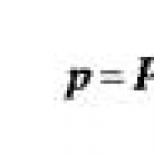Nevus of the sebaceous glands. Nevus Jadasson: neoplasm of the sebaceous glands. Removal with liquid nitrogen
Jadassohn's nevus is a benign skin neoplasm caused by the growth and malformation of skin components, namely: sebaceous and apocrine glands, hair follicles, epithelial cells and connective tissue elements.
In almost 70% of cases it is present from birth, in 30% it develops in infancy and early childhood.. The nevus of Yadasson develops on the scalp, face, back of the neck, and occasionally on other parts of the body. There is no dependence on gender or race, hereditary predisposition has not been established, although cases of family diseases of the nevus of the sebaceous glands have been described.
Photo 1. In most cases, Yadasson's nevus is congenital. Source: Flickr (Derek Fox).
Symptoms of the nevus of the sebaceous glands
In the absence of complications, the nevus is painless, does not cause itching or other sensations. It is a plaque of a soft-elastic consistency, round or oval, slightly raised above the level of the skin, smooth or covered with papules, pink, sandy, brown or yellow. Sizes vary from 0.5 to 9 cm.
Reasons for development
During embryonic development, many pluripotent (poorly differentiated) cells are laid in the skin of the fetus, from which all elements of the skin are formed during development. For unknown reasons in the process of differentiation and maturation of pluripotent cells occurs failure, which leads to excessive formation of sebaceous glands, hair follicles, etc. In connection with their active division, there is a local increase in the number of skin glands, other elements that merge into a single formation - a malformation.
Sebaceous nevus in children and newborns
As already mentioned, Yadasson's nevus is congenital or develops in the first 1.5 - 2 years of a child's life. Before puberty, it has a slightly different structure, namely, it is devoid of hair follicles, smooth or with small tender papillae. It can develop both relatively slowly and quite quickly, reaching in diameter up to 9 cm. In the case of a “normal” course of a nevus, having reached a certain size, it stops increasing and only its structure changes during life due to hormonal changes in the body.
 Photo 2. Yadasson's nevus is located on the scalp, rarely on other parts of the body. Source: Flickr (Janniken20).
Photo 2. Yadasson's nevus is located on the scalp, rarely on other parts of the body. Source: Flickr (Janniken20). Main stages of development
Features of the development of Yadasson's nevus are associated, first of all, with its structural components, which are based on the sebaceous glands, which undergo significant changes throughout life.
At birth and before the onset of puberty, they are poorly developed, present in small numbers and practically do not secrete. In the future, the sebaceous glands increase significantly and begin to actively secrete sebum.
- In childhood, it has a smooth surface or is covered with delicate papillae, devoid of hair follicles.
- During puberty, the nevus becomes covered with yellow or brown papules that are closely adjacent to each other. The changes are associated with the differentiation of the sebaceous glands, which takes place during the puberty.
- In adult sexually mature people, Yadasson's nevus can take on a variety of forms due to the frequent development in its thickness of both benign and. Perhaps the appearance of hairs, scales, foci of keratinization.
Can a nevus become malignant?
This skin tumor develops from poorly differentiated embryonic cells, which in one quantity or another will remain in it throughout life. The tendency of pluripotent cells to accelerate division and potential differentiation into any elements of the skin determines high risk of developing malignant pathologies.
Jadosson's nevus can degenerate into benign cysts and hydradenomas, keratoacanthomas, as well as into such forms of skin cancer as squamous cell carcinoma, cancer of the apocrine glands. Often there are cases of the development of several different types of tumors at once inside a similar nevus.
This is interesting! Scientist V. Lever put forward the theory that the development of benign and malignant tumors is not a sign of malignancy, but just one of the stages in the development of a nevus. This theory is confirmed by the fact that basaliomas that have developed against the background of Yadasson's nevus do not metastasize and remain small.
Possible complications of Yadasson's nevus
Despite the entertaining theory of V. Lever, the development of malignant and often fatal species against the background of such a nevus takes place. If basaliomas do not differ in pronounced aggressiveness, then squamous cell carcinoma or cancer of the apocrine glands can lead to the death of the patient.
