Pacemaker: what is it, efficiency, installation operation
From this article you will learn: for what diseases a pacemaker is installed, how it is done. Types of pacemakers. Contraindications for installation, possible complications. Life with a pacemaker: recommendations and limitations.
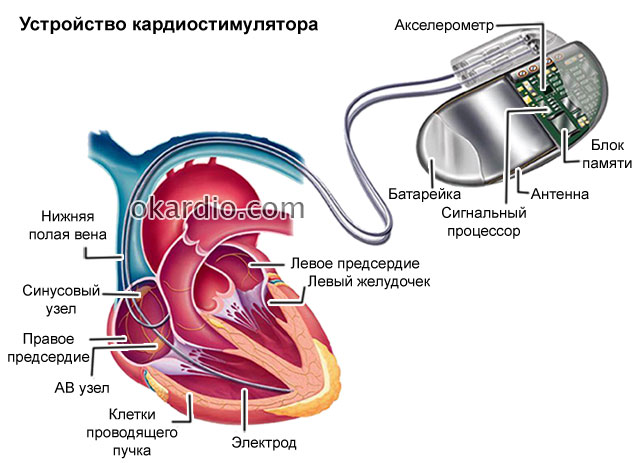
A pacemaker (pacemaker, artificial pacemaker, EKS, IVR) is a special device that, with the help of electrical impulses, sets the correct rhythm to the heart. The pacemaker saves the patient from sudden death due to either ventricular fibrillation. It maintains or imposes the correct rhythm on the heart. Some pacemakers can also stop arrhythmias as soon as they occur.
Installs and configures the EX-a qualified arrhythmologist. Further maintenance of this device is also handled by this doctor. You will need to visit him from time to time to check the operation of the pacemaker and, if necessary, to reprogram the device.
How a pacemaker works
What is a pacemaker and what are its components?
- Generator (source) of electrical impulses, which is placed under the skin on the right or left side of the chest. This is a miniature device weighing about 50 g, equipped with its own battery.
- Electrodes. They are carried out directly to the chambers of the heart, which must be affected. Through them, an electrical impulse is conducted from the source to the heart. Depending on the type of pacemaker, there can be from one to three electrodes.
The part of the device that is placed under the skin is covered with a titanium coating, so the risk of rejection is almost zero.
Indications and contraindications for the installation of a pacemaker
A pacemaker is implanted in patients with bradyarrhythmias (arrhythmias with a slow heartbeat), intracardiac blockades (impaired impulse conduction through the heart) and tachyarrhythmias (arrhythmias with an accelerated heartbeat).
Indications for the installation of EX:
![]()
Symptoms that indicate the installation of a pacemaker:
- With bradyarrhythmias: the pulse is below 40 beats per minute in the daytime, pauses in the heartbeat for more than 3 seconds.
- With tachyarrhythmias: fainting and pre-syncope on the background of attacks of tachyarrhythmias, increased risk.
There are no absolute contraindications.
Postponement of the operation is possible when:
- acute inflammatory diseases;
- exacerbation of peptic ulcer of the gastrointestinal tract;
- acute phase of mental illness, in which the patient's contact with doctors is impossible.
There are no age restrictions: a pacemaker can be installed at any age.
Examination before installing a pacemaker
To make a decision to implant a pacemaker, the arrhythmologist will need the results of the following diagnostic procedures:
Varieties of pacemakers
According to functionality, they distinguish:
- Pacemakers - have only the function of setting the heart to the correct rhythm.
- Implantable defibrillators-cardioverters - in addition to imposing the correct rhythm on the heart, they can also stop arrhythmias, including ventricular fibrillation.
Patients with bradyarrhythmias are placed on conventional pacemakers, and patients with tachyarrhythmias and an increased risk of ventricular fibrillation are placed on pacemakers with the function of defibrillation and cardioversion.
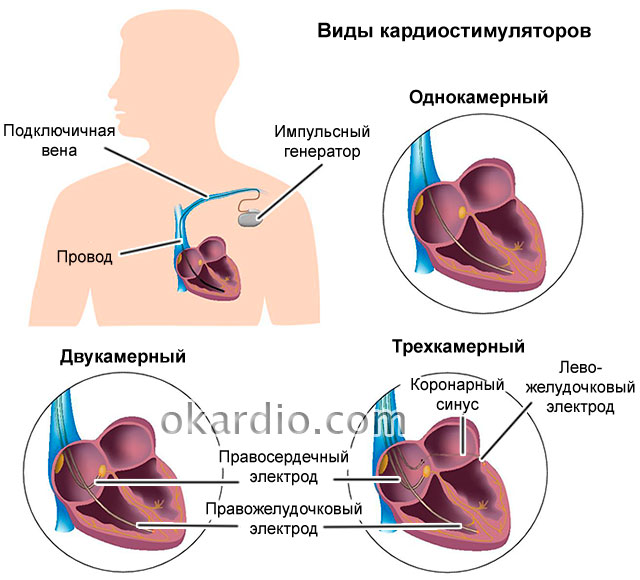
Depending on the zone of influence, single-chamber, two-chamber and three-chamber EKS are distinguished. Single chamber pacemakers are connected to one of the atria or one of the ventricles. Two-chamber - to one atrium and one ventricle. Three-chamber (another name for such a pacemaker is a cardioresynchronizing device) - to one of the atria and both ventricles.
