timely visit a doctor who conducts further monitoring of the patient.
Despite the possibility of returning, in fact, to the old life, a patient with a pacemaker should still adhere to some rules. The first and main thing is to regularly timely visit a doctor who conducts further monitoring of the patient.
The following sequence of visits is usually assigned:
- Three months after the installation of a pacemaker.
- Six months after the first postoperative visit.
- Once every six to twelve months by agreement with the doctor for a scheduled examination.
- Unscheduled - in cases of sensation of electrical discharges, the return of symptoms of the disease, the appearance of signs of inflammation at the installation site of the device.
- After the expiration of the life of the pacemaker declared by the manufacturer (usually it is 6-15 years).
Like any implantable medical device, a pacemaker has its pros and cons. A lot has already been said about the pluses, that is, the positive effect of the device on the functioning of the heart and the body as a whole. But it's important to remember that living with a pacemaker after surgery means paying attention to details that previously seemed unimportant.
You will have to refrain from such types of work and actions:
There will also be a number of restrictions in everyday life. Special care should be taken when working with electrical appliances, and especially with powerful power tools, to avoid any electric shock. The mobile phone should be kept at a distance of no closer than 20-30 cm from the place where the pacemaker is installed.
It is also recommended not to bring a camera, player and other portable electronics near the device. Otherwise, patients with a pacemaker live a full life, getting rid of the problems associated with heart rhythm disturbances.
In what cases is it necessary to replace the device and how is it carried out?
During a scheduled visit to the doctor, the pacemaker is diagnosed and, if necessary, reprogrammed. However, in some cases it may be necessary to replace the device.
Such cases include:
- End of the warranty period;
- Low remaining battery power;
- Occurrence of unrecoverable faults.
A special case is the replacement of the stimulator to install a more modern and functional model. The process of replacing a pacemaker is similar to the process of installing it, and is also performed under local anesthesia. During the operation, the condition of the electrodes is monitored and, if necessary, new ones are installed.