Extremely rare diffuse(common) forms given diseases. They are characterized not only by skin lesions, but also by affecting the central nervous system, cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and genitourinary systems. With such forms of the disease, there is a characteristic triad of symptoms: the presence of a linear nevus of Yadasson on the skin, mental retardation of varying severity, and epilepsy (there may be both small and large seizures).
A colleague sent a patient for a consultation, and I had the opportunity to take a rather rare photograph - the growth of basal cell carcinoma against the background of Yadassohn's nevus.
In principle, such a photograph and such a case would probably be of interest only to specialists, if not for one “but”.
Nevus Yadasson is most often a congenital pathology. Benign, but prone to malignancy - in 5-30% of cases (and this is a lot), various tumors develop in these nevi, including malignant ones. More often - basal cell carcinoma, which is not particularly dangerous, but sometimes more malignant variants.
The patient sent for consultation lives with this nevus all his life, and the nodular formation appeared ... about 15 years ago. I will not comment on this and, moreover, I will not look for the cause in anyone (the patient did not turn to dermatologists / oncologists, and doctors of other specialties rarely encounter this type of nevus, and the patients themselves are used to living with it and do not show these nevi to doctors when they turn to them for other reasons), but rather I will describe the nevus itself.
This nevus is a malformation of the sebaceous glands, so it is also called sebaceous nevus. In two thirds of cases, it is congenital, in one third of cases it manifests itself in early childhood. Very rarely, this nevus can manifest itself at a later age, in adolescents, but it happens. Sometimes there are family cases of the presence of these nevi.
It arises from the cells of the ectoderm (from which, among other things, our integumentary tissues are formed) due to mutations that have not been completely studied, and is a hypertrophied sebaceous glands, together with other glands and deformed hair follicles. Refers to hamartomas - benign tumors resulting from a violation of the embryonic development of organs and tissues, consisting of the same components as the organ where they are located, but differing in their incorrect location and degree of differentiation.
Outwardly, this nevus is a flat plaque, sometimes oval, sometimes asymmetrical, with a granular, warty surface and a yellowish tint. Sizes can be different - from half a centimeter to large, 10-centimeter formations. It is located more often on the scalp, but can be in other places. The nevus itself is not covered with hair, and its not very aesthetic appearance leads to the fact that its owners begin to cover it with hair and not show it to anyone. Including doctors. Which is in vain.
By itself, the nevus does not cause any unpleasant sensations. With age, this nevus changes - so, in childhood, the nevus is usually represented by a uniform fine-grained plaque of yellow-pink, pink, orange color, and in adolescence, the elements of the nevus become larger, it becomes more heterogeneous, sometimes with large warty elements.
Most often, this nevus does not cause any health problems, but, as mentioned above, in 5-30% of cases, various tumors, including malignant ones, can form in it.
This behavior of Yadasson's nevus is the reason why many experts recommend removing it before adolescence. However, this is not an unambiguous question.
Thus, from 1996 to 2002, researchers from the Miami Children's Clinic analyzed 757 cases of Yadasson's nevus removal in children under 16 years of age, and no cases of basal cell carcinoma were recorded in this group, and therefore the expediency of operations in childhood was questioned. A similar study, with fewer patients, had previously been conducted in France.
The feasibility of prophylactic removal in adults is still an open topic. In any case, both children and adults with the presence of Yadasson's nevus are shown periodic preventive examinations by an oncologist or dermatologist so that it does not work out like our patient.
Let's get back to it, though.
When viewed on the scalp of the patient, a formation of about 7 cm is determined, clinically interpreted as a nevus of Yadasson. On the surface of the nevus, nodular formations with areas of pigmentation are noted. With dermatoscopy, tree-like vessels are determined in nodular formations, based on a combination of signs, the clinical diagnosis is basal cell carcinoma that arose against the background of Yadasson's nevus.


The patient underwent a biopsy of the formation, histological verification:

The prognosis for life and health is favorable. Local recurrences of basal cell carcinoma are possible, but with adequate supervision by an oncologist, which I hope will now be carried out, nothing threatens the patient. The nevus, of course, will be removed completely, but this is quite an easily endured procedure.