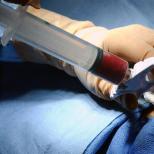
 Click on photo to enlarge
Click on photo to enlarge pacemaker implantation surgery
This surgery is performed under local anesthesia. The implantation process takes about an hour.
The operation to install a pacemaker is as follows:
- Anesthetize the area of the chest with local anesthesia.
- One or more electrodes are passed through the vein to the desired chambers of the heart.
- Check the parameters of the electrodes with an external device.
- A small incision is made in the chest. A bed is formed in the subcutaneous fatty tissue for the main part of the device.
- Install the device, connect to it the electrodes held to the heart.
- Sew up the incision.
In most cases, the source of electrical impulses is located on the left. However, left-handers or in the presence of extensive scars on the left side of the chest can install it on the right.
Postoperative period
After the installation of the pacemaker is over, you will be given sick leave for 3-4 weeks. Except in cases where the pacemaker was installed after a heart attack (then the sick leave may last longer).
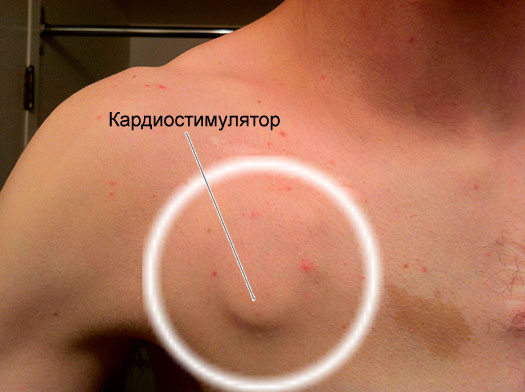 Type of pacemaker after implantation
Type of pacemaker after implantation You will stay in the hospital under the supervision of doctors for 5-9 days. During this period, pain is possible in the area of implantation of the device.
Among other possible complications in the first week after the installation of the device are possible:
- hematomas in the area of the operation;
- bleeding;
- swelling at the site of implantation of the device;
- infection of the postoperative wound;
- damage to blood vessels;
- pneumothorax;
- thromboembolism.
The risk of complications is no more than 5%.
Your doctor may prescribe painkillers to relieve pain. You will also need to take acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin) to prevent blood clots. Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent or treat postoperative wound infection.
Further rehabilitation
Throughout the month, after you have already been discharged from the hospital, you will need to visit an arrhythmologist once a week to check if the device is working properly.
Within 1.5–3 months after implantation of the pacemaker, any physical activity on the arms, shoulders and pectoral muscles, as well as weight lifting, is prohibited. Also, you can not sharply raise your left (or right, if the device is installed on the right) hand up and sharply take it to the side.
Within 1-3 months after the installation of the device, you can not engage in physical education. Only therapeutic exercises prescribed by a doctor are possible.
Complications in the future
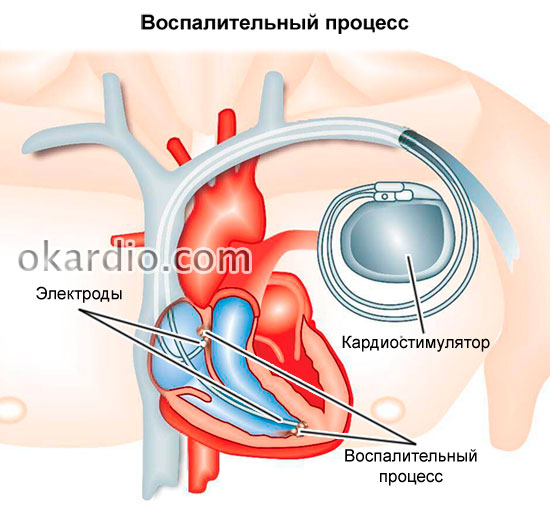
In a remote time after installing the device, you may experience:
- Swelling of the arm from the side where the pulse generator is located.
- Inflammatory process in the heart at the site of electrode attachment.
- Displacement of the device from the bed in which it was installed.
- Fatigue during physical exertion (more often develops in older people).
- Stimulation of the diaphragm or chest muscles by an electrical impulse (possible if the device is installed incorrectly, as well as due to its malfunctions).
The risk of developing these complications is 6-7%.