Nevus sebaceous glands, or nevus Yadassohn, is a benign nodular tumor on the head (hamartoma) caused by congenital dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. The skin growth is referred to as the seborrheic type (translated as "seborrhea" - the flow of fat). It looks like a relief crowding of waxy plaques from yellow to light brown in color. According to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD), benign neoplasms of the skin of the scalp and neck are assigned code D 23.4.
Reasons for the appearance
A sebaceous nevus appears immediately after the birth of a child or in the first years of life. What causes affect the change in the structure of the dermis is not known for certain. There are only assumptions that the process of intracellular mutation is triggered due to unnatural growth, blockage of the sebaceous and sweat glands, impaired development of skin cells, hair follicles (follicles).
Risk factors
Based on the analytical material on sebaceous formations, medical science has identified several factors that negatively affect a pregnant woman and fetus:
- hormonal abnormalities;
- frequent and chronic diseases;
- reduced immunity;
- inheritance of the altered gene;
- acne;
- violation of psycho-emotional balance;
- unfavorable environment;
- exposure to UV rays, chemicals.
The course of the disease, stages of development
Seborrheic nevi on the scalp occur with equal frequency in both sexes. They exist for a long time asymptomatically, but do not go away on their own. In accordance with age-related changes in the sebaceous glands, the development of a benign formation is divided into 3 stages:
- in infants it is with smooth papillae without hairline;
- in adolescents, it resembles rounded, closely spaced warts of a yellow, light brown hue;
- in adolescence, the tendency to oncological changes increases, more often in the form of basilioma (skin cancer), less often in the form of cancer of the apocrine (sweat) glands, skin squamous cell carcinoma.
Complications of neoplasm
Like any benign tumor, sebaceous nevus is unpredictable. It can spread to adjacent areas of the skin, causing mutations in the form of:
- benign adenoma on the face, on the skull in the hair zone;
- rhinophyma - an ugly growth of nasal tissues;
- blepharitis - 2-sided inflammation of the eyelids with blurred vision.
 Jadasson's nevi tend to grow into nerve endings, bone structures, the genitourinary, and vascular systems. If the central nervous department is affected, epilepsy develops, inhibition of mental development.
Jadasson's nevi tend to grow into nerve endings, bone structures, the genitourinary, and vascular systems. If the central nervous department is affected, epilepsy develops, inhibition of mental development.
With age, under the influence of negative internal and external factors, a seborrheic neoplasm can be malignantly degenerated in about 15 cases out of 100.
A sebaceous nevus can turn into a basilioma or a particularly dangerous adenocarcinoma of the glands. The latter quickly spreads through the skin, destroying the natural structure of cells. Adenocarcinoma is able to revive after surgical removal.
Harbingers of dangerous changes can be:
- fusion of closely spaced Yadasson nevi into a tuberous aggregation up to 10 cm in diameter;
- intensive growth of a congenital skin defect in 1-2 months;
- bleeding;
- the appearance of crusts, sores, additional relief;
- a change in an even color to a multi-colored, very dark, with the formation of contrasting rims;
- manifestation of itching, burning, pain and other kind of sensitivity.
These signs do not always indicate the instability of seborrheic moles. An asymmetric, dark, bumpy formation can calmly behave for many years. At the same time, a histological examination, prescribed by a doctor only because the patient began to inexplicably “feel” a skin growth, can reveal oncocells.
Treatment
Considering the complexity of identifying dangerous transformations, each dubious outgrowth must be studied in a clinical setting.
Traditional treatment of the disease
The only way to get rid of seborrheic nevus and cancer risks is surgical removal. Dermatologists, oncologists recommend surgical treatment already in early childhood or at least before puberty.
Reliably, painlessly removing the growth is possible only in the conditions of an oncological dispensary with a traditional surgical scalpel. Doctors do not trust delicate operations on the head with electric and laser knives, liquid nitrogen. After them, a high percentage of relapses.
The confident hand, the experienced eye of the surgeon allow you to more accurately clean out the pathological focus to the boundaries of healthy tissues. Although in complex cases, 2-4 staged operations within a short time are not excluded.
Depending on the area and location of the lesion, the age category of the patient, operations are performed under local or general anesthesia. At the end, a small wound is sutured. A large wound surface, the face area require skin plasty.
During the postoperative week, regular drug treatments and dressings are done. The removed biomaterial is sent for histological examination to detect cancer cells. If the answer is positive, an additional examination for metastases is performed.
Alternative treatment
At home, it is impossible to radically get rid of a seborrheic neoplasm. Medicine does not give a 100% guarantee of success even for a qualified surgical intervention, since the mechanism of cellular mutations has not yet been studied in depth.
The people live with recipes that have come down from the time when effective medical care was not yet available. Unfortunately, there are no statistics reflecting the benefits and harms of home remedies for congenital nevus.

Hemlock application
Recipe for adults only! Hemlock is considered an effective tool for strengthening immunity, preventing malignant degeneration. But this poisonous plant should be used with extreme caution, homeopathic doses. Fresh crushed hemlock inflorescences are loosely placed in a glass jar with a capacity of 0.5 l. Fill to the top with vodka. In winter, 30 g of dry grass is taken for 0.5 liters of vodka. In both cases, having tightly sealed the container, the drug is sent to a dark place to infuse for 14 days. If you need urgent application, you can limit yourself to 3 days.
Hemlock tincture is taken on an empty stomach with water. Breakfast is scheduled in an hour. Begin treatment with 1 drop in half a glass of water. Further, the daily dose increases strictly by 1 drop. From the 14th day to the 25th, the drops are diluted with 150 ml of pure water. If 25 drops caused nausea and other signs of poisoning, you need to reduce the dosage or stop taking it until you feel normal. If the process goes smoothly, then from the 26th to the 40th day the medicine is dissolved in 200 ml of water. 
On the 41st day, the number of drops is reduced to 39 and then they move according to the scheme in the opposite direction - up to 1 drop. The second course begins without a break, followed by another one. It is believed that an 8-month course of herbal medicine is able to treat oncoprocesses.
You can use folk remedies only after consulting a doctor.
Prevention and prognosis
Due to the lack of knowledge of cellular mutations, it is not possible to formulate preventive advice. There are only reinsurance measures - a timely visit to the doctor and the removal of Yadasson's nevus surgically. In this case, the forecast will be the most favorable.
Nevus of the sebaceous glands of Jadassohn(syn.: nevus of the sebaceous glands) - a frequent organoid epidermal nevus, caused by proliferation and malformation, primarily of the sebaceous glands, as well as other components of the skin (epithelial cells, hair follicles, connective tissue, apocrine glands). Described by A.N. Mehregan and H. Pinkus in 1965. Is the result of differentiation of pluripotent cells towards mature sebaceous and apocrine structures; it is the pluripotent nature of these cells that explains the development of other tumors of the skin appendages against its background.
Nevus of the sebaceous glands in 2/3 of cases it is congenital in nature, it can occur in infancy and only sometimes in later childhood. It develops, as a rule, sporadically, although isolated family cases have been described. The gender distribution is the same.
Usually a nevus of the sebaceous glands located on the scalp (on the border with the neck, in the temple, forehead) or the central part of the face, rarely in other places.
Clinically nevus of the sebaceous glands of Jadassohn manifests as an asymptomatic, solitary, flat, soft, elastic, shiny plaque of an oval or linear shape with a diameter of 0.5 to 9 cm or small hemispherical nodules of pink, yellow, orange or sandy color with a grooved or somewhat papillomatous surface, devoid of hair. Sometimes it can have a keratotic surface. The three-stage course is due to the age differentiation of the sebaceous glands:
1) in infants and young children, the elements of the nevus are devoid of hair, smooth or with a delicate papillary surface;
2) in the pubertal period, lesions become similar to mulberries, because their surface is covered with closely adjacent hemispherical, often warty papules from yellow to dark brown;
3) in adulthood, in about 20% of cases, benign or malignant tumors develop in the thickness of the nevus, including papillary cystadenoma, hydradenoma, apocrine cystadenoma, keratoacanthoma, infundibuloma, basalioma, squamous cell carcinoma, and cancer of the apocrine glands.