Life with a pacemaker
Regularly visit an arrhythmologist to examine the pacemaker and, if necessary, reconfigure it. If there is no arrhythmologist in your city, then you will have to go to the clinic where he is, since ordinary cardiologists do not have special skills and equipment for diagnosing and reprogramming pacemakers. A consultation with an arrhythmologist lasts about 20 minutes.
Also, for people with ECS, there are restrictions in everyday life, as well as in the areas of physical activity, the use of electronics, household appliances and tools, in undergoing medical procedures, as well as in professional activities.
Limitations in daily life
Avoid putting pressure on the area where the electrical pulse generator is installed.
Avoid blows to the chest and falls on it. This can lead to both a breakdown of the pulse generator and a displacement of the electrodes located in the heart.
Do not stay near transformer boxes, electrical panels, power lines for a long time.
Do not stand for a long time near the "frames" at the entrance of shops and at airports.
Physical education and sports with a pacemaker
Physical activity and moderate sports activities are allowed for people with an established pacemaker (with the exception of the first 1.5–3 months after surgery).
Only sports in which there is a risk of impact to the pacemaker area, extreme sports, as well as excessive loads on the upper body are prohibited.
You can not engage in boxing, hand-to-hand combat and other martial arts, any kind of wrestling, football, rugby, basketball, hockey, parachuting, etc. It is also undesirable to engage in shooting.
In the gym, exercises on the pectoral muscles using weights are prohibited.
Use of household appliances, electronics, tools
No risks have been identified with the correct use of the following devices:
- Fridge.
- Dishwasher.
- Electronic balance.
- Ionizing air filters, air humidifiers, automatic fragrances.
- Hair curlers and straighteners.
- Calculator.
- Battery powered flashlight, laser pointer.
- Printer, fax, scanner, copier.
- Barcode Scanner.
The use of other devices is also permitted. The only rule is to keep the necessary distance between the device and the pacemaker.
More about the distance in the table.
| Minimum distance to pacemaker | List of devices |
|---|---|
| 20 cm | TV remote control and other devices, hair dryer, sewing machine, vacuum cleaner, massager, mixer, electric knife, electric shaver, electric toothbrush, control panel on an exercise bike, treadmill, mobile phone, laptop, circular saw, screwdriver, soldering iron, meat grinder, games set-top boxes, Wi-Fi routers, modems, bluetooth headsets, radios, music and video players, electric guitar, TV, PC. |
| 31 cm | Ignition system for motorcycles and cars, boat engines, car battery, lawn mower, chainsaw, snow blower, induction hob, microwave oven. |
| 61 cm | Welding equipment up to 160 amperes. |
It is forbidden to use and be closer than 2.5 m from welding equipment over 160 amperes.
Restrictions in professional activity
Contraindicated professions:
- loader;
- electrician;
- electrician;
- welder.
There are no restrictions on working with a computer.
If the pacemaker was installed in connection with severe heart failure, it is possible to assign a disability of 3-2 groups.
Prohibited medical procedures
Patients with an established pacemaker should not undergo:
- MRI (however, there are some models of stimulators that allow you to undergo an MRI - check with the doctor who installed the device for you);
- Physiotherapeutic and cosmetic procedures using electric, magnetic and other types of radiation. These are electrophoresis, diathermy, heating, magnetic therapy, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, etc. You can check with your doctor for a complete list.
- Ultrasound with the direction of the beam directly to the device.
Before any medical procedure or surgery, tell your doctor that you have a pacemaker.
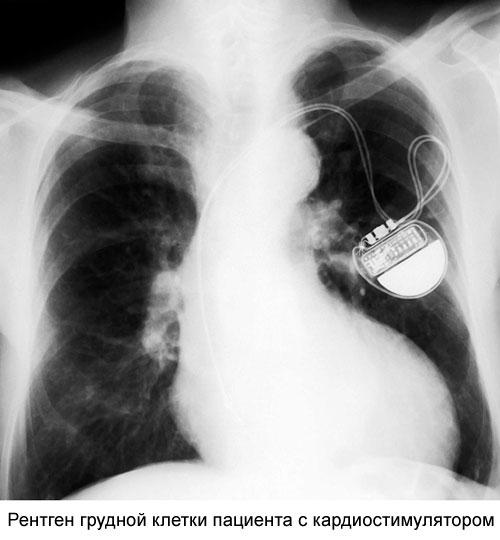
Forecast: service life, efficiency
The warranty period for pacemakers is 3 to 5 years, depending on the manufacturer. The service life for which the battery of the device is designed is 8-10 years. After the battery is discharged or the device fails, the pacemaker will need to be replaced.
Often, the electrodes placed to the heart are still in good condition. In such cases, they are not touched, but only the main part of the device, the generator of electrical impulses, is replaced. If the device breaks down before the expiration of the warranty period, a free replacement under warranty is possible, unless the device breaks down through your fault.