In particular, basalioma against the background of nevus sebaceous glands develops in 5-20% of cases. However, it occurs much more often than benign skin tumors. Often there is an association of benign and malignant neoplasms of the skin in one patient. It is important to consider that, despite the sometimes inherent aggressiveness of histological signs, most skin cancers that have developed against the background of nevus sebaceous glands are characterized by a low degree of malignancy and metastasize only in exceptional cases.
The possibility of developing malignant neoplasms against the background of the nevus of the sebaceous glands at an early age, W. Lever served as the basis for the hypothesis that the development of a basalioma against the background of such a nevus is not a malignant transformation, but the result of a decrease in the differentiation of primary epithelial germ cells and a subsequent increase in their proliferative activity. The validity of this assumption is confirmed by the fact that nevus-associated basaliomas, despite the development in young patients, are usually small in size and lack signs of aggression.
Histologically typical nevi of the sebaceous glands consist of lobules of mature sebaceous glands in the upper and middle parts of the dermis, there is also an increase in the number of other epithelial structures (dilated apocrine sweat glands, abortive hair follicles). There are three stages of histological development of the nevus.
1. Early stage - manifested by hypoplasia of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
2. Mature stage - characterized by acanthosis, papillomatosis of the epidermis, an abundance of hyperplastic sebaceous glands, underdevelopment of hair follicles, good development of apocrine glands.
3. Tumor stage.
rare common sebaceous nevus can be systemic with damage to the central nervous system, eyes, bone, vascular, genitourinary and other systems. The very rare Yadasson sebaceous nevus syndrome includes the triad of linear sebaceous nevus, epilepsy, and mental retardation.
Differential diagnosis of the nevus of the nevus of the sebaceous glands of Yadassohn carried out with aplasia of the skin, characterized by a smoother papyrus-like surface; syringocystadenomatous papillary nevus, which has a pinker than yellow, nodular rather than velvety surface; early juvenile xanthogranuloma (rapidly developing dome-shaped papule or nodule) and solitary mastocytoma, which have a characteristic histological structure; hypertrophy of the brain tissue or encephalopathy, in which a subcutaneous node can also be determined, but the contents are associated with the brain.
Treatment of the nevus of the sebaceous glands of Yadassohn. In connection with the threat of malignant transformation, prophylactic surgical removal of the nevus is accepted no later than the onset of early adolescence. Electrocautery and cryosurgery can lead to relapse.
Nevus of the sebaceous glands of Yadassohn is a very unpleasant and repulsive disease. Ideas about him were formed in the 80s of the last century. The reason for its appearance is excessive growth and deviations from the normal development of the sebaceous glands. It manifests itself as a formation on the surface of the body, which consists of skin cells, transformed sweat and sebaceous glands, as well as an undeveloped hair follicle.
The probability of diagnosing it for people of different races, nationalities and genders is the same. In infants, it occurs on average in the amount of 3 out of 1,000 people.
Symptoms of the disease
The tubercles above the skin surface are round or oval (rarely elongated) yellow, orange, pink, sandy, or a combination thereof. Most often appear on the head or face in the hair growth zone, extremely rarely in other places (behind the ear, on the neck, on the temples). In most cases, the disease appears in newborns or young children and is caused by genes.
Some symptoms of the disease develop only by adolescence.
Initially, it appears as an elastic growth with a soft surface. Over time, it grows with frequent papillomas, cracks. They can bleed and become infected. In place of the nevus, there is no hairline, the appearance is disturbed.
Stages of development of Nevus Yadasson
Depending on the stage of the course, the disease manifests itself in different ways:
- At the first stage, foci-spots with papillae are formed, there is no hairline on the formation. This manifestation is typical for newborns.
- In the second stage, rounded formations appear, similar to warts. Usually there are several of them, in contact with each other. Develop during puberty.
- In the third stage, the disease becomes chronic and develops by adolescence. At this stage, the nevus can develop into adenoma of the sebaceous glands, other diseases. It is dangerous because if left untreated, a malignant tumor can occur on the skin. The nevus increases as the body grows, in 5-30 cases out of 100 it turns into a benign or malignant tumor. Such a disease develops slowly and gives metastases in very rare cases.
At first glance, a harmless linear skin defect can provoke not only oncology, but also deviations in the functioning of the central nervous system, blood vessels, organs of vision, as well as epilepsy and mental retardation. The nevus of the sebaceous gland can degenerate into various types of skin cancer:
- hidradenoma - a tumor of the sweat glands. Rarely found, usually appears on the face, less often - on the lips, arms, legs, stomach (in the navel);
- apocrine cystadenoma - a tumor that forms on various parts of the limbs, is more often diagnosed in males;
- apocrine gland carcinoma - a rare tumor of the sweat glands, observed in the armpit, groin and other places;
- keratoacanthoma - a rapidly developing benign tumor;
- squamous cell carcinoma is an aggressive formation that is formed from epithelial cells and mucous tissues.

Causes of the nevus of the sebaceous glands of Yadassohn
The sources of the appearance of the considered form of the disease have not yet been identified. It is known that it can be inherited. Disturbances in the work of the gastrointestinal tract, proliferation of glandular tissue, imbalance of hormones, pink acne, damage to the build-up, the action of chemicals and heat contribute to the development of formations. Studies show that a nevus develops into a malignant tumor in 20% of patients.
Diagnostics
When the first signs of a nevus appear, you should consult a dermatologist. First of all, he conducts a visual examination of the patient's tissues and finds out the factors that could accompany the disease (for example, the presence of a similar problem in parents). With visual diagnostics, a preliminary diagnosis can be obtained.
If necessary, collects cells for analysis in the laboratory. Histological analysis allows you to determine the nature of the disease, the depth of its spread. In some cases, a smear is taken to determine whether the cells can change their nature. In this case, the focus itself is damaged, but information is obtained that allows us to measure the risk of transition to the oncological stage.
Modern clinics often turn to video dermatoscopy. When using this diagnostic method, the neoplasm is repeatedly increased and the analysis of changes in the structure of cells is carried out. Differential diagnosis of the disease in question is carried out with the following pathologies:
- solitary mastocytoma - characterized by a different histological structure;
- aplasia of the dermis - has a smooth surface of the formation, similar to moles;
- juvenile xanthogranuloma - it is characterized by active growth and clear boundaries of the neoplasm;
- papillary syringocystadenomatous nevus - has the appearance of a nodule of a rich pink hue.

Treatment
The most effective solution in the fight against the nevus of the sebaceous glands is its removal. You should not wait for its development and distribution, it is best to carry out the manipulation before puberty, but not earlier than reaching two years. In addition to medical indications, such a solution will avoid aesthetic problems - scars and the like.
Such an operation is performed by surgical intervention, using liquid nitrogen or an electric knife, laser removal, exposure to low temperature, and more. Getting rid of the disease occurs in oncology centers with the participation of dermatologists. Based on the results of the removal, the patient is sent for a second histological examination. If the presence of atypical cells is diagnosed, then an examination is carried out for the spread of metastases in different organs.
The most effective operation is to surgically remove the neoplasm, in which case there is a minimal risk of a revival of the disease in the same place.
Manipulations are carried out under local or general anesthesia, if the affected epidermal layer of cells remains, they are repeated. Any actions of doctors in the head area is a serious and complicated matter. The medical worker takes into account not only the area and the affected area, but also the age of the patient. There are cases when, according to the results of the operation in question, plastic surgery is necessary to restore the aesthetic component.
The resulting wound is treated with antiseptics, dressings are performed. It is important to maintain the cleanliness and sterility of dressings to prevent pathogenic bacteria and other substances from entering the epidermis. After healing, the sutures are removed.
Due to the fact that the specific causes of the appearance of a nevus have not been found to date and the period of the first signs of the disease falls on the first years of a person’s life, it is almost impossible to prevent it. Therefore, parents should be attentive to changes in the skin of their baby. In order to avoid serious consequences, it is important to observe skin hygiene, diagnose and treat the disease in